Different kinds of bodily problems affect our bodies. However, it may be confusing to diagnose the nature of the problem.
]Inflammation and swelling are two such bodily issues that emerge due to several internal and external factors. In addition, there are visible differences between inflammation and swelling.
Key Takeaways
- Inflammation is a body’s response to injury or infection, while swelling is an increase in size or volume due to fluid retention.
- Inflammation can cause swelling, but swelling may also occur without inflammation.
- Inflammation involves redness, heat, and pain, whereas these symptoms may not always accompany swelling.
Inflammation vs Swelling
Inflammation is a complex process that involves the activation of various immune cells and the release of inflammatory mediators to eliminate the source of injury or infection. Swelling is the visible manifestation of the accumulation of fluid and immune cells in the affected tissue.
Inflammation refers to a process whereby the white blood cells in the human body and their by-product provide protection from various infections.
Some problems associated with inflammation are cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and asthma. Moreover, some categories of arthritis that occur due to inflammation include gouty arthritis and psoriatic arthritis.
The treatment may also involve the use of pain medications and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Swelling refers to a process wherein a part of the human body expands in size. Swelling is an outcome of inflammation. There are multi-facet reasons for swelling.
Some of these causes include insect bites, rash, pregnancy, menstruation, injury, and infections.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Inflammation | Swelling |
|---|---|---|
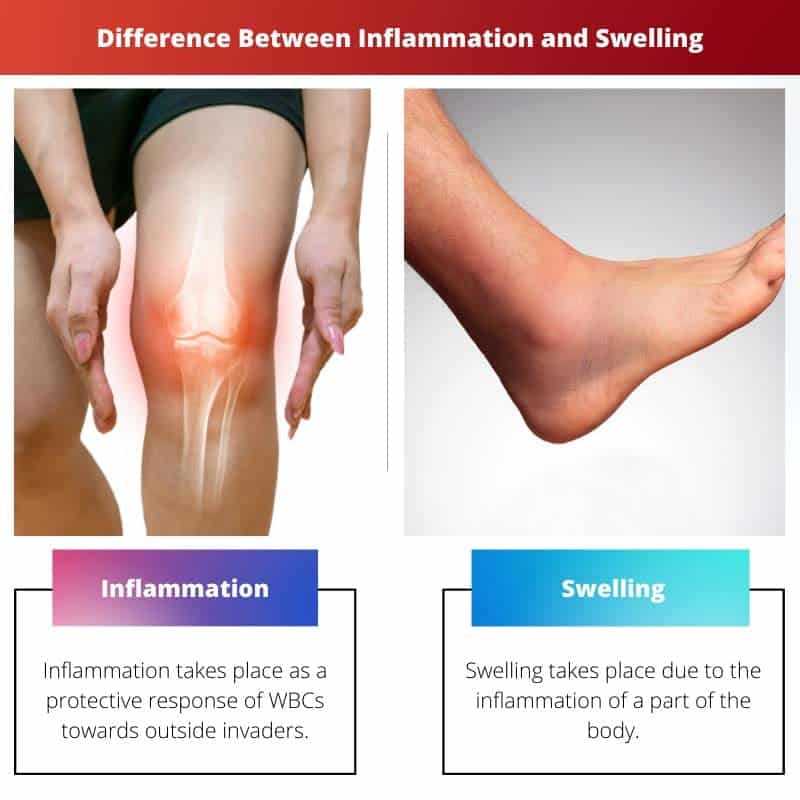
| Definition | Inflammation takes place as a protective response of WBCs towards outside invaders. | Swelling takes place due to the inflammation of a part of the body. |
| Types | There are two types of inflammation: chronic inflammation and acute inflammation. | There are five types of swelling: oedema, acute, chronic, effusion, and hemarthrosis. |
| Cause | Inflammations occur as a response of the immune system. | Swelling is merely the enlargement of any part of the body. |
| Relationship | Inflammation is not an outcome of swelling. | Swelling is an outcome of inflammation. |
| Symptoms | Symptoms of inflammation include loss of appetite, redness, fatigue, headaches, and muscle stiffness. | Symptoms of swelling include nausea, fever, dizziness, insomnia, vomiting, and pain. |
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation refers to a process whereby the WBCs in the human body and their by-product provide protection from various infections. The sources of infection can be bacteria, fungi, viruses, or protozoa.
Inflammation, thus, is a bodily response produced by the immune system in the absence of any invaders to fight off.
There can be two categories of inflammation. Inflammation may occur for a short period of time or continue for a significantly larger time period.
Some problems associated with inflammation are cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and asthma. Some categories of arthritis that occur due to inflammation include gouty arthritis and psoriatic arthritis.
There are several symptoms of inflammation. Some of these include redness, joint pain, joint stiffness, swollen joint, fever, chills, fatigue, headaches, loss of appetite, and muscle stiffness.
The diagnosis of inflammation includes the doctor inspecting the patient’s medical history and administering a physical exam.
The treatment of inflammation involves a detailed procedure that aims to correct, control, or slow down the disease process. The treatment may also involve the use of pain medications and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Several other medications include corticosteroids, antimalarial medications, as well as biologic drugs.

What is Swelling?
Swelling refers to a process wherein several parts of the human body expand in size. Swelling is an outcome of inflammation. Swelling may take place in the internal parts of the body or on the outer skin and muscles.
There are several causes of swelling. Some of the common causes of swelling are insect bites, illnesses, or injuries.
However, internal swelling may be an outcome of medications of various sorts or a serious injury. Some symptoms of swelling include vomiting or pain in the affected area.
There are other symptoms of internal swelling. They include nausea, fever, dizziness, fatigue, insomnia, vomiting, flu-like symptoms, and pain.
There are multi-facet reasons for swelling. Some of these causes include fluid retention, pregnancy, menstruation, injury, hormonal changes, heart failure, anaphylaxis, and a venomous insect bite.
Diabetics may also be prone to swelling due to several reasons.
The diagnosis of swelling includes X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs. The treatment of swelling involves either a surgical procedure or other methods like chemotherapy or radiation.
There are some home remedies to cure swelling, such as avoiding salt or wearing a support hose. To conclude, swelling is a curable medical problem that occurs due to several reasons.
Main Differences Between Inflammation and Swelling
- Inflammation takes place as a protective response of WBCs toward outside invaders. On the other hand, swelling takes place due to the inflammation of a part of the body.
- Symptoms of inflammation include swollen joints, fever, chills, loss of appetite, and muscle stiffness. In contrast, symptoms of swelling include nausea, fever, dizziness, fatigue, insomnia, vomiting, flu-like symptoms, and pain.
- Inflammation is not an outcome of swelling. In contrast, swelling is an outcome of inflammation.
- There are two types of inflammation: chronic inflammation and acute inflammation. On the other hand, there are five types of swelling: oedema, acute, chronic, effusion, and hemarthrosis.
- Inflammations occur as a response to the immune system. In contrast, swelling is merely the enlargement of any part of the body.