A cell is what makes every living being. The cell gives every individual structure and helps properly function these structures.
Cytosol and cytoplasm are two such components of a cell. They are misused because their terms are similar.
Key Takeaways
- Cytosol is the liquid matrix found within cells, composed primarily of water, dissolved ions, and various biomolecules, providing a medium for cellular reactions and processes to occur.
- Cytoplasm refers to the entire contents of a cell, excluding the nucleus, and includes the cytosol, organelles, and other cellular structures suspended within it.
- The main difference between cytosol and cytoplasm is their composition, with cytosol being the liquid portion of the cytoplasm and the cytoplasm encompassing all the cell’s contents outside the nucleus.
Cytosol vs. Cytoplasm
The difference between the cytosol and cytoplasm is that the cytoplasm is the gelatine-like translucent fluid that fills the cells. In contrast, the cytosol is the liquid in the cytoplasm where the components are suspended.
The cytoplasm is the transparent gelatinous fluid present between the walls of a cell. This fluid houses all the other components in the cell other than the nucleus.
The cytosol is a component of the cell as well as the cytoplasm. The liquid or aqueous part of the cytoplasm is called the cytosol. This is where the organelles of the cytoplasm remain afloat.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Cytosol | Cytoplasm |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The liquid portion of the cytoplasm where the components are suspended. | The gelatinous fluid that is present between the cell walls and nucleus. |
| Chemical reactions | Their chemical reactions occur in the prokaryote. | They involve greater cellular activities like glycolysis and cell division. |
| Fundamental components | Water, soluble small and large molecules | Organelles, cytosol, and cytoplasmic structures |
| Composition | Mainly water, ions, molecules, and proteins of different sizes are soluble. | 80% spherical water, nucleic acids, enzymes, lipids, and amino acids |
| Functions | It ensures the suspended and dissolved organelles are in the right place during metabolism. | They freeze the organelles in the right position for efficient metabolism. |
What is Cytosol?
The cytosol is that part of the cytoplasm where the organelles are suspended. They are the liquid portion. Since the cytoplasm does not include the nucleus, the cytosol also would not.
Water constitutes most of the cytosol, so they are neutral. The prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells’ metabolic and other chemical reactions occur in the cytosol.
