Muscular dysfunctioning is a serious issue faced by many people. From atrophy to dystrophy, this lack of movement could result in a lack of muscles and power in the body.
Key Takeaways
- Atrophy is the wasting away of muscle tissue due to lack of use or injury, while dystrophy is a genetic disorder that causes progressive muscle weakness and degeneration.
- Atrophy can be reversed with exercise, while dystrophy is a chronic condition with no cure.
- Atrophy affects only the muscles that are not being used, while dystrophy affects all muscles.
Atrophy vs. Dystrophy
Atrophy refers to the reduction in size or wasting away of a tissue or organ due to a decrease in the number or size of cells, caused by aging or disease. Dystrophy is the degeneration of tissues or organs due to a defect in the development or maintenance of cells, leading to functional impairment.

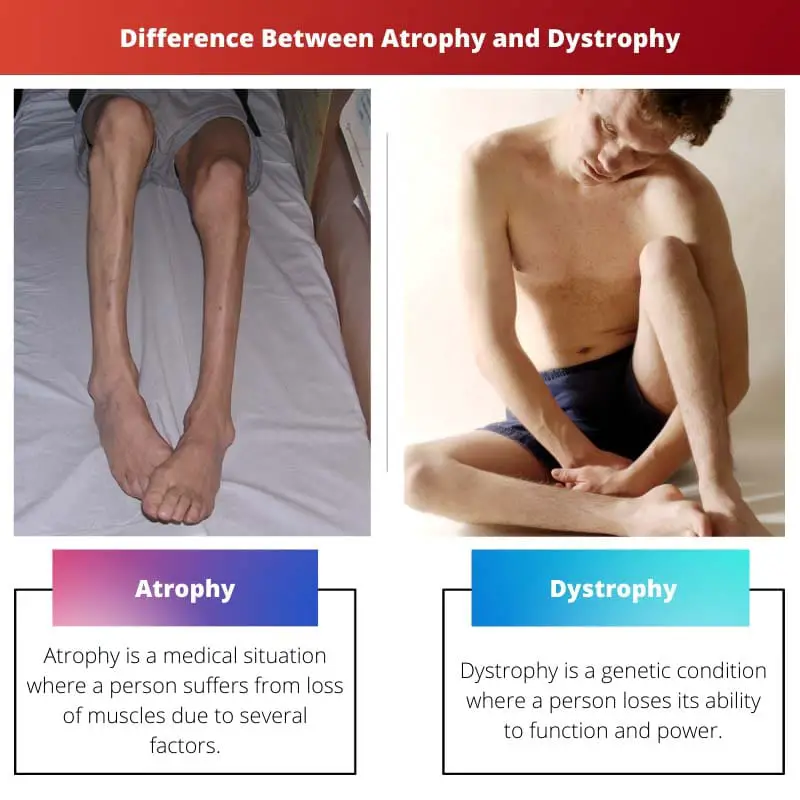
Atrophy is a medical situation where a species loses its body muscles because of mutations, poor feeding, acute circulation, or even loss of hormonal support.
Muscular dystrophy is a genetic condition where a species suffers from progressive mass loss and weakening of muscles with time. Well, it’s because of a lack of a protein called dystrophin that builds the muscles and allows them to function correctly.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Atrophy | Dystrophy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Atrophy is a medical situation where a person suffers from loss of muscles due to several factors. | Dystrophy is a genetic condition where a person loses their ability to function and power. |
| Causes | Atrophy causes degeneration of muscles or even loss of mass in the body. | Dystrophy is caused due to lack of protein that affects the functionality of muscles. |
| Symptoms | Muscle loss, weakness, loss of force, strength in muscles, and high tissue loss. | There’s gradual retardation in muscle, less strength, decreased movements like walking—mobility challenges. |
| Treatment | Atrophy can be cured by physiotherapy when you regularly exercise and improve your nutrition and lifestyle. | Dystrophy is a genetic challenge and hence cannot be treated. But to eliminate pain to some extent, occupational therapies would work. |
| Risk wise | Atrophy is a mild problem that can be cured. | Dystrophy is a risk-full disease, or even loss of life can happen. |
What is Atrophy?
Well, atrophy is a challenge where a person suffers from mass loss due to lack of nutrition, acute scanty of food, suffering from some chronic or acute diseases like polio.
Cells at a certain age undergo atrophy, not under physiologic conditions. This also results in reduced metabolic activities and a lack of active participation in sports or work.
The symptoms could be like your arms won’t be similar anymore. Either one would shrink, or maybe both. Weakness in one limb. Physically inactive for a long time. Inactive or lack of enthusiasm to participate in work and sports.
Before things go wrong, you must consult a specialist who can recommend physiotherapy to help you become atrophy-free.
What is Dystrophy?
Muscular dystrophy is a combination of genetic diseases that destroys the body cells and organs, weakening muscles and power.
Well, most people lose the ability to walk and eventually need supporters or wheelchairs to facilitate themselves. Since it’s a genetic challenge, there’s no such cure, but various therapies can eliminate it up to a more significant extent.
Symptoms include trouble walking, loss of arm reflex, posture, lack of enthusiasm, bone thinning, lack of energy, breathing challenges, mild impairments, pain in joints, difficulty standing and sitting, lung and heart weakness, and swallowing challenges.
As said earlier, there’s no treatment as such. But treatment include assisted ventilation, medication, surgeries to correct body postures, treating scoliosis, and surgeries to treat cardiac problems.

Main Differences Between Atrophy and Dystrophy
- Atrophy can be treated since it’s a disease that isn’t genetic, while dystrophy has no treatment.
- Several surgeries and therapies will eventually help the patient, while only therapies can work to ease to some extent.