The graph of technological growth in the electronic world has potentially increased. In contrast, integrated circuits have transformed the world of electronics. Be it computers, mobile phones, or other home appliances, you name it, they have become a mandatory part of the household. All because of the small size and low-cost integrated circuits (ICs). The three famous ICs, FPGA, Microcontroller, and Microprocessor, are moving the electronic world around them.
Key Takeaways
- FPGAs are highly customizable, allowing for parallel processing and reprogrammable hardware configurations.
- Microcontrollers integrate a processor, memory, and peripherals in one chip, making them ideal for low-power, embedded systems.
- Microprocessors are high-performance, general-purpose CPUs that require external components, like memory and input/output devices.

FPGA vs Microcontroller vs Microprocessor
FPGAs are integrated circuits that provide flexibility but have limited space. The microprocessor is an electronic device that performs arithmetic and logic operations but has limited processing power. A microcontroller is a single integrated chip limited to the task it is wired with.
FPGA stands for field-programmable gate array. It is an integrated circuit with logic gates that the user can reprogram as per its requirement. Hence the name field-programmable is used. The FPGA is configured using hardware description language (HDL).
A microcontroller is also called a small computer on a single IC chip. It contains single or multiple processor cores with memory and programmable peripherals. The idea behind the design of microcontrollers is their application in the embedded form.
A microprocessor is also a single-chip computer processor with data processing control and logic. The microprocessor manages the functions performed by the central processing unit. It contains arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry to perform the required tasks.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | FPGA | Microcontroller | Microprocessor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Execution of tasks | FPGA executes all tasks in parallel | The microcontrollers execute tasks one by one | The microprocessor executes the tasks in sequence |
| Peripherals | No built-in peripherals but contains logic gates | Built-in peripherals | No built-in peripherals |
| Flexibility of tasks | Can perform any task | Performs specific tasks | Performs specific tasks |
| Hardware structure | Non-fixed | Fixed | Fixed |
| Processing power | High | Medium | Limited |
What is FPGA?
FPGA stands for field-programmable gate array. It is an integrated circuit used in numerous electronic devices. As the name reveals, these ICs are reprogrammable. The user can configure it according to its required tasks.
FPGA has multiple logic gates. These can perform as simple logic gates, for example, AND and XOR, and can also be configured to perform complex functions with combinations. Most FPGAs include memory elements.
FPGAs can start system software development in parallel with hardware. They can enable the performance simulation very early in development. They also allow numerous system trials and design iterations before the final architecture.
The user, in the form of hardware description language HDL or a schematic design, defines the behavior of FPGA. HDL is suited for large structures, while schematic allows easier visualization of a design and its modules.
The design of the FPGA is simulated on multiple stages in a design flow. FPGA can be used to solve any computable problem. They are faster for some applications reason being their parallel functioning nature.
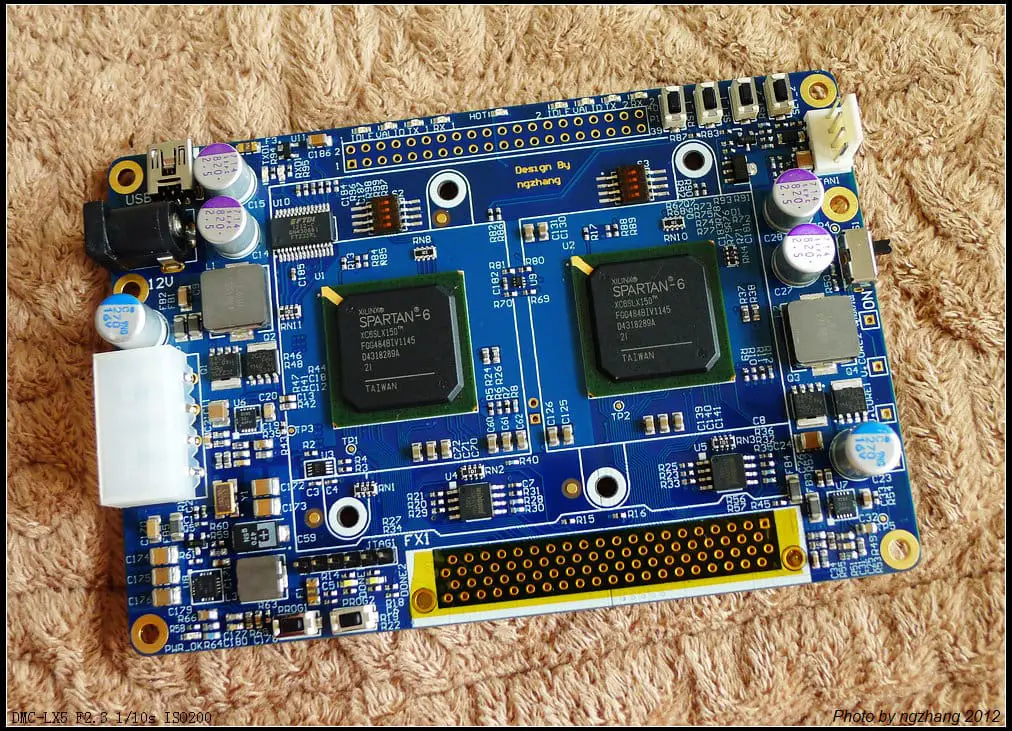
What is Microcontroller?
