For decades, sexually transmitted disease (STD) or genital sensitivity as well as communicable diseases, sometimes known as sexually transmitted infection (STI), has existed.
Human sexual activity, IV injections, lactation, and delivery are all ways for HIV to be spread. And two such illnesses are chlamydia and gonorrhoea, however, there are significant variances between the two.
Key Takeaways
- Chlamydia is caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis, while gonorrhea results from Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
- Chlamydia infections may cause no symptoms but can lead to serious reproductive issues if untreated; gonorrhea symptoms include discharge and painful urination.
- Both chlamydia and gonorrhea are sexually transmitted diseases treatable with antibiotics, but antibiotic-resistant strains of gonorrhea have emerged.
Chlamydia vs Gonorrhea
Chlamydia is known for causing asymptomatic infections in many cases and is caused by Chlamydia trachomatis. Neisseria gonorrhoeae causes gonorrhoea, tends to produce more noticeable symptoms, and can lead to more severe complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease and infertility.

It involves inflammation in the human genital tract and the eyes. Gonorrhea, but on the other side, is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is also a common condition with a 2 to 30-day incubation time.
Chlamydia is a bacteria-caused sexually transferred infection (STI). In the initial stages of chlamydia, most individuals have no noticeable symptoms. Around 90% of females and 70% of men with STIs exhibit no symptoms.
However, Chlamydia can still create health concerns in the future.
Delayed chlamydia can lead to significant consequences, so it’s critical to undergo frequent tests and discuss any issues with your physician or health professional.
Without the need for a contraceptive or other barrier devices, gonorrhoea transmits from person to person during oral, anal, or vaginal intercourse. Celibacy and good condom or barrier technique use are the greatest defences against infection.
Symptoms appear 2 to 14 days following exposure. However, some persons who get gonorrhoea never show any symptoms.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Chlamydia | Gonorrhea |
|---|---|---|
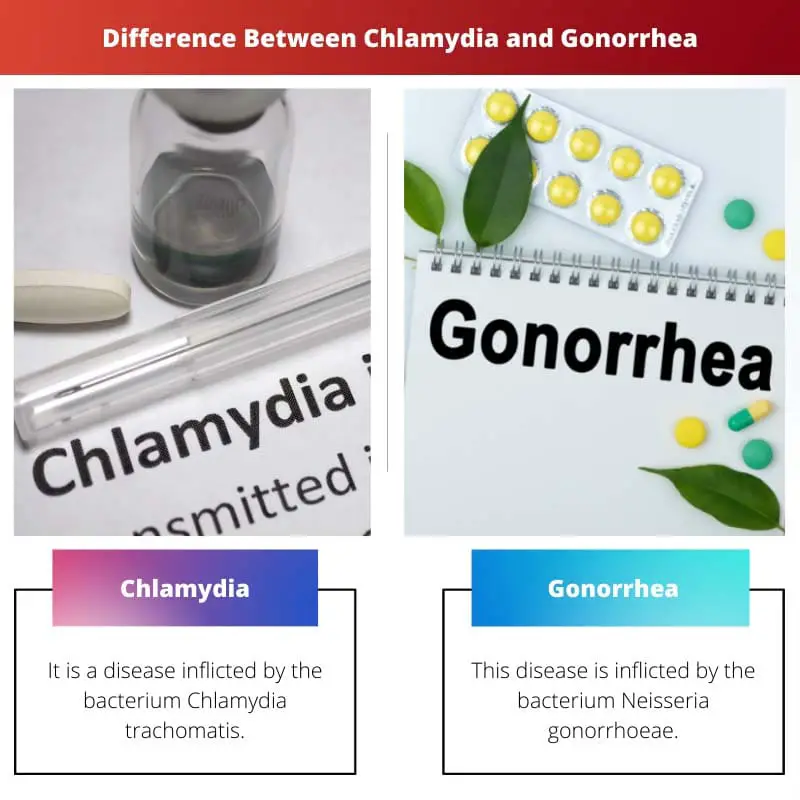
| Bacteria | It is a disease inflicted by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. | This disease is inflicted by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
| Severity | It is not a severe disease but if left untreated it can extrapolate to several other symptomatic STDs which can be fatal for the patient. | It is a serious condition and must be treated as soon as possible. A person with gonorrhea most likely has chlamydia too. |
| Cause | Unprotected sexual intercourse and communicable contact with the affected person. | It is caused by oral, anal, or vaginal contact. It can pass on from mother to the baby as well. |
| Symptoms | Dyspareunia, penile inflammation in males and vaginal discharge in females. | Urination occurs more or urgently, inflammation or redness at the entrance of the penis, a pus-like secretion from the penis, the testicles may enlarge or hurt. |
| Medicines Used | Daily dosage of azithromycin or consuming doxycycline twice weekly for 7 to 10 days. | Ceftriaxone, an injection-based antibacterial medicine, combined with azithromycin, an oral amoxicillin (Zithromax). |
What is Chlamydia?
Chlamydia trachomatis is an organism that lives outside of the body. This implies it does not infiltrate the cells of your body. Rather, HPV dwells in the uterus, the urethra, and other bodily channels other than the genital area.
It requires 7 to 15 days for effects to appear following exposure.
A prevalent spread through sexual contact illness may or may not result in symptoms. Chlamydia affects individuals of different ages, however, it is most prevalent in young females.
Many people with chlamydia may not display signs, yet they can still infect others through sexual activity. Signs may also include vaginal discomfort and vaginal or penile incontinence.
Antibiotic medication is advised for both the sick patient and the patient’s sex partners. Other prevalent sexual transmission illnesses should be screened for. Chlamydia does not create any symptoms.
As a result, you may be unaware that you have it.
Even if a person has no indications of chlamydia, they can spread diseases to others. If you ever do get signs, they may well not present for many weeks after having intercourse with an infectious person.
Symptoms include:
- Urinating with discomfort or a burning feeling
- The desire to pee more often
- Heavy menstrual periods or spotting
- Throat ache
What is Gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is an STD bacterial illness that affects both women and men. The urethral tube and opening, rectum, or mouth are the most commonly affected areas by gonorrhoea. Gonorrhea can also contaminate the cervix in females.
Gonorrhea is most transmitted through vaginal, oropharyngeal, or anal sex. However, kids born to infected moms might become infected during labour. The eyes are the most affected by gonorrhoea in infants.
The best approach to avoid sexually transmitted illnesses is to avoid sex, use a contraceptive if you do engage in sex, and be in a mutually steady relationship.
The bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae causes gonorrhoea. Gonorrhea germs are most commonly spread from one person to another through sexual intercourse, which can include oral, anal, or vaginal contact.
It is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is also a frequent illness with a two to fifteen days gestational period. It can be passed on through intimate intercourse, or a woman might pass it on to her kid after birth.
Mucus, low abdomen ache, and pain during contact are common symptoms in women.
Symptoms in males include secretions from the penis as well as a burning feeling when peeing. It can induce epididymitis and prostatitis, including pyelonephritis in males if they remain unattended.
It can induce chronic granulomatous illness and septic arthritis in females’ hands, wrists, feet, and ankles. It can also cause septic miscarriage in pregnant women and damage to the limbs and the heart.

