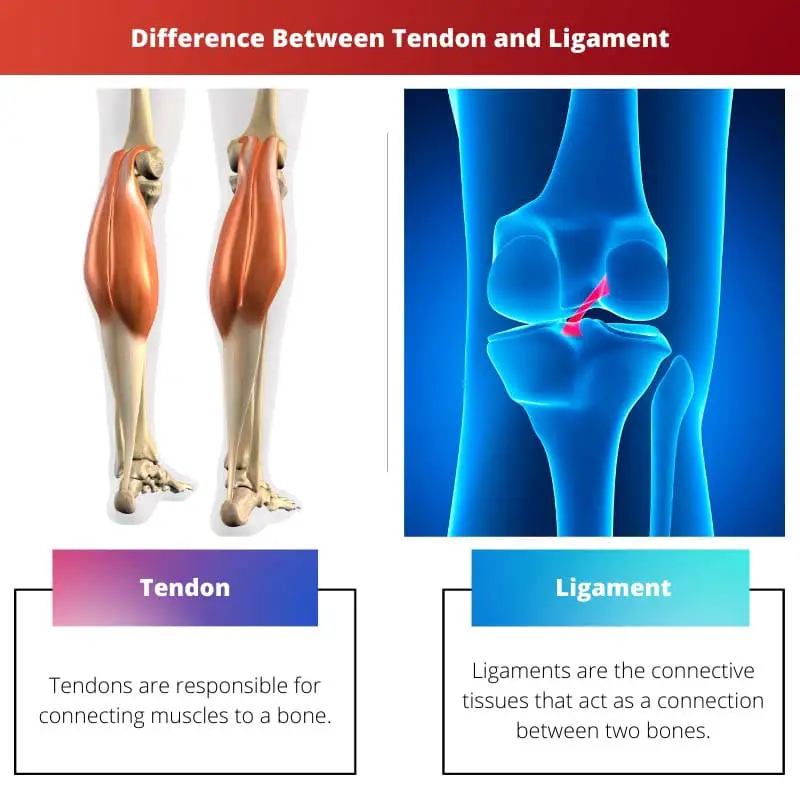
Tendons are tough, flexible bands of fibrous tissue that connect muscles to bones, enabling movement and transmitting force. Ligaments, however, are strong, elastic bands of tissue connecting bone to bone, stabilizing joints and limiting excessive movement to prevent injury.
Key Takeaways
- Tendons and ligaments are both types of connective tissue in the body.
- Tendons connect muscle to bone and transmit the force of muscle contraction to the bone.
- Ligaments connect bone to bone and provide stability and support to joints.
Tendon vs Ligament
Tendons are composed of collagen fibers and are highly resistant to tension, allowing them to transmit the force generated by muscles to the bones they are attached to. Ligaments are also composed of collagen fibers but are more elastic than tendons, allowing them to stretch and recoil.
Both fall under the category of Dense Granular Connective Tissues. Without these, the human body cannot properly work the muscular and skeletal systems.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Tendon | Ligament |
|---|---|---|
| Connects | Muscle to bone | Bone to bone |
| Function | Transmits force from muscle to bone for movement | Provides stability and support to joints |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, more rigid | More flexible, some elasticity |
| Color | White | Yellowish |
| Blood supply | Poor | Limited |
| Healing time | Slower due to poor blood supply | Slower due to limited blood supply |
| Example | Achilles tendon (connects calf muscle to heel bone) | ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) in the knee |
What is Tendon?
Tendons are dense, fibrous connective tissues that consist primarily of collagen fibers arranged in parallel bundles. These collagen fibers provide tensile strength, allowing tendons to withstand high levels of force and tension. Within the tendon structure, there are also specialized cells called tenocytes, which produce and maintain the collagen matrix.
Function of Tendons
The primary function of tendons is to connect muscles to bones, facilitating movement by transmitting the forces generated by muscle contractions to the bones they are attached to. This transmission of force allows muscles to exert control over skeletal structures, enabling various movements such as walking, running, and gripping objects. Tendons also play a crucial role in maintaining the stability of joints during movement.
Tendon Adaptations
Tendons possess unique adaptations that enable them to withstand the demands placed upon them during physical activity. These adaptations include increased collagen content, alignment of collagen fibers along the lines of tension, and the presence of specialized structures like fascicles and tendon sheaths. Additionally, tendons have a limited blood supply, relying on diffusion for nutrient delivery and waste removal.
Common Injuries and Treatment
Despite their strength and resilience, tendons are susceptible to injury, due to overuse, trauma, or degenerative changes associated with aging. Common tendon injuries include tendinitis (inflammation of the tendon), tendinosis (degeneration of the tendon), and tendon ruptures. Treatment involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and in severe cases, surgical intervention to repair or reconstruct the damaged tendon.

What is Ligament?
Ligaments are strong bands of fibrous connective tissue composed primarily of collagen fibers, similar to tendons. However, ligaments differ in their organization and function. They are more elastic and contain a higher proportion of elastic fibers compared to tendons. Ligaments also have a lower cell density compared to tendons and contain fibroblasts, which are responsible for maintaining the ligament’s structure and integrity.
Function of Ligaments
The primary function of ligaments is to connect bones to other bones within joints, providing stability and limiting excessive movement. Ligaments play a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity of joints by preventing excessive joint motion in various directions. They act as passive restraints, resisting forces that would otherwise cause dislocation or instability during movement.
Ligament Adaptations
Ligaments exhibit structural adaptations that allow them to withstand the stresses encountered during joint movement. These adaptations include a high density of collagen fibers oriented in parallel bundles, which provide tensile strength and resistance to stretching. Additionally, the presence of elastic fibers allows ligaments to recoil after stretching, contributing to their elasticity and ability to maintain joint stability.
Common Injuries and Treatment
Ligament injuries are common, occurring due to sudden trauma or repetitive stress on the joint. Common ligament injuries include sprains, which involve stretching or tearing of the ligament fibers. Ligament sprains are graded based on the severity of the injury, ranging from mild stretching to complete tears. Treatment for ligament injuries involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), followed by physical therapy to restore strength and range of motion. In severe cases, surgical repair or reconstruction may be necessary to restore joint stability.
Main Differences Between Tendon and Ligament
- Attachment Points:
- Tendons connect muscles to bones, facilitating movement and transmitting forces generated by muscle contractions.
- Ligaments connect bones to other bones within joints, providing stability and limiting excessive movement.
- Composition and Structure:
- Tendons are primarily composed of collagen fibers aligned in parallel bundles, providing tensile strength and resistance to stretching.
- Ligaments contain both collagen and elastic fibers, giving them elasticity and the ability to recoil after stretching.
- Function:
- Tendons facilitate movement by transmitting muscle forces to bones, enabling various physical activities.
- Ligaments stabilize joints by preventing excessive movement and maintaining structural integrity, reducing the risk of dislocation or injury.
- Injury Patterns:
- Tendon injuries result from overuse, trauma, or degenerative changes, leading to conditions such as tendinitis or tendon ruptures.
- Ligament injuries commonly occur due to sudden trauma or repetitive stress on the joint, resulting in sprains or tears.
- Treatment Approaches:
- Treatment for tendon injuries involves rest, physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgical repair.
- Ligament injuries may require a combination of rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), followed by physical therapy, and sometimes surgical intervention for severe cases.