The cytosol is a complex mixture of salt, water, and dissolved ions and molecules. The protein filaments present in the cytosol are what form the cytoskeleton filaments.
The cytosol is also the site for cell communication, along with the transport of the metabolites produced to the right sites for further functioning of the cells.

What is Cytoplasm?
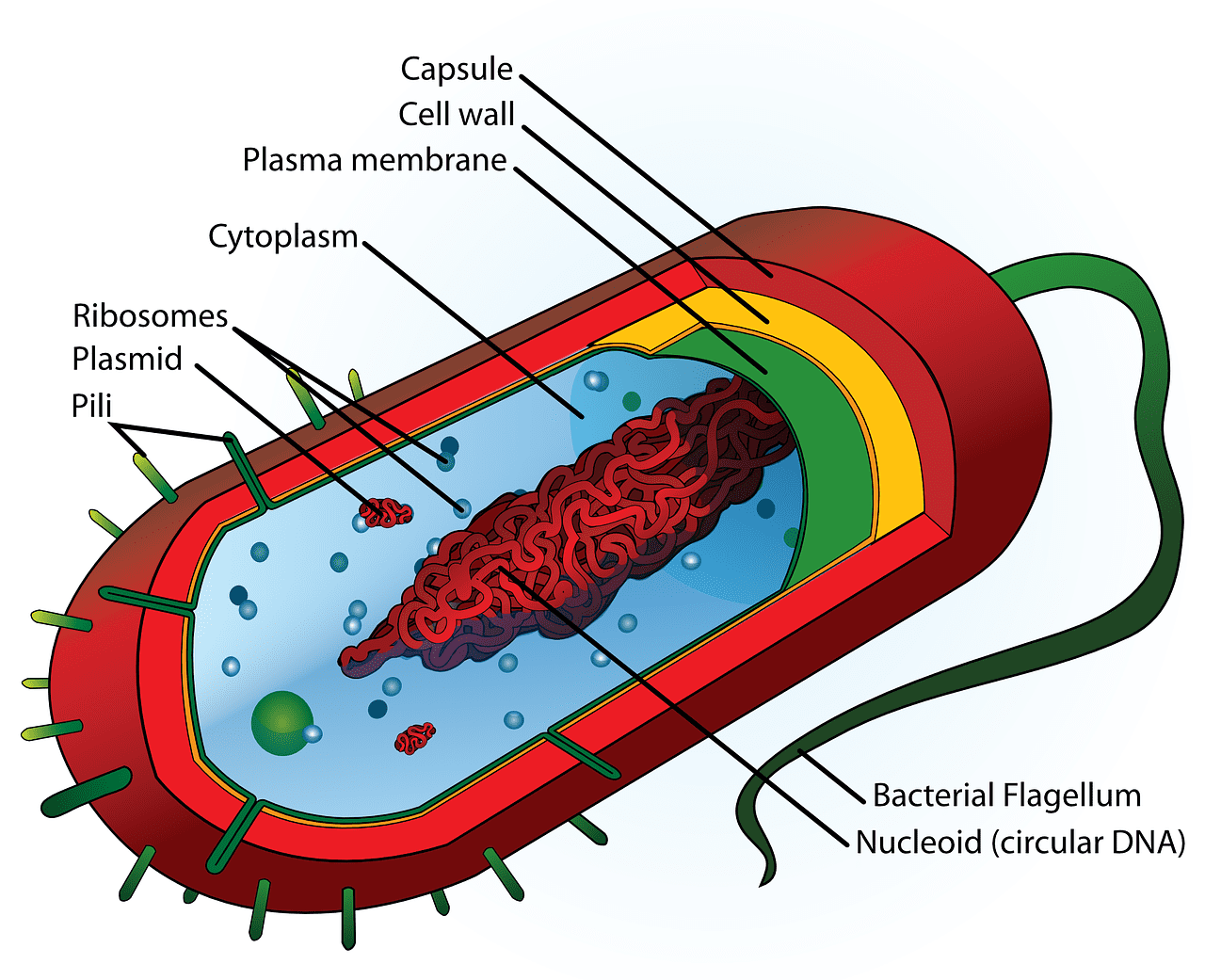
The cytoplasm is the gelatinous translucent fluid between the cell walls and the nucleus and consists of every component present in the cell, excluding the nucleus.
It is everything inside the plasma membrane in a prokaryotic cell. But in a eukaryotic cell, since it has a nucleus, it is everything between the plasma membrane and the nucleus.
The cytoplasm contains 80% spherical water, cytosol, and organelles. The organelles are the various structures in the cell for functioning, like the Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, etc.
Almost all metabolic activities and functioning happen in the cytoplasm because it comprises a cell’s organelles. Some of the activities include cell division, glycolysis, etc.
Main Differences Between Cytosol and Cytoplasm
- The composition of the cytosol and cytoplasm also vary to a great extent. The cytosol is composed of 70% water, soluble ions, soluble small and large molecules, and proteins.
- The cytosol reaches the dissolved and suspended molecules in the liquid form to the right position. At the same time, the cytoplasm freezes these molecules in these positions for efficient metabolism.
- https://science.sciencemag.org/content/190/4220/1204.abstract
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0014482788903333

I think the article could have been more engaging.
It’s information overload.
I agree with you. It’s not very reader-friendly.
I disagree with the article. It’s not as clear as I’d like it to be.
I think it’s very articulate and covers a lot of ground.
I think the article is too wordy.
Great article! Very informative! This is my first time reading something so detailed about cells.
I agree! I’m learning a lot from it.
The article is quite academic, and the main differences section is a bit dense.
I found the main differences section extremely helpful, it’s one of the best parts.
The article is very well-researched.
Yes, the references are solid.
I think the article is fascinating. I learned a lot.
It’s a bit heavy on the science jargon.
I really enjoyed reading it.
Informative but it doesn’t cover the practical applications of this knowledge.
Practical applications would be a good addition.
Very interesting article.
Definitely mind-opening