The term ‘plankton’ comes from a Greek word that means “wanderer” or “drifter,” which refers to the tiny species that float along ocean currents and drift along in bodies of fresh water.
Zooplankton and phytoplankton are the two types of plankton found in the oceans. Even though they live in the same waterbody, have identical sizes, and are both vital to the marine environment, the two different forms of plankton have distinct characteristics.
Key Takeaways
- Phytoplankton is autotrophic, while zooplankton is heterotrophic.
- Phytoplankton is the primary producer in the food chain, while zooplankton is the primary consumer.
- Phytoplankton can photosynthesize, while zooplankton cannot.
Phytoplankton vs. Zooplankton
Phytoplankton are a group of photosynthetic microorganisms that drift near the surface of the water and use sunlight to produce energy through the process of photosynthesis. Zooplankton are small, heterotrophic organisms that feed on phytoplankton and other zooplankton. They include a diverse array of animals, such as small crustaceans, rotifers, and jellyfish.

Phytoplankton is free-flowing autotrophic plankton. It is referred to as microalgae. They can be photosynthetic plankton or chemosynthetic algae in marine habitats and freshwater. Phytoplanktons are the primary producers of the oceanic environment.
Zooplankton is a group of floating organisms. They are heterotrophic and are found in both freshwater and marine habitats. They are primarily found in lower regions of the water body.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Phytoplankton | Zooplankton |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Phytoplankton is a free-floating plant-like structure on the water’s surface. | Zooplankton is an animal-like group of free-floating organisms on the water’s surface. |
