A compact mark indicates a dense, tightly packed structure, suggesting efficiency and solidity. Conversely, a spongy mark implies a softer, more porous composition, suggesting flexibility or a cushioning effect.
Key Takeaways
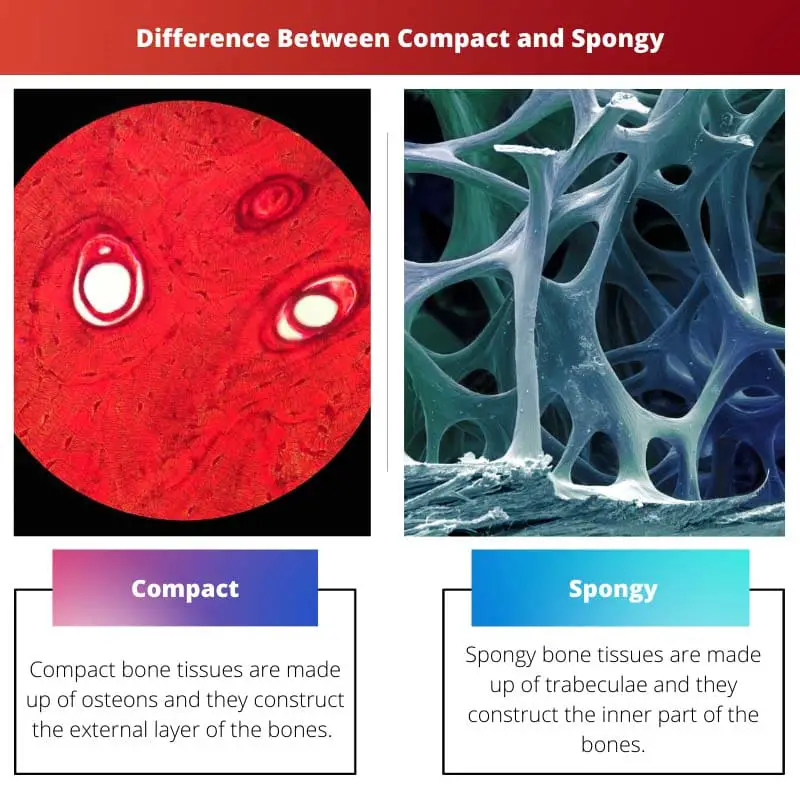
- Compact bone is dense and forms the outer layer of bones, while the spongy bone is porous and fills the inner layer.
- Compact bone provides strength, while spongy bone supports and protects internal organs.
- Compact bone has few spaces, while spongy bone contains numerous spaces containing bone marrow and blood vessels.
Compact vs Spongy
Compact means something which is very tightly closed together having a bulky shape. A compact thing is well organized and compressed. Spongy refers to something mushy and well absorbing. Spongy things have pores and airy surfaces.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Compact Bone | Spongy Bone |
|---|---|---|
| Other Names | Cortical bone | Cancellous bone, trabecular bone |
| Structure | Dense, solid with tightly packed osteons (cylindrical structures) | Porous, honeycomb-like with thin struts called trabeculae |
| Density | High | Low |
