A microprocessor is just the CPU. A microprocessor is an inclusive device comprised of millions of semiconductors. Not every microprocessor, meanwhile, are a CPU.
As a consequence, CPU throughput is improved.
The CPU is not impeded by processes that could be performed by other microprocessors, and because they are all functioning together, the outcomes are shown quicker, more consistently, with far less breakdown or unavailability.
Key Takeaways
- A CPU is the central processing unit of a computer, while a microprocessor is a smaller, more specialized type of CPU used in embedded systems and other devices.
- A CPU can perform a wide range of tasks, while a microprocessor is designed to perform a specific set of functions.
- A CPU is found in desktop and laptop computers, while microprocessors are in various devices, including smartphones, cars, and medical equipment.
CPU vs Microprocessor
Microprocessor is the electronic chip containing a computer system’s processing unit, while the CPU is the overall component that performs the processing. The CPU is composed of some components and communicates with other parts of the system to execute instructions and perform calculations.

The designation central processing unit, or CPU, was utilized many years ago to denote the section of the system that conducted the essential processing.
Older CPUs were made up of massive vacuum valves that were linked simultaneously and took up a lot of volume. The CPU was substantially shrunk with the introduction of compound semiconductors and microprocessors.
The previously massive and bulky CPU was shrunk to a relatively small chunk of technology with all the linkages previously inscribed into it.
A microprocessor is a highly sophisticated inclusive circuit that contains millions of neurons in a compact chip. The wiring that permits the CPU to work and the processors is contained therein.
The microprocessor was so sophisticated that it obliterated all previous computing kinds.
It has attempted to incorporate a few aspects, such as a modest amount of information known as the cache.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | CPU | Microprocessor |
|---|---|---|
| Consists | Memory and I/O are all consolidated into a single chip. | That just a Central Processing Unit is present. |
| Used in | It is found in personal computers. | A microprocessor is a sophisticated and costly device that must process many instructions. |
| Nature | A CPU is simple, having fewer commands to process. | It lacks RAM, ROM, I/O units, modems, and various peripherals. |
| Peripherals | It has RAM, ROM, and perhaps additional peripherals on a single chip. | The CPU uses an inbuilt controlling bus. |
| Uses | It connects to RAM, ROM, and numerous peripherals through an external bridge. | It connects to RAM, ROM, and numerous different peripherals through an external bridge. |
What is CPU?
The CPU has a management module, logic, elementary unit, registers, and a tiny amount of memory known as a database. One phase at the moment, the processing unit interprets commands.
It follows these instructions by the computer software that is now operating. In that perspective, the CPU executes distinct commands, which are then concatenated to complete a job,
which is referred to as a computer program.
The arithmetic unit performs mathematical operations. If the computer program requests a mathematical simulation, the reasoning unit passes the request to the instruction set, which does the process.
When the procedure is finished, the results are saved in the CPU cache or returned to the logical section for additional processing. The control module determines how and when the messages are delivered.
One more word on a unique type of processor: the linear processor, sometimes an array chipset. This CPU runs on a processor architecture that contains one-dimensional code arrays known as vectors.
Compared to a scalar engine, whose directives act on specific data elements. Most CPUs nowadays are vectors.
Although with the latest models of microprocessors, the CPU remains the core functional unit that governs computer activity.
This underscores why CPU makers devote so much work to adjusting and improving the computing capability of these devices.

