The majority of people love to get mesmerized by their surroundings. People get awed by the wonders the environment possesses, including versatile living organisms.
Two among them are protozoa and algae. Although, these two sets of organisms can be differentiated quickly based on their structure and looks. In this article, we will study how algae differ from protozoa.
Key Takeaways
- Algae are a diverse group of photosynthetic organisms, while protozoa are single-celled animals that consume other organisms or organic matter.
- Algae can be found in various aquatic environments and produce oxygen, while protozoa are found in aquatic and terrestrial environments and play a vital role in nutrient cycling.
- Algae are used in various applications such as food, medicine, and biofuels, while protozoa are used in research and as indicators of environmental health.
Algae vs Protozoa
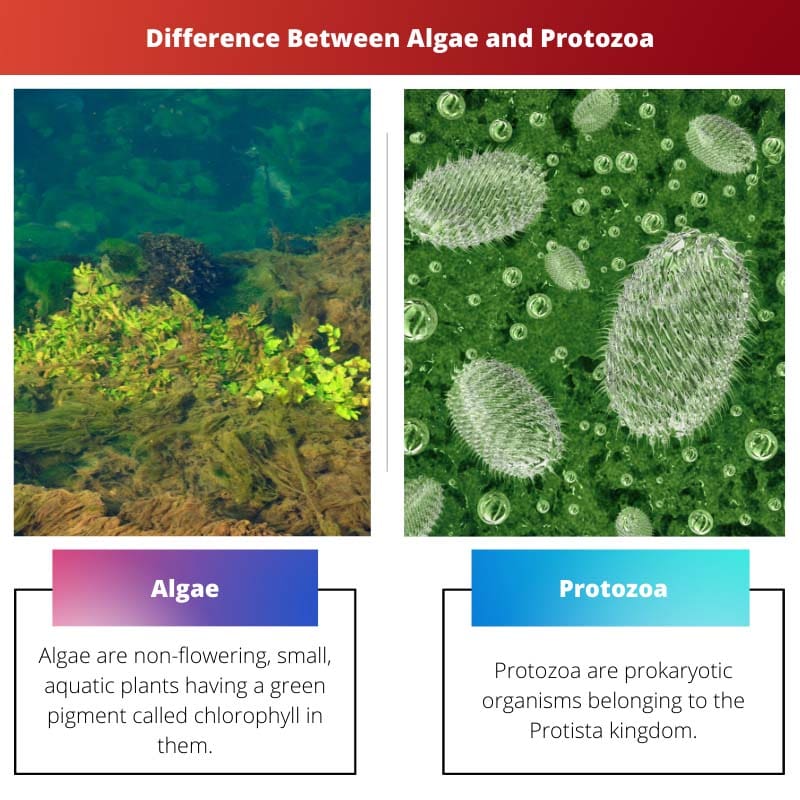
Algae are a diverse group of aquatic organisms that can be unicellular or multicellular and are green or brown in color, playing a vital role in the ecosystem by producing oxygen. Protozoa are also unicellular organisms but have more complex cellular structures and are motile.

The cell wall of algae is made up of a substance called cellulose. The spore is the resting unit of algae. Some examples of algae are cyanobacteria, brown algae, Seaweeds, red algae, and green algae.
Protozoa are prokaryotic organisms, i.e., single-celled animals. Protozoa are prokaryotic organisms belonging to the Protista kingdom. Protozoa are organisms possessing animal-like characteristics.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Algae | Protozoa |
|---|---|---|
| Cells | Multicellular/Eukaryotic; some are single-celled too. | Single-celled/Prokaryotic; some are multicellular too. |
| Definition | Algae are non-flowering, small, aquatic plants with a green pigment called chlorophyll. They lack roots, actual stems, vascular systems, and leaves. | Protozoa are prokaryotic organisms belonging to the Protista kingdom. |
| Characteristics | Algae are organisms possessing plant-like characteristics. | Protozoa are organisms possessing animal-like characteristics. |
| Method Of obtaining Energy | Algae make their food. Hence they are autotrophs. | Protozoa are not capable of making their food. Hence they are heterotrophs. |
| Significance | Photosynthesis | Phagocytosis |
| Chlorophyll | Chlorophyll is present. | Chlorophyll is absent. |
| Cell Wall | The cell wall of algae is made up of a substance called cellulose. | The cell wall is absent. |
| Resting Unit | Spore | cyst |
| Examples | Cyanobacteria, brown algae, Seaweeds, red algae, green algae. | Euglena, Amoeba, Entamoeba histolytica, Paramecium, Leishmania. |
| In humans | Algae produce toxic chemicals which are hazardous to humans. | Protozoa are capable of causing diseases in humans, such as malaria, by plasmodium. |
| Importance | Algae produce around 70% of oxygen in the atmosphere. | Most aquatic food chains depend upon protozoa as their foundation. |
What is Algae?
