In Chemistry, different compounds are formed by different types of bonds between the molecules.
Various factors determine what type of bond should be formed between different molecules, and the type of molecules plays a huge role in the formation of such bonds.
A bond is an attractive force acting between two molecules.
Key Takeaways
- Ionic bonds form between metals and non-metals through the transfer of electrons, while covalent bonds form between non-metals through electron sharing.
- Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points, while covalent compounds have lower melting and boiling points.
- Ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved in water or melted, but covalent compounds do not.
Ionic Bonds vs Covalent Bond
Ionic bonds are formed between atoms through the transfer of electrons, creating ions that are attracted to each other due to their opposite charges. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, creating a mutual attraction that holds the atoms together.
An ionic bond is formed in the case of ionic compounds. Ionic compounds are made of molecules containing charged ions, which could be either positively or negatively charged.
Thus this creates a force of attraction between the molecules as opposite charges attract each other. This force of attraction results in the formation of the bond.
Covalent bonds are formed between non-metals. This type of bond is formed due to sharing of electrons between two molecules.
As one of the molecules in a covalent compound is electron deficient, it receives the required number of electrons from the donor molecules to create a stable covalent compound.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Ionic Bond | Covalent Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Creation | Ionic bonds are formed due to the transfer of ions between molecules | Covalent bonds are formed due to sharing of electrons between two molecules |