| Appearance | It looks like cloudy patches when in place, green-colored to brown color. | These are transparent. Found in varying shapes and sizes. |
| Found in | They are located on the water’s surface as they require sunlight. | Found in more profound and darker ocean regions, away from sunlight. |
| Mode of nutrition | They produce their food by photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. They are autotrophic. | They depend on phytoplankton and other zooplankton. They are heterotrophic. |
| Functions | They act as food for zooplankton and help indicate marine health (e.g., in the case of red tides). | They act as food for higher heterotrophs. Helps in the indication of the presence of the toxic substance in the marine environment. |
| Photosynthesis | Phytoplanktons are capable of photosynthesis. | Zooplanktons are incapable of photosynthesis. |
| Energy | Phytoplanktons get energy using photosynthesis. | Zooplanktons get their energy by feeding on other plankton. |
| Food chain supply position | Primary producers | Primary or secondary consumers |
| Examples | Cyanobacteria, Blue-green algae, diatoms, dinoflagellates, and coccolithophores | Meroplankton, crustaceans (krill), mollusks, holoplankton, chordates, radiolarians, protozoans, and foraminiferans |
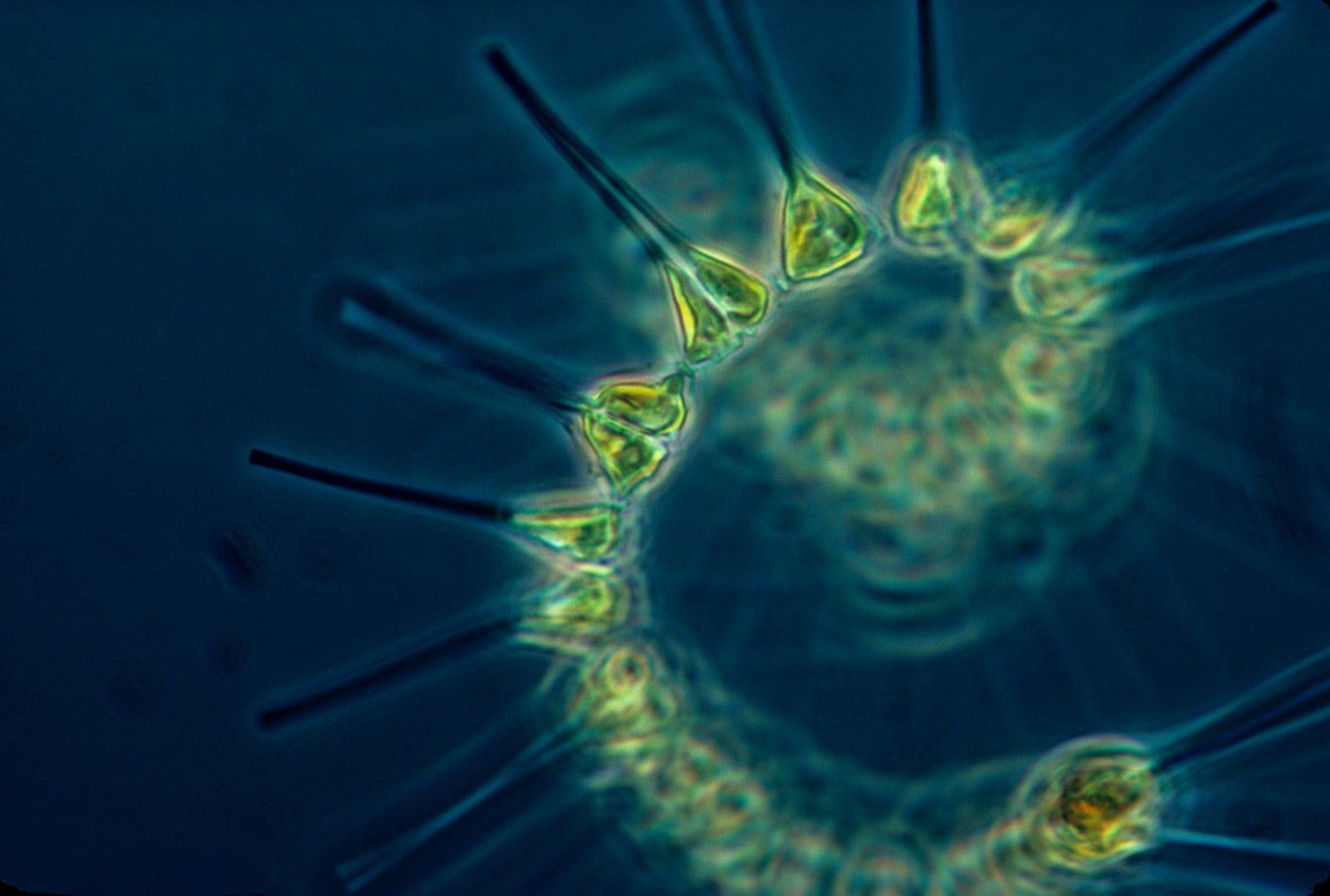
What is Phytoplankton?
Phytoplankton is free-flowing autotrophic plankton and is also known as microalgae. They can be either photosynthetic plankton or chemosynthetic algae.
Phytoplanktons are photosynthetic plants that obtain energy through photosynthesis and take up nutrients from their surrounding environment.
They are tiny microorganisms and cannot be seen by our naked eye, but they appear cloudy when present in the masses. Phytoplankton constitutes approximately 1% of the world’s total biomass.
What is Zooplankton?
