Although they can have a similar appearance, bruises and hematomas are not the same, small blood vessels under the skin burst and bleed, resulting in a bruise. Blood pooling outside of a blood artery leads to a hematoma.
While some of the same factors can lead to both bruises and hematomas, hematoma-causing injuries are frequently significantly more severe.
A bruise and hematoma are easily confused due to their comparable soreness and a reddish appearance. Hematomas and bruises, however, differ slightly from one another.
Technically speaking, a hematoma is similar to a bruise, but hematomas are frequently considerably more serious than bruises, according to Jenna Liphart Rhoads, a registered nurse and nursing educator at NurseTogether.
Key Takeaways
- Bruising and hematoma result from blood pooling under the skin due to broken blood vessels, but a hematoma is larger and more localized than a bruise.
- Bruising is minor and resolves independently, while hematomas may require medical intervention in severe cases.
- Both bruises and hematomas can be caused by trauma, but hematomas may also occur after surgery or in conjunction with certain medical conditions.

Bruising vs Hematoma
Bruising refers to the purple-black or blue staining of the skin after healing from an injury and bleeding under the skin. It is also called a contusion. When blood gets collected outside the blood or skin, giving a discolored round swollen shape due to any injury or accident, it is called Hematoma.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Bruising | Hematomas |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Any injury affected by small blood vessels | An accumulation of blood in the area of an injury |
| Diagnosis | The appearance of the affected area | The presence of a bruised area. In the case of the head, an MRI or CT can diagnose a subdural hematoma. |
| cause | Hitting your body against a hard object or walking into something | Phlebotomist injuring a blood vessel; hitting your head, breaking a bone. |
| Treatment | Applying Ice pack on the affected area then take a rest | Also, using an ice pack works but Surgery is required for a subdural hematoma |
| symptoms | A red area that changes from to purple then yellow over a number of days | Swelling, pain and a bruise in the affected area of injury. However, signs of head hematomas are headache,nausea, dizziness and confusion |
What is Bruise?
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is bleeding into the skin brought on by the rupture of tiny blood vessels. If there isn’t a breach in the skin, the blood will remain there and stain it. Muscles and bones can also bleed when they are bruised.
Petechiae and purpura are two other kinds of subcutaneous bleeding. Purpura is more than 2 mm in size and is caused by petechiae, which generates tiny pinpoint spots smaller than that. Ecchymosis refers to a huge bruise that is more than one centimetre in size.
When you harm yourself in any way, a bruise results. Bruising is frequently caused by slamming against something or falling. After having an IV inserted into your arm, bruises are also typical.
Some persons have a higher chance of getting bruised. People who have purpura simplex, for instance, bruise very quickly. Bruises are more likely to occur when taking aspirin and anticoagulant medications.
However, physical characteristics are used to make diagnoses. When a bruise first develops, it is initially red. Later, it turns into a purple patch, and then it turns yellow after a few days. Bruises can be a sign of significant underlying illnesses, thus it is recommended to see your doctor if you bruise frequently and for no apparent cause.
In addition, bruises heal on their own. Applying an ice pack to the injured area will work, although it is not always necessary.