| State of compound | The compounds formed are present only in solid-state | The compounds formed are present in all states of matter |
| Type of molecules | The bonding occurs between a metal and a non-metal | The bonding occurs between two non-metals |
| Polarity | Ionic compounds are nonpolar | Covalent compounds are polar |
| Melting Point | Ionic compounds have higher melting points | Covalent Compounds have lower melting points |
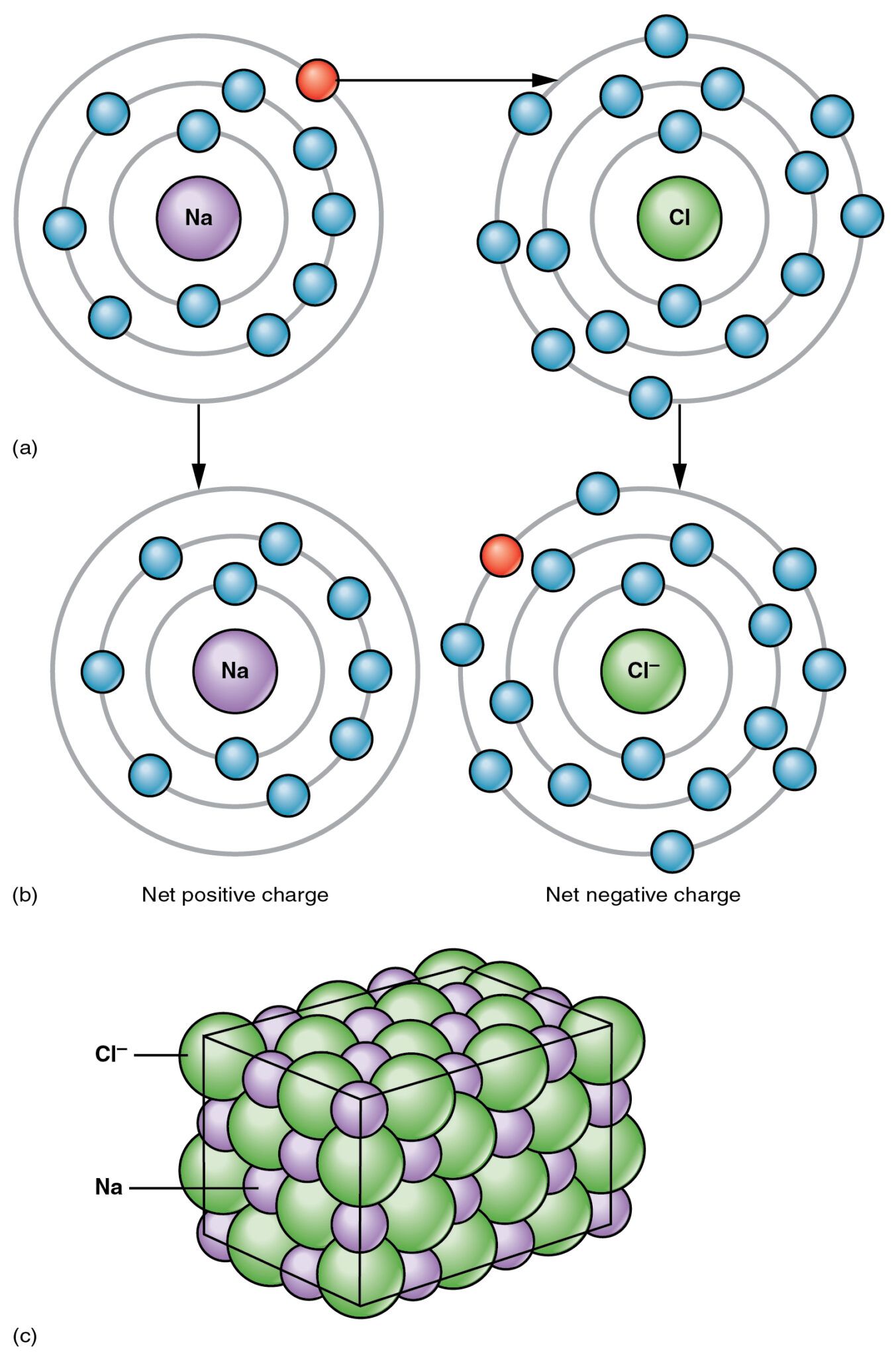
What is Ionic Bond?
An ionic bond is one of the three types of bonds that occur between molecules, forming an ionic compound.
The bond occurs between a metal and a non-metal, and one of the most common examples of such a compound is salt (NaCl), in which Sodium (Na) is a metal and Chlorine (Cl) is a non-metal.
It is a strong bond and cannot be broken as easily as in the case of covalent bonds. The bond occurs due to a sharing of electrons between the metal and the non-metal.
One of the molecules in an ionic compound is electron deficient, while the other molecule is electron-rich, creating a force of attraction between the two molecules.
The electrostatic force of attraction results in the interaction between the two molecules, sharing electrons from the electron-rich atom to the electron-deficient atom.
The donor atom or molecule completely transfers the atom to the receiver molecule or atom, resulting in a strong and clean bond between the two molecules.
Such ionic compounds’ characteristics are their high melting points and high electrical conductivity in a molten or dissolved state. Ionic compounds are also highly soluble in water.
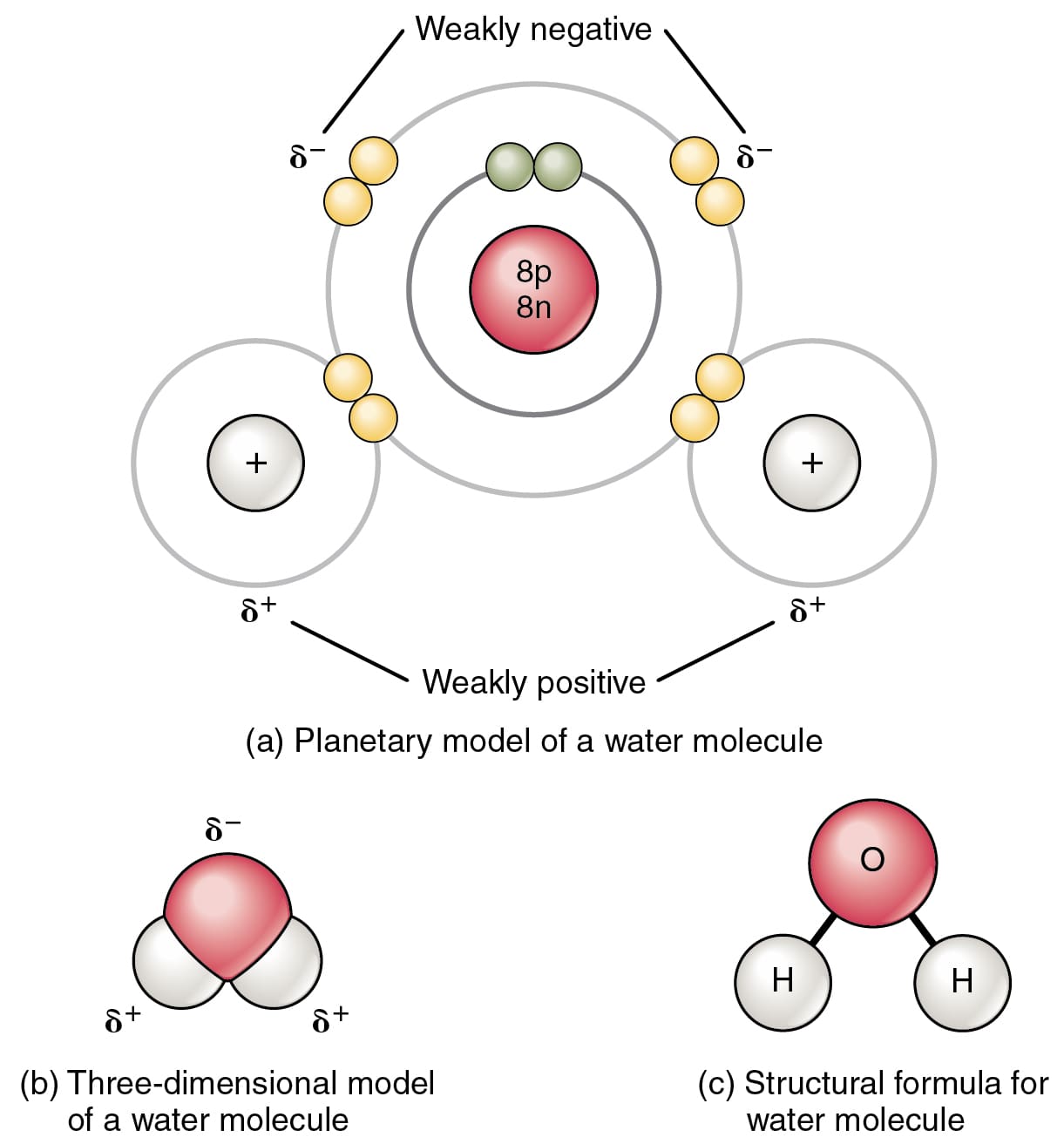
