In the language of science, the Cell is called the fundamental unit of life. It is the main base upon which the whole world sustains. Cells are the tools that maintain the shape and operation of every living organism, plant, etc.
As the cell has so many responsibilities on its shoulder, it also needs something to assist it in its functions. We have various helpful elements inside a cell that assist it in its form and function.
Microtubules and Microfilaments are two of these elements. These two aid cells, although they are significantly distinct from one another.
Key Takeaways
- Microtubules are larger, cylindrical structures composed of tubulin proteins, while microfilaments are thinner, helical structures made of actin proteins.
- Microtubules provide structural support and help in cell division, whereas microfilaments facilitate cell movement and muscle contraction.
- Microtubules are more rigid and resistant to bending, while microfilaments are more flexible.
Microtubules vs Microfilaments
Microtubules are a type of cytoskeletal filaments that are long, hollow tubes made of tubulin and are involved in cell division and intracellular transport. Microfilaments are also protein filaments, but thinner, made of actin. They play a role in cell movement and muscle contraction.
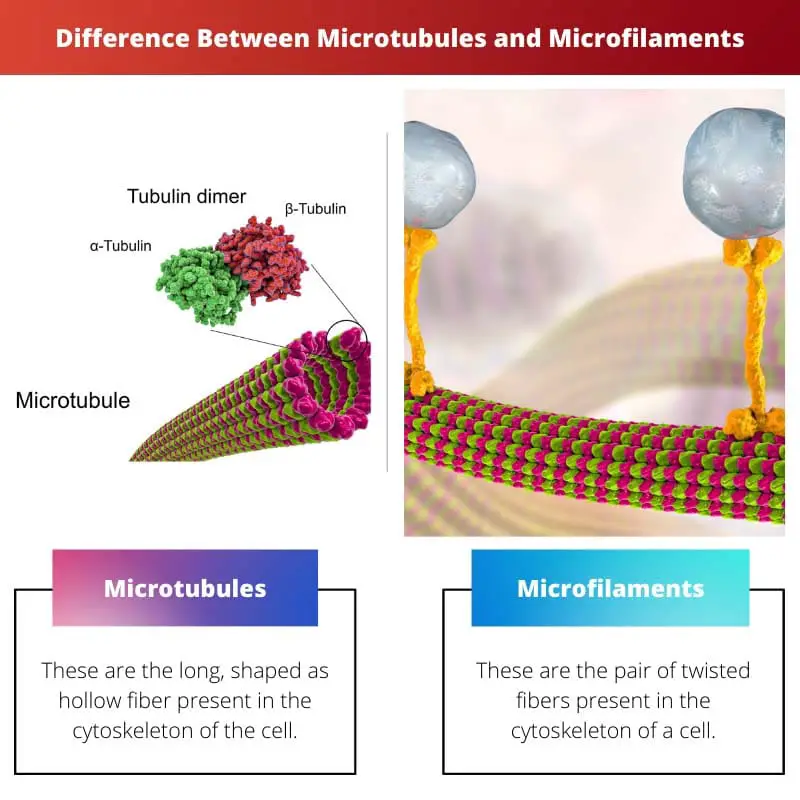
Microtubules, as the name itself suggest, have a structure of tube-like hollows. The main component which contributes to the making of Microtubules is Tubulin.
Microtubules are more of a component of a Eukaryotic cell, and they help in the maintenance of the Cytoplasm. They also have the largest size compared to everything that is present in the cytoplasm.
While Microfilaments, on the other hand, are more of a DNA-like structure, having two strands revolving around one another, forming a twisted figure. Unlike Microtubules, it is built up of Actin protein.
These are the smallest parts of the cytoplasm, judging by their size, and they play an important role in cell shrinkage.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Microtubules | Microfilaments |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | These are the long, shaped as hollow fiber present in the cytoskeleton of the cell. | These are the pair of twisted fibers present in the cytoskeleton of a cell. |
| Shape | These have the shape of a tube-like structure which happens to be hollow from the inside. | These have a shape like DNA. |
| Size | Largest fibers of cytoplasm. | Smallest fibers of cytoplasm. |
| Function | Transportation of particles in the cell and development of cell walls. | Responsible for the process of cytokinesis mainly. |
| Made up of | Tubulin protein | Actin protein |
| Diameter | Around 25 nanometers | Around 7 nanometers |
| Rigidity | More rigidity than Microfilaments | Less rigidity compared to the Microtubules |
| Nature | Microtubules in some cases are able to move and have growth over a period of time. | There is no scope for growth and movement. |
What are Microtubules?
Microtubules are one of the many fibres which find their presence in the cytoskeleton of a cell. Cytoskeleton can be understood as a big room present in the cytoplasm of a cell comprising many types of proteins, bacteria, etc.
These are only present in a cell that is Eukaryotic (a cell that has a nucleus).
A better understanding of these fibres can be made by referring them to a big group of multiple evenly joined strands. They create a linear structure and are thick in their shape. Their creation is done when dimer alpha and beta-tubulin are polymerized. They are primarily green in color.
The main task of Microtubules is the formation of a cytoskeleton. As mentioned earlier, it is the part of the cell which maintains stability in a cell.