| Weight | Heavy | Light |
| Strength | High – provides structural support and withstands force | Lower – absorbs shock and distributes weight |
| Location | Outer layer of long bones, diaphysis (shaft) of long bones | Inner layer of long bones, epiphyses (ends) of long bones, flat bones, and irregular bones |
| Function | Provides strength, rigidity, and protects internal organs | Absorbs shock, reduces weight, and allows for red blood cell production in cavities |
| Color | White | Pinkish red |
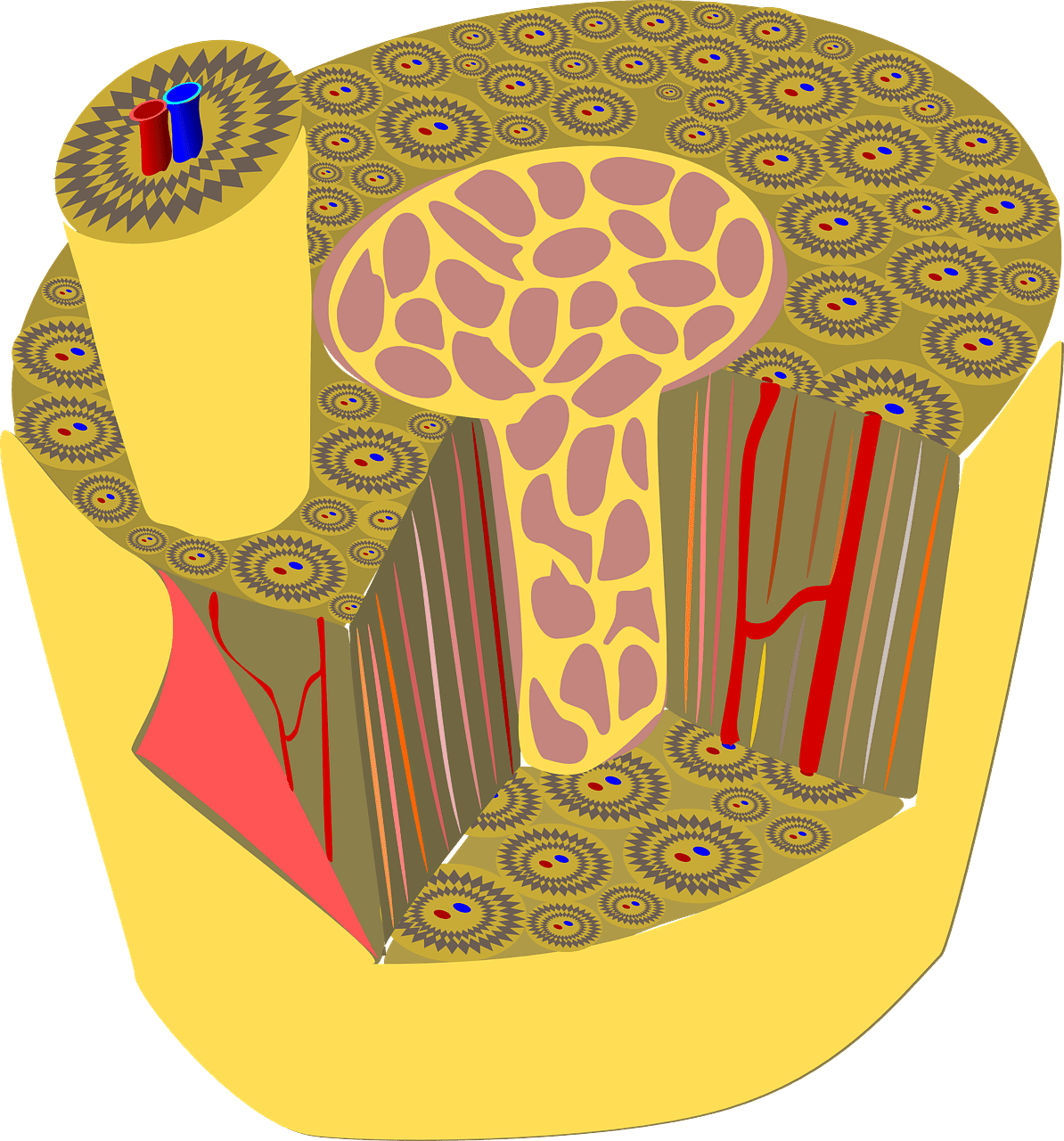
What is Compact?
Compact refers to a state or condition characterized by being closely and firmly packed together, resulting in a dense structure. In various contexts, compactness implies a lack of spaciousness or roominess, with elements closely bound or consolidated.
Physical Attributes
In physical terms, compactness can manifest in diverse forms. For instance, in materials science, a compact substance is one with molecules or particles densely arranged, leading to high density and increased strength. In structural engineering, a compact design denotes efficient use of space and minimal voids, contributing to stability and robustness.