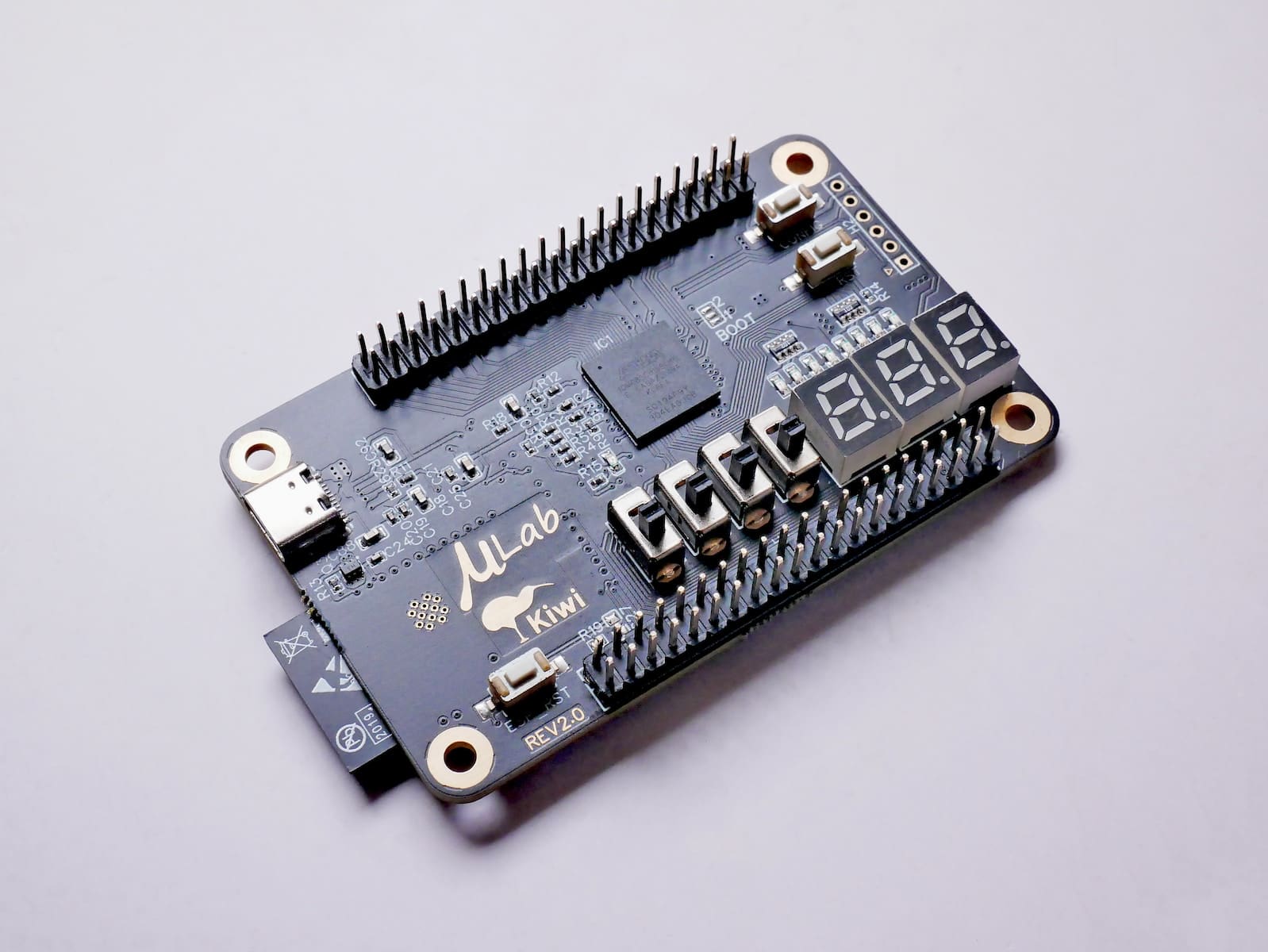
A microcontroller is a single-chip integrated circuit. Memory like ferroelectric RAM, NOR flash, or OTP ROM is too included in the chip. A small amount of RAM can also be found.
Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications. These are used in automatically controlled devices. For example, implantable medical devices, automobile engine control systems, appliances, office machines, remote controls, toys, power tools, and other embedded devices.
Microcontrollers have built-in memory, and input/output devices, which make them reduced in size and economical to control more devices. Microcontrollers are popular and economical in data collection, sensing, and actuating as edge devices.
Microcontrollers have low power consumption. They can operate at frequencies as low as 4 kHz. Generally, they can retain their functionality during waiting for an event. They are suited for long-lasting battery applications. Only some of the microcontrollers have the feature of a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). This enables the processor to output analog signals or voltage levels.

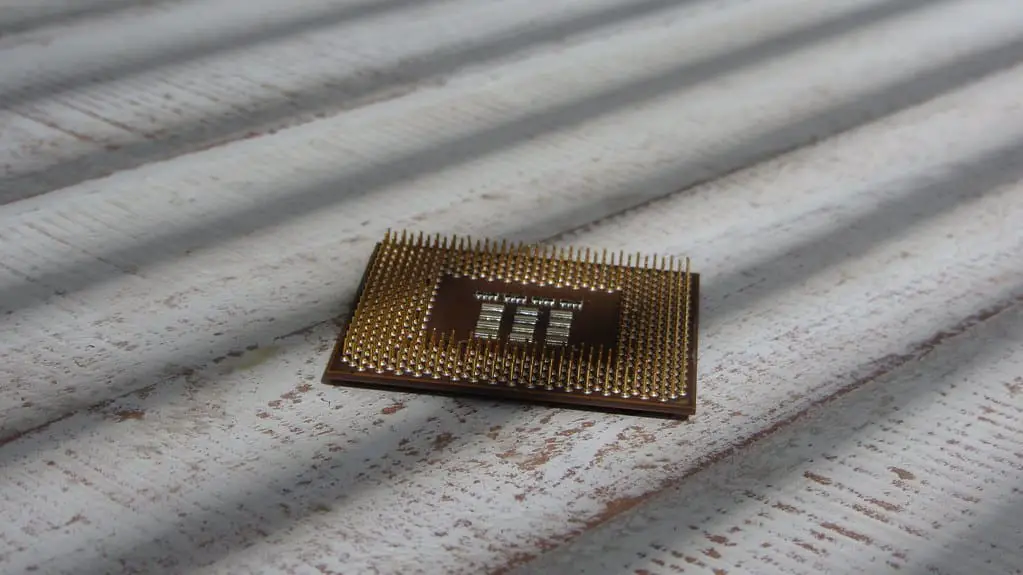
What is Microprocessor?
A microprocessor is a computer chip with single or multiple integrated circuits. It can interpret and execute programming instructions and perform arithmetic operations too.
It is a clock-driven processor that accepts binary data as input, then processes this data according to the stored instructions in its memory and gives the output in binary form. They contain both combinational logic and sequential digital logic.
These ICs are produced by a highly automated metal-oxide-semiconductor fabrication process (MOS). They have a low unit price and increased reliability because of the lesser connection fails.
There were many items that were not computer related and still had microprocessors. These include household appliances, vehicles and their accessories, toys, light switches/dimmers, tools and instruments, electrical circuit breakers, smoke alarms, battery packs, and audio/visual components.
Since the capacity of the microprocessor is increasing, it has almost obsoleted the other forms of computers from the computer market.
Main Differences Between FPGA and Microcontroller and Microprocessor
- FPGA is a field-programmable circuit, while microcontroller and microprocessor are not.
- FPGA can perform many tasks per the user’s requirements, while microcontroller and microprocessor can only perform specified tasks configured by the manufacturer.
- Microcontrollers can be built with a power-saving system, while microprocessors and FPGAs lack such a feature.
- FPGAs are programmed using VHDL, and microcontrollers are programmed using C or C++, and microprocessors are programmed using assembly language.
- FPGA’s power consumption is the highest compared to the microcontrollers and microprocessors.