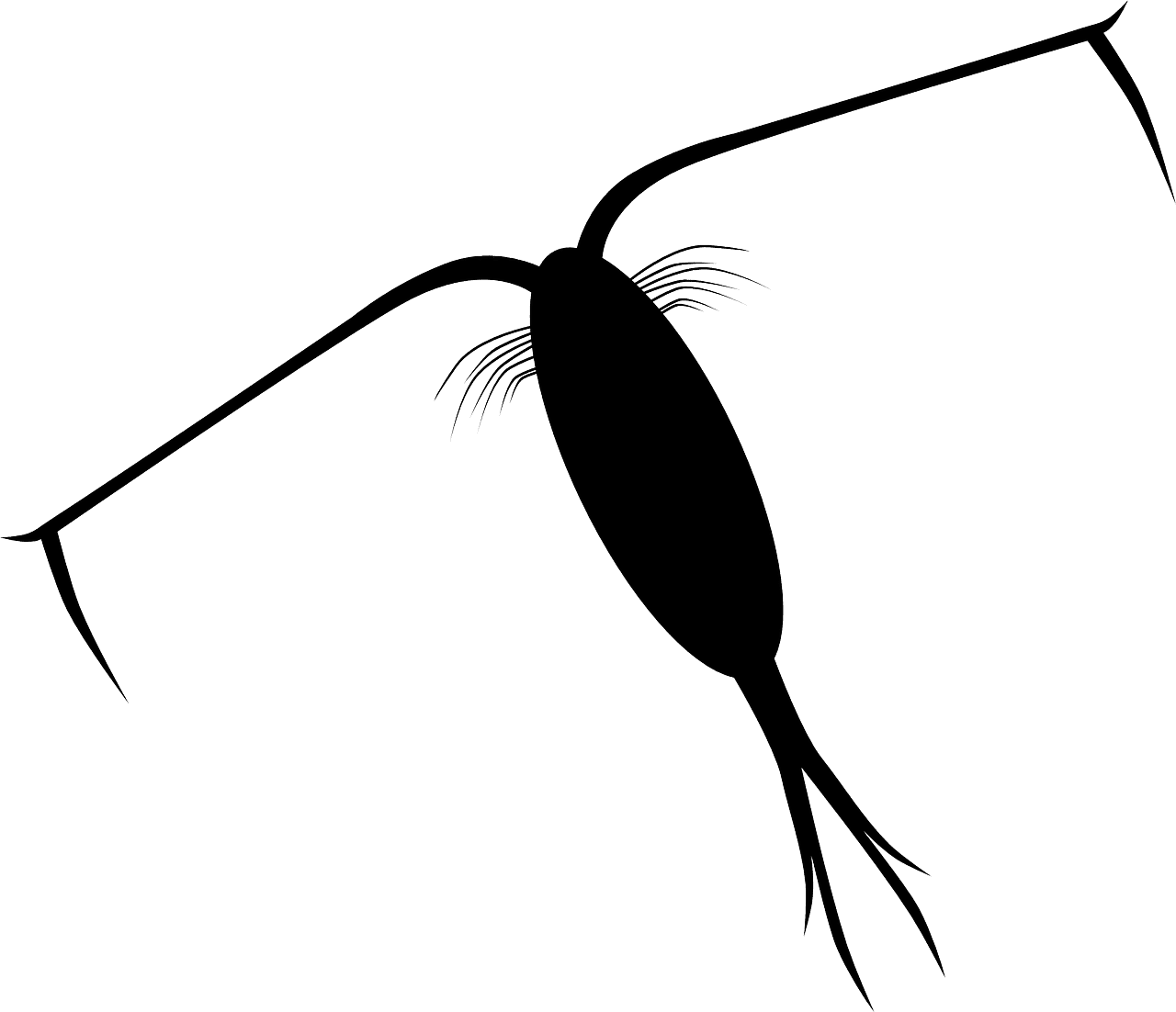
Zooplankton is a group of floating organisms, heterotrophic in nature, found in both freshwater and marine habitats. They are primarily found in lower regions of the water body.
Zooplankton is found in deeper parts or the middle parts of the oceans as they do not require sunlight and tend to travel to the surface to feed and escape their predators.
Some typical examples of zooplankton are meroplankton, crustaceans such as krill, mollusks, chordates, radiolarians, jellyfish, protozoans, and foraminiferans.
Main Differences Between Phytoplankton and Zooplankton
- Phytoplanktons are found on the water body’s surface, while zooplankton is located on both characters and the interior of the water body.
- Phytoplanktons prepare their food, i.e., They are capable of photosynthesis, while zooplanktons are not.



