Blockchain and data science are two of the most promising new technologies, with the potential to transform multiple sectors and fundamentally alter the way businesses and organizations operate.
One could think that these innovations are mutually incompatible, with one charting its own course and being used independently of the others.
Key Takeaways
- Blockchain is a decentralized and secure technology for recording transactions, while data science involves analyzing and interpreting large datasets.
- Blockchain technology powers cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, whereas data science is used across various industries for decision-making and predictive analytics.
- Both fields require different skill sets, with blockchain focusing on cryptography and distributed systems and data science emphasizing programming, statistics, and machine learning.
Blockchain vs Data Science
Blockchain is a database mechanism that allows transparent information sharing within a business network. It focuses on recording and validating data. Data science is the study of data to extract meaningful insights for business. It focuses on developing valuable insights from data for problem-solving.
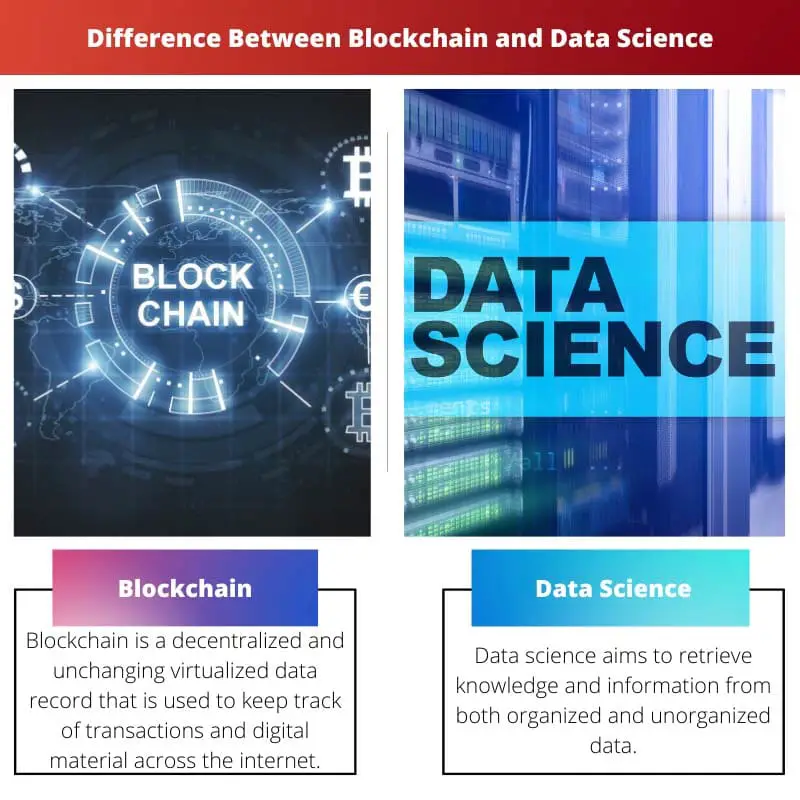
Blockchain is a decentralized and unchanging virtualized data record that is used to keep track of transactions and digital material across the internet.
An asset can be anything from a car to a house to real estate to any other direct or indirect commodities, such as branding, private knowledge, trademarks, and patents.
As a result, any substantial virtual asset is appropriate for trading and surveillance on a blockchain network.
Data science aims to retrieve knowledge and information from both organized and unorganized data.
Stats, data processing, machine training, and other sophisticated technologies are utilized in this sector to comprehend and evaluate actual processes utilizing data.
Some examples of data science applications include internet engines protocol, digital advertising, and recommender systems.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Blockchain | Data Science |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Records and validates data. | It analyses data. |
| Aim | To allow digital information to be recorded and distributed immutably. | To construct the means for extracting business-focused insights from data. |
| Purpose | Data integrity | Data prediction |
| Applications | Real-time transactions. | Provides in-depth data analysis. |
| Benefits | Mutual user consensus safety, speed, etc. | Enhances efficiency, improves the quality of data, etc. |
| Uses | Used in digital wallets, store patients’ data in the healthcare industry securely, micropayments, etc. | Building predictive causal analytics models or prediction models using machine learning. |
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger that is made up of several nodes that are coupled together without the use of a central server. Blockchain technology, as the name suggests, is based on the notion of a chain of interconnected blocks.
The functioning of pay-outs over a blockchain network gets significantly smoother than any other technique since blockchain is not regulated by any centralized body. To perform payments on the blockchain, users do not require third-party authorization.
Immutable distributed ledger technology is used in the blockchain system. As a result, once data has been recorded into the register, it cannot be modified.
Additionally, since its data is unchangeable and users can follow information back to its origin, blockchain delivers incredible reliability.
When a user begins a transfer on a blockchain network, the transaction is initially encapsulated in a block.
Following the formation of a block, the intended transaction is confirmed across a peer-to-peer network, which is made up of computers called nodes, who then legitimize the transaction.
Additionally, whenever a transaction is affirmed, it is coupled with the other blocks in the register to introduce a unique data block. Cryptocurrencies, agreements, documents, and any other relevant data may be included in a verified payment.
The majority of data is housed on centralized servers, which are frequently targeted by cyber attackers; numerous incidents of hacks and privacy violations demonstrate the concern.
On the other side, blockchain returns data control to the people who created it, making it difficult for thieves to access and change data on a broad scale.

What is Data Science?
Data is sometimes referred to as the “new oil” in economic jargon, which is why major corporations such as the renowned Amazon, Facebook, or Google have significant amounts of data under their control.
Data Science has applications in practically every business, from personalized healthcare advice to real-time transportation route optimization. Data Science, like Blockchain, provides high-paying job possibilities in a variety of fields.
Organizations may now store vast amounts of data thanks to the emergence of big data. By uncovering hidden data patterns from raw data, data science helps organizations to make better judgments and forecasts.
It all comes down to obtaining data insights from historical trends that show different data viewpoints that were previously undiscovered.
Data science is used to create predictive causal advanced analytics, for as determining the likelihood of consumers completing future credit card or loan payments on schedule.
Prescriptive analytics, for example, may employ the technology to develop models with the ability to make judgments about how to adapt them using dynamic factors, such as a self-driving automobile.
Data science aids businesses in increasing efficiency by allowing them to make quick and informed decisions, resulting in increased profitability.
It enhances the accuracy of records/knowledge while also assisting in the delivery of improved products and services based on client preferences and tendencies.
Data science strives to improve data quality and assist in the delivery of desired services and goods based on client trends and preferences.

Main Differences Between Blockchain and Data Science
- Blockchain records data along with validating it while data science analyses data for actionable insights.
- Blockchain aims to allow the available digital information to be recorded, validated, and then distributed. However, data science aims to get business-focused insights from data.
- The purpose of blockchain is to maintain data integrity meanwhile the purpose of data science is accurate data prediction
- While blockchain allows for real-time money transfers, data science allows for in-depth data analysis.
- Blockchain transactions are performed with reciprocal customer consent and provide security, speed, and accessibility, while data science aids organizations in increasing efficiency, improving data and information quality, and so on.
- Blockchain is used in digital wallets, micropayments, etc. meanwhile, data science is utilized in predictive causal analytics models or prediction models with the help of machine learning.
References
- https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3390566.3391681
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nadeem-Javaid/publication/335621124_Analyzing_and_Securing_Data_using_Data_Science_and_Blockchain_in_Smart_Networks/links/5d9add8992851c2f70f21acb/Analyzing-and-Securing-Data-using-Data-Science-and-Blockchain-in-Smart-Networks.pdf