What is Covalent Bond?
A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond between molecules that leads to the formation of a covalent compound.
It is the weakest of the three types of chemical bonds, and the molecules in a covalent compound can be easily separated.
Covalent bonds are formed between two non-metals, and the bonding of metals of molecules depends on the number of electrons valence shell.
Bonding occurs by sharing of electron pairs, and this sharing of electrons occurs to maintain the chemical balance between the molecules or atoms.
The sharing of electrons between two unstable molecules creates a stable valence shell in both molecules.
When both atoms have reached their full valence state, a bond is formed between the two atoms or molecules.
The shared pair of electrons is present between both atoms to maintain the stability of the compound.
The most common example of a covalent bond is between the two Hydrogen atoms in an H2 molecule.
In an H2 molecule, the two Hydrogen atoms share two electrons leading to a covalent bond.
The key factor required for the formation of a covalent bond is the electronegativities of the molecules. Two atoms with similar electronegativities result in a covalent bond.
Main Differences Between Ionic and Covalent Bond
- Ionic bonds are formed due to the transfer of ions between molecules. Covalent bonds are formed due to sharing of electrons between atoms.
- Ionic compounds are only present in a solid state. Covalent compounds are present in all states of matter.
- An ionic bond is formed between a metal and a non-metal. A covalent bond is formed between two non-metals.
- Ionic compounds are non-polar, whereas covalent compounds are polar
- Ionic compounds have very high melting points, whereas covalent compounds have low melting points.