Main Differences Between Chlamydia and Gonorrhea
- A bacterial pathogen, Chlamydia trachomatis, causes chlamydia, whereas gonorrhoea is inflicted by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
- Chlamydia symptoms take around months and a lot more to unfold completely, whereas gonorrhoea symptoms appear in a couple of days.
- Chlamydia does not require massive doses of antibiotics to treat, however, gonorrhoea requires high doses of antibiotics to cure entirely.
- A patient with Chlamydia does not always have gonorrhoea, but a patient with gonorrhoea also has a very high likelihood of having Chlamydia.
- Chlamydia can induce reactive arthritis, whereas gonorrhoea can cause fever and, in certain cases, discharge from the patient’s urethra.
- https://www.webmd.com/sexual-conditions/understanding-chlamydia-treatment
- https://www.medscape.com/register?client=205502&scode=msp&action=complete&lang=en®ister=true&form=about&urlCache=aHR0cHM6Ly9lbWVkaWNpbmUubWVkc2NhcGUuY29tL2FydGljbGUvMjE4MDU5LW1lZGljYXRpb24

The article provides too much information and can be overwhelming for readers who may not be familiar with the topic.
This article contains detailed and useful information to educate and protect people from these diseases.
Absolutely! I’m glad that we have access to such insightful articles.
This article presents an important warning about the risks of contracting these diseases and the severity of untreated cases.
Absolutely. The seriousness of these diseases is evident from the information provided.
Interesting article with thorough explanations, a great resource to raise awareness about these diseases.
The amount of information and statistics is overwhelming, but it’s interesting to see that these diseases can cause serious issues if untreated.
Yes, it’s alarming that many people with these diseases do not show any symptoms. The educational aspect of this article is valuable.
There is a lot of information provided, but it would have been beneficial to simplify the content and make it easier to understand.