Algae are microscopic which are unicellular. These types of unicellular Protozoa are called microalgae. In contrast, the types of multicellular protozoa are called macroalgae.
Algae are multicellular organisms or eukaryotic organisms. Algae are non-flowering, tiny aquatic plants with a green pigment called chlorophyll. They lack roots, actual stems, vascular systems, and leaves.

What is Protozoa?
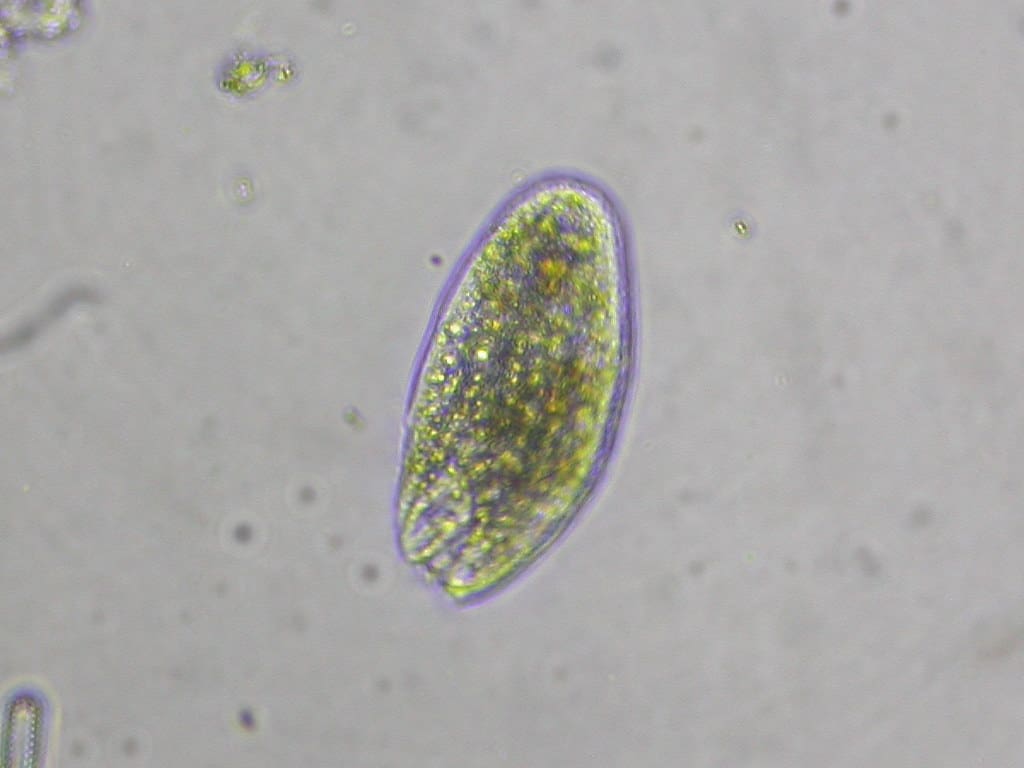
Protozoa are free-living organisms. However, sometimes they infect higher-order animals as well. As they lack a cell wall, thus they possess a variety of shapes.
Chlorophyll is absent in protozoa. The cell wall is absent in protozoa. A cyst is the resting unit of protozoa. Some examples of protozoa are Euglena, Amoeba, Entamoeba histolytica, Paramecium, and Leishmania. Some protozoa are capable of causing diseases in humans, such as malaria by plasmodium.
Main Differences Between Algae and Protozoa
- Algae produce toxic chemicals which are hazardous to humans. At the same time, some protozoa are capable of causing diseases in humans, such as malaria by plasmodium.
- Algae produce around 70% of oxygen in the atmosphere. At the same time, most aquatic food chains depend upon protozoa as their foundation.