What is Microprocessor?
Millions of pixels comprise the CPU. These are little electrical gadgets that contain an energetic battery.
They have an on/off switch that directs the current along a specific channel to get the intended outcome. Both gadgets’ circuitry becomes entangled, resulting in a smooth operation.
Cognition, internal and external storage devices, network cables, graphics and video components, and other analog joysticks, such as a mouse or keyboard, send electrical impulses to the CPU.
The controlling hardware that links to the baseboard is the microprocessor. The foundation houses all of the individual microprocessors, yet they all interact to create what is recognized as a machine.
These are the mathematical activities or outcomes that are exhibited, such as network, visual, or audio processes. Even if different efficiency chips are present on microprocessors, the CPU will evaluate the output.
Microprocessors are in charge of regulating the logic in nearly all contemporary technology. The internal operation of a microprocessor is determined by its characteristics and functions.
It is restricted by the frequency of diodes that can be installed on the circuit, the variety of bundle dismissals that can link the engine to the other elements of the system,
the frequency of linkages that can be made, and the quantity of heat generated by the integrated circuit.
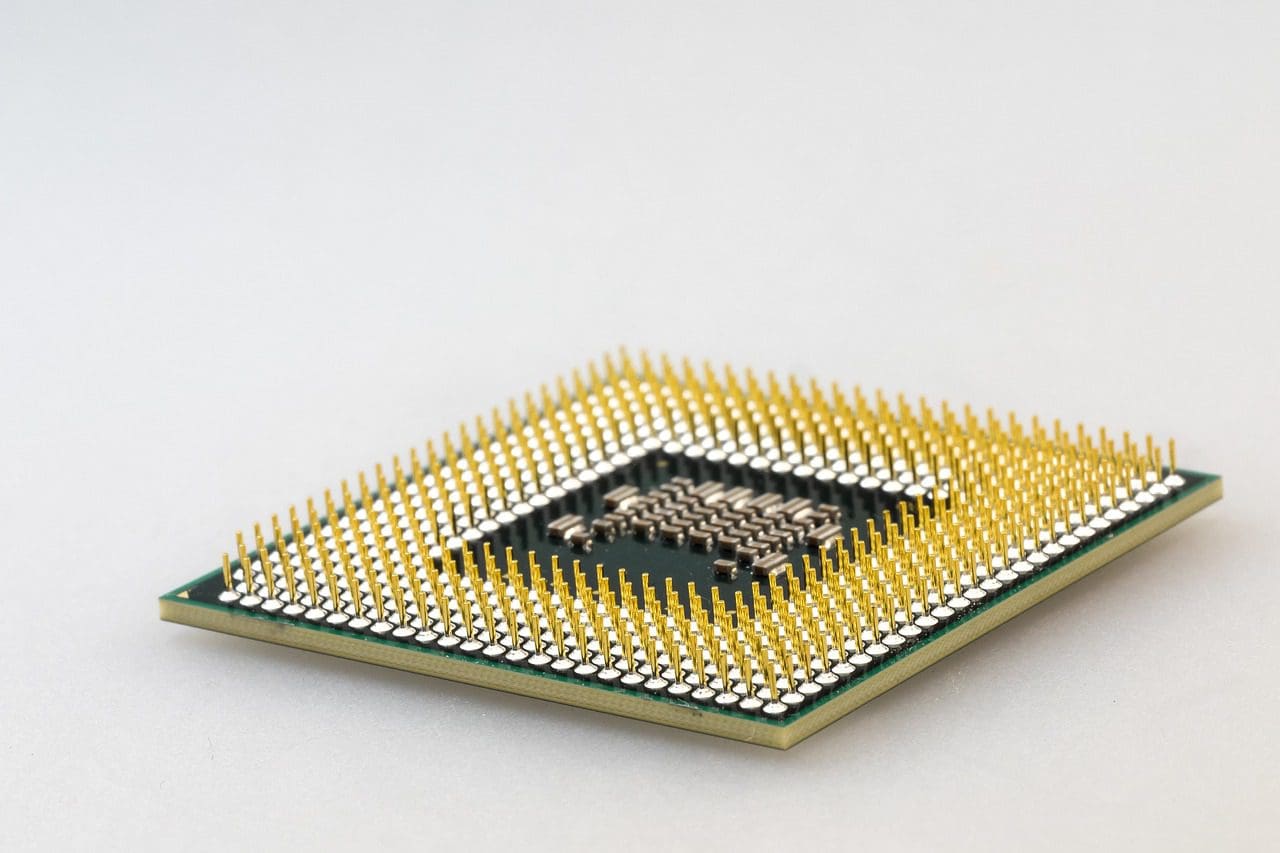
Main Differences Between CPU and Microprocessor
- CPU is primarily applied in embedded systems. At the same time, the microprocessor is most prevalent in personal computers.
- In CPU, memory and I/O are incorporated into a single semiconductor. Microprocessor, on the other hand, where just a Central Processing Unit is present.
- A CPU is compact, simultaneously limiting commands to process. In comparison, the microprocessor is a complex and exorbitant device that must decode a substantial rate of orders.
- CPU has RAM, ROM, and perhaps numerous accessories on a single device. On the other hand, the microprocessor excludes RAM, ROM, I/O processors, thermostats, and various capabilities on the transistor.
- The CPU employs an intrinsic governing bus. Microprocessor interfaces to RAM, ROM, and numerous accessories across an auxiliary bridge.

The article tends to be very repetitive and verbose. The author should be more clear and concise.
The post is very comprehensive and well executed. It doesn’t lack in depth or precision.
The author of this post doesn’t seem to be very competent in the subject. The material seems quite doubtful.
The article is poorly argued. It lacks consistency and coherence.
I actually agree with you, Candice White. The post lacks strong arguments.
I disagree with you. The post is very informative and unlike you, I think the author did an excellent job.
The article gave me a lot of knowledge on the topic, I appreciate the trouble the author went through to write such an informative piece.
Yes, the article gave me a lot to think about. Very well researched.
I found the post very comical. The author seemed to be trying too hard, but the result is quite entertaining. I had a good time reading.
I agree with you, Collins Imogen. The post was so funny and entertaining.
I don’t agree. The author’s tone is very serious, it’s clear that they put a lot of effort into this.