The brain stem is an essential part of the brain and that plays a role as a connector of various parts of the brain to the spinal cord. It is located at the bottom of the brain, which looks like a branch.
The brain stem consists of three things. Pons and Medulla are two different parts situated in a brain stem.
Key Takeaways
- The pons is located in the upper part of the brainstem, connecting the cerebellum to the rest of the brain.
- The medulla oblongata is found at the lower end of the brainstem, controlling autonomic functions like breathing and heart rate.
- The pons is involved in facial sensations and expressions, while the medulla manages vital bodily functions.
Pons vs Medulla
The pons is a part of the brainstem located between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata. The medulla oblongata is located at the base of the brainstem, just above the spinal cord. It also helps to regulate digestion, swallowing, and coughing. It is a crucial part of the brainstem.
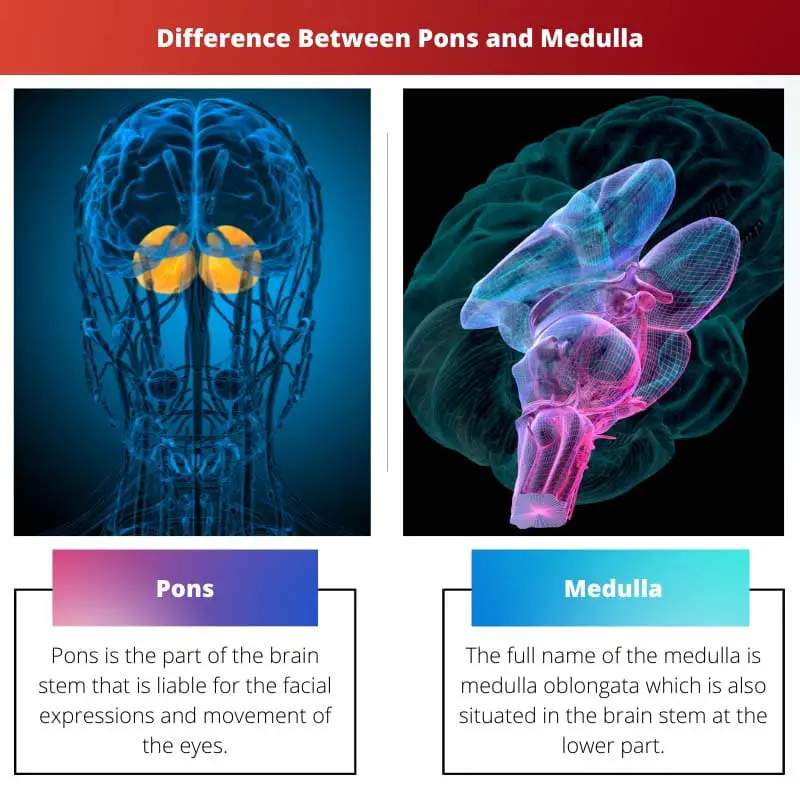
Pons is part of the brain stem that is liable for the facial expressions and movement of the eyes. Many brain nerves that contain sensory information travel and connect to the pons.
Some nerves even have their origin points located at pons. Pons is fragile and can have a tumour that can be life-threatening.
The full name of the medulla is medulla oblongata which is also situated in the brain stem at the lower part.
It works as a connector between the spinal cord and other parts of the brain, which is how it becomes a very important part of the brain. The main work done by the medulla is to transmit signals between the body and the brain.
Comparison Table
| Parameters Of Comparison | Pons | Medulla |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Pons is one of the three parts of the brain stem that is situated on top of it. | The medulla is also one of the three parts of the brain stem is located in the bottom area. |
| Structure | Pons looks like a horseshoe and is made of transverse nerve fibers. | The medulla looks like a branch and made tissues known as lymph epithelial. |
| Work | Pons is a point where sensory nerves of the brain connect or originate. | The medulla is a part where the brain and body meet and communicate with each other. |
| Responsibility | The work required or done by the transverse nerve is provided and managed by pons | The medulla is responsible to give body signals from the brain to move in a rhythm. |
| Effect | Pons affect things such as the ability to hear, the sensation of the skin, movement of eyes, taste in the mouth, etc. | The medulla is responsible for activities that are automatically going on such as breathing and pumping. |
What is Pons?
Pons is a significant part of the brain stem. It is located between the medulla oblongata and cerebellum.
The structure of the pons is like a broad horseshoe. Pons is made of fibres known as transverse nerves that help the medulla to connect with the cerebellum.
Pons is the point where all the cranial nerves either originate or terminate.
These nerves help in the transportation of information, which is sensory to the brain. It also circulates motor impulses through the brain.
The pons is used as a pathway by nerve fibres so that they can connect to the Cortex within the cerebellum. Pons work with the medulla to play an important role in the process of breathing.
For rapid or required eye movement, the active functioning of the pons is very essential. Without the functioning of the pons, facial expressions can not be generated.
The information pons is liable to deliver are taste, sensation, hearing, eye movement, etc. The position of the pons is a very crucial area where the spinal cord connects to the brain system.
Two sections of the pons are the pontine tegmentum, which refers to the interior area, and the basilar pons, which refers to the outer area.
When it comes to the term autonomic nervous system, which is accountable for the body’s multiple functions, pons makes a remarkable contribution to this system.
What is Medulla?
The special feature of the Medulla oblongata is that it takes only 0.5% of the weight of the entire brain, yet it manages to perform a very vital role in keeping the body and brain in a rhythm.
For example, glands in the human body release hormones only when they get a signal from the medulla to do so.
The process of breathing entirely depends on the Medulla, even the beating of the heart can not be constant without being in touch with Medulla.
The medulla is responsible for all the involuntary acts the human body commits. Even though it is very small, it consumes almost 20% of energy to work.
If Medulla is removed from the brain stem, there is no way in which the brain and body will be able to communicate with each other. The name itself means “little mind” in Latin.
The medulla is right above the hole known as the foramen magnum. It is a medium for spinal tracts to circulate information such as eye function, pain, tone of the muscles, sensation, control of the muscles, touch, vibrations, etc.
If a person’s medulla is broken, he can be suffered from problems or diseases such as vomiting, trouble in balancing, hiccups, loss of sensation in different limbs, damaged breathing system, etc.
Main Differences Between Pons and Medulla
- The information broadcasted by pons is from the cerebellum to the cerebrum. In contrast, the information broadcasted by the medulla is to the brain from the body.
- Pons works for sensory nerves by being the origin and termination point. On the other hand, Medulla works as a connector between the body and the brain.
- Pons is placed on top of the brain stem. In contrast, Medulla is located in the lower part of the brain and top of the spinal cord.
- Transverse nerve fibres are the material that forms pons, while the Medulla is made of lymph epithelial tissues. Nerves are used to transmit signals.
- Pons is accountable for acts like the movement of or breathing, while Medulla is a medium that transmits sensation signals from the brain to the body and vice versa.