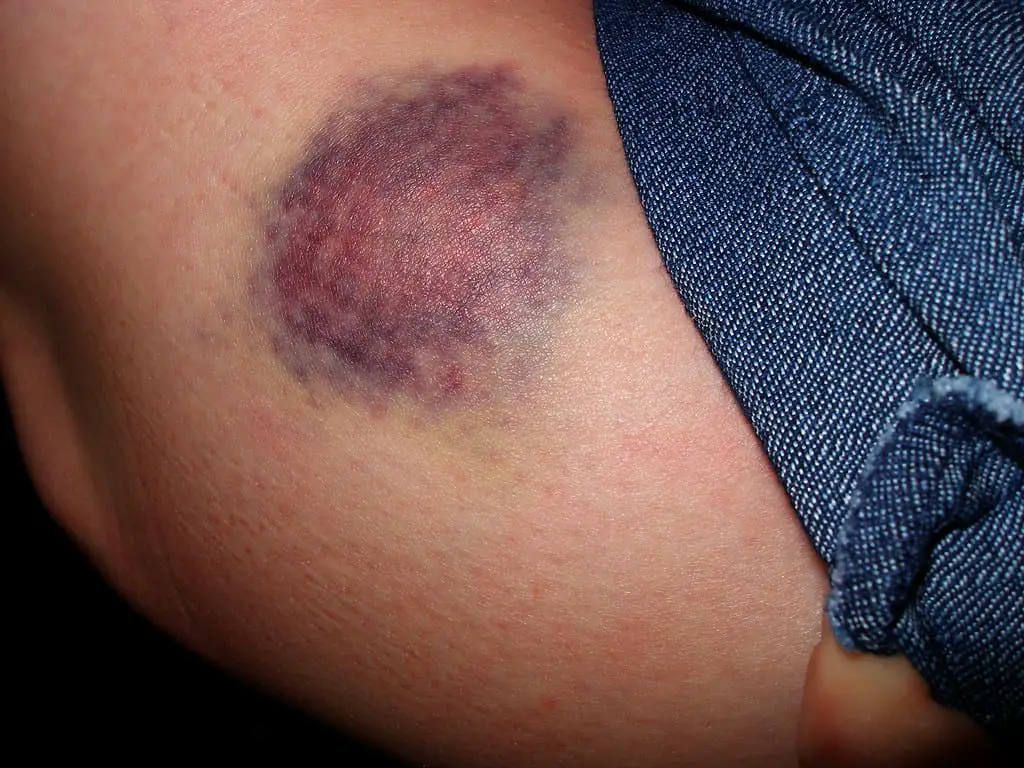
What is Hematomas?
A hematoma, a blood collection, frequently develops after being bruised. It is a more serious wound than a straightforward bruise. It is caused by bleeding from a vascular structure, which includes important organs.
Hematomas can develop in several locations, even deep within the body. You will see discolouration resembling a bruise when it occurs close to the skin.
A shattered bone is just one of the many possible causes. Hematomas can also be brought on by head trauma. A blood test can become complicated if a phlebotomist unintentionally pokes a needle through a blood vessel wall. Hematomas can also be caused by leukaemia and blood coagulation issues. Hematatoma risk factors include alcoholism and using anticoagulant medication.
However, it can be identified by observing the presence of a bruised region. The area will also hurt. Neurological symptoms such as disorientation, headaches, nausea, and dizziness may be present in the case of a subdural hematoma. The person frequently has a history of hurting their head.
While the type of hematoma will determine the course of treatment, simple hematomas under the skin can be treated by applying an ice pack for about 20 minutes at a time, reducing discomfort and swelling. An IV or blood test-related hematoma disappears on its own. To avoid harm to the cerebrum, a hematoma in the brain or between the brain and dural membrane must be surgically drained.

Main Differences Between Bruising and Hematomas
- A bruise is an injury that results in small blood vessels breaking and leaking under the skin. The skin becomes painful to the touch and turns discolored as a result. Bruises change color as they start to heal, going from red to blue, purple, or black. The bruise will first turn yellow or green, then ultimately light brown as the body starts to absorb the blood and repair the area.
- While a hematoma develops when a major blood artery is injured, it’s a moderate to a severe injury that results in blood gathering, pooling, and clotting under the skin, giving it a spongy, rubbery, or lumpy feeling. Hematomas can develop anywhere in the body and are not a cause for alarm. Some, however, constitute medical crises, such as an intracranial hematoma or brain haemorrhage.
- Another distinction is that a bump, a sickness like leukaemia, or both might bring on bruising. A hematoma may develop as a result of phlebotomy, trauma, shattered bones, or bleeding on the brain.
- Bruises are also identified based on how they appear. The appearance of a bruise and a CT or MRI scan are used to diagnose hematomas (for brain hematoma).
- Additionally, bruises have a reddened region that, over several days, turns purple, then yellow. Although a hematoma looks like a bruise, it also exhibits symptoms like pain and swelling. Dizziness and nausea are other symptoms of a brain hematoma.
- Furthermore, treating a bruise is not needed, but you can use an ice pack. Treating a hematoma involves using an ice pack; in the case of a subdural hematoma, surgery is needed.
