With increasing hype of higher resolution video output, technological advances have brought us to the two jargon, DVI and D-Sub, which are quite confused because of their similar appearance and, to some extent, their names.
However, DVI and D-Sub are significantly different from each other.
Key Takeaways
- DVI (Digital Visual Interface) is a video display interface connecting a video source to a display device, such as a computer monitor or TV, supporting digital and analog signals.
- D-Sub (short for D-Subminiature) is an older video display interface, also known as VGA (Video Graphics Array), primarily used for connecting analog video sources to display devices, such as CRT monitors.
- DVI and D-Sub are video display interfaces, but DVI supports both digital and analog signals, while D-Sub is an older interface used mainly for analog video connections.
DVI vs D-Sub
The difference between DVI and D-Sub is that DVI is designed to transmit analogue and digital signals, whereas D-Sub only transmits digital signals. This difference also makes a significant difference in their video output quality.

Another sizable difference is that DVI was explicitly designed for visual displays. In contrast, D-Sub was intended for display and several other purposes, such as serial and parallel ports, gaming pads, and even connecting mice.
DVI is also notably different from D-Subs since D-Subs are pretty outdated. DVIs are newer with improved specifications to support higher resolution videos than D-Subs equivalent for monitor interface.
Comparison Table
| Parameter of Comparison | DVI | D-Sub |
|---|---|---|
| Used for | Only for Visual Displaying | For several purposes such as VGA, serial port, parallel port, mouses etc. |
| Types | 3types: DVI-A, DVI-D, DVI-I | 5 shell sizes and many other configurations |
| Signal transmission | DVIs transmit both analogue and digital signals | D-Sub equivalent to DVI, VGA, only transmits analogue signals |
| Video Quality | Can transmit more explicit and higher resolution videos than D-Sub | Cannot transmit higher resolution as well as DVI |
| Age | It was introduced in 1999, still very much in use | It was introduced in 1957, primarily outdated |