Practical Applications
Compactness finds application across numerous domains. In technology, compact devices are favored for their portability and space-saving properties, exemplified by compact smartphones or laptops. In urban planning, compact cities prioritize efficient land use, promoting sustainability and accessibility.
What is Spongy?
Spongy refers to a texture or structure characterized by being soft, porous, and yielding under pressure, akin to that of a sponge. This term conveys a sense of resilience, flexibility, and absorbency, associated with materials or substances that contain numerous interconnected voids or pores.
Physical Attributes
In the physical realm, sponginess manifests in various forms and materials. Biologically, spongy tissues in organisms, such as the spongy bone in vertebrates or the spongy mesophyll layer in plant leaves, serve essential functions in providing support, storing nutrients, or facilitating gas exchange. In materials science, sponginess can be engineered deliberately, as seen in foam materials like sponge rubber or memory foam, which offer cushioning, shock absorption, and insulation properties.
Practical Applications
The spongy characteristic finds diverse applications across industries. In construction, materials with spongy properties, such as insulation foam or porous concrete, aid in thermal regulation and soundproofing. In healthcare, spongy materials like wound dressings or tissue scaffolds promote healing by absorbing exudates and providing a conducive environment for tissue regeneration. Additionally, in consumer products, spongy materials are utilized in mattresses, upholstery, and footwear to enhance comfort and impact absorption.
Main Differences Between Compact and Spongy
- Structure:
- Compact: Dense, tightly packed structure with minimal voids.
- Spongy: Soft, porous structure with numerous interconnected voids or pores.
- Characteristics:
- Compact: Implies solidity, stability, and efficiency in terms of space usage.
- Spongy: Suggests resilience, flexibility, and absorbency, capable of yielding under pressure.
- Applications:
- Compact: Commonly utilized in contexts requiring strength, stability, and minimal space usage, such as in materials engineering, product design, and urban planning.
- Spongy: Found in applications where cushioning, shock absorption, or insulation properties are desirable, such as in healthcare, construction, and consumer goods.
Last Updated : 01 March, 2024

Piyush Yadav has spent the past 25 years working as a physicist in the local community. He is a physicist passionate about making science more accessible to our readers. He holds a BSc in Natural Sciences and Post Graduate Diploma in Environmental Science. You can read more about him on his bio page.

I appreciated the clear and logical organization of information in distinguishing between compact and spongy bone tissues.
It’s evident that the author has taken a systematic approach to explain the subject effectively.
The article undoubtedly presents the subject matter in a well-structured manner.
The detailed breakdown of the key characteristics, functions, and differences between compact and spongy bone tissues has greatly enhanced my understanding of this topic.
The article provides valuable insights into these intricate structural components of bones.
The in-depth explanation and comparison of compact and spongy bone tissues have certainly broadened my understanding of skeletal structures.
It offers a comprehensive and cohesive analysis of a crucial aspect of the human skeletal system.
I concur with the article’s detailed and meticulous examination of the distinct features and roles of compact and spongy bone tissues.
The wealth of information provided truly enriches our knowledge on the subject matter.
The detailed analysis of the differences in nature and composition of compact and spongy bone tissues is commendable.
The article effectively highlights the nuanced disparities between the two bone tissues.
This is a fascinating explanation of the foundational differences between compact and spongy bone tissues and how they support the human body.
The details on the structure and functions of compact and spongy bone tissues are well laid out. A great source of information.
I don’t think the article covers the topic thoroughly enough. Some details were omitted.
I found it to be quite informative. I believe it provided a satisfactory level of detail.
The comparison between compact and spongy bone tissues, elucidated with comprehensive details, is enlightening.
Indeed. A well-structured and informative piece of work.
The systematic approach makes it easy to grasp the differences between the two bone tissues.
The distinctions made between compact and spongy bone tissues were insightful and valuable for better understanding these essential components of the skeletal system.
The comparative analysis indeed sheds light on the significance of these bone tissues.
The comprehensive comparison table clearly outlines the differences between compact and spongy bone tissues with precision and clarity.
Agreed, it serves as a useful reference for those seeking detailed knowledge on the subject.