Microtubules facilitate the transportation of various elements under the cell and maintain the cell’s shape during its movement from one place to another. They also acquiesce to the regulation of genes in a cell.
What are Microfilaments?
It is no wonder that a cell in itself comprises a whole different world comprising numerous elements. Microfilaments are one of these elements present inside of a cell and aiding it in its functions.
Microfilaments seem like DNA because of their structure. In other words, there are two strands of fibres in Microfilaments that happen to be twisted and revolve around themselves.
These strands create a 3D ladder-like structure. These are around 7 nm in diameter and the thinnest of all other fibres present in the cytoplasm.
Made up of Actin protein, these fibres are held responsible for the process of Cytokinesis. In simple terms, they play a crucial role in managing the stability and motility of a cell.
Another name for Microfilaments is stress fibres, as they also play the part of the resistance in a filament’s fracture. So to summarize, their main work is to keep up with the cytoskeleton’s shape during a cell’s movement.
Main Differences Between Microtubules and Microfilaments
- Microtubules are the long, shaped hollow fibre present in the cytoskeleton of the cell. On the other hand, Microfilaments are the pair of twisted fibres present in the cytoskeleton of a cell.
- Microtubules are shaped as hollow tubes, while Microfilaments are shaped as two strands revolving around each other.
- Microtubules are created by tubulin, while Microfilaments are made up of actin.
- The diameter of Microtubules is 25 nm approximately, but the diameter of Microfilaments is around 7 nm.
- Microtubules are the long and thick fibres of the cytoplasm. On the other hand, Microfilaments are relatively thin fibres.
- Microtubules bear the responsibility of transporting things in the cell and creating cell walls in plant cells. While Microfilaments have the responsibility of maintaining a cell’s shape during tensile forces.
- Microtubules are more rigid compared to Microfilaments.
- Microtubules have a dynamic nature because of their ability to move and grow. But Microfilaments are static in nature because of their inability to grow out or move away.
References
- https://www.nature.com/articles/nrc1317
- https://science.sciencemag.org/content/171/3967/135.abstract

The article has effectively explained the roles of both microtubules and microfilaments in cell structure and function. The nature and diameter differences between microtubules and microfilaments are well discussed, contributing to a better understanding of these cellular elements.
I found the article to be very enlightening. The content is precise and clearly articulated, making it easier to grasp the concepts.
Microtubules are long, hollow tubes made of tubulin and are involved in cell division and intracellular transport. On the other hand, microfilaments are thinner, helical structures made of actin and play a role in cell movement and muscle contraction. This distinction is well explained in the article, providing clarity on their functions.
I found the article provided a comprehensive understanding of microtubules and microfilaments. It helps in distinguishing the functions of these two important cell components.
The article’s comparison table effectively summarizes the key differences between microtubules and microfilaments. The informative content and clear explanations contribute to a better understanding of these cellular components.
I appreciate the article’s detailed descriptions and comparisons of microtubules and microfilaments. It’s a valuable resource for academic learning.
The article has clearly outlined the differences between microtubules and microfilaments, emphasizing their structural and functional variances. It’s an excellent piece of scientific writing that makes it easier to comprehend these cellular components.
The detailed comparison and descriptions of microtubules and microfilaments make this article a valuable resource for understanding these cellular structures.
I agree. The information provided in the article is presented in a clear and concise manner, making it accessible to readers.
The article effectively explains the roles and differences between microtubules and microfilaments, providing valuable insights into these essential cellular components.
Microtubules are more rigid and resistant to bending, while microfilaments are more flexible. Microtubules are involved in cell division and intracellular transport, while microfilaments facilitate cell movement and muscle contraction. The comparison table provided in the article is very informative and helps in understanding the key differences between microtubules and microfilaments.
The article has clearly explained the nature, function, and structure of microtubules and microfilaments. It’s a well-written piece.
I agree. The detailed comparison between microtubules and microfilaments provides a good overview of their structure and functions.
The comprehensive explanation of microtubules and microfilaments in the article is beneficial for readers to understand their cellular functions. The contrasting properties of microtubules and microfilaments are well articulated, providing clarity on their roles within the cell.
The article’s in-depth comparison of microtubules and microfilaments contributes to a better understanding of their structural and functional variances.
I found the article to be very informative and helpful in understanding the differences and functions of microtubules and microfilaments.
The article provides a comprehensive overview of microtubules and microfilaments, elucidating their structural differences, functions, and nature. It’s an informative piece that enhances the understanding of these important cell components.
Microtubules and Microfilaments are two of the basic elements that assist cells in their form and function. Microtubules are long, hollow tubes made of tubulin, whereas microfilaments are thinner, helical structures made of actin proteins. Both microtubules and microfilaments are important for cell movement and muscle contraction.
You have discussed the differences between microtubules and microfilaments very well.
Microtubules are composed of tubulin proteins and provide structural support, whereas microfilaments are made of actin proteins and play a role in cell movement and muscle contraction. The detailed comparison between microtubules and microfilaments in the article is very informative and easy to understand.
The article has done an excellent job of explaining the main differences between microtubules and microfilaments. The comparison table is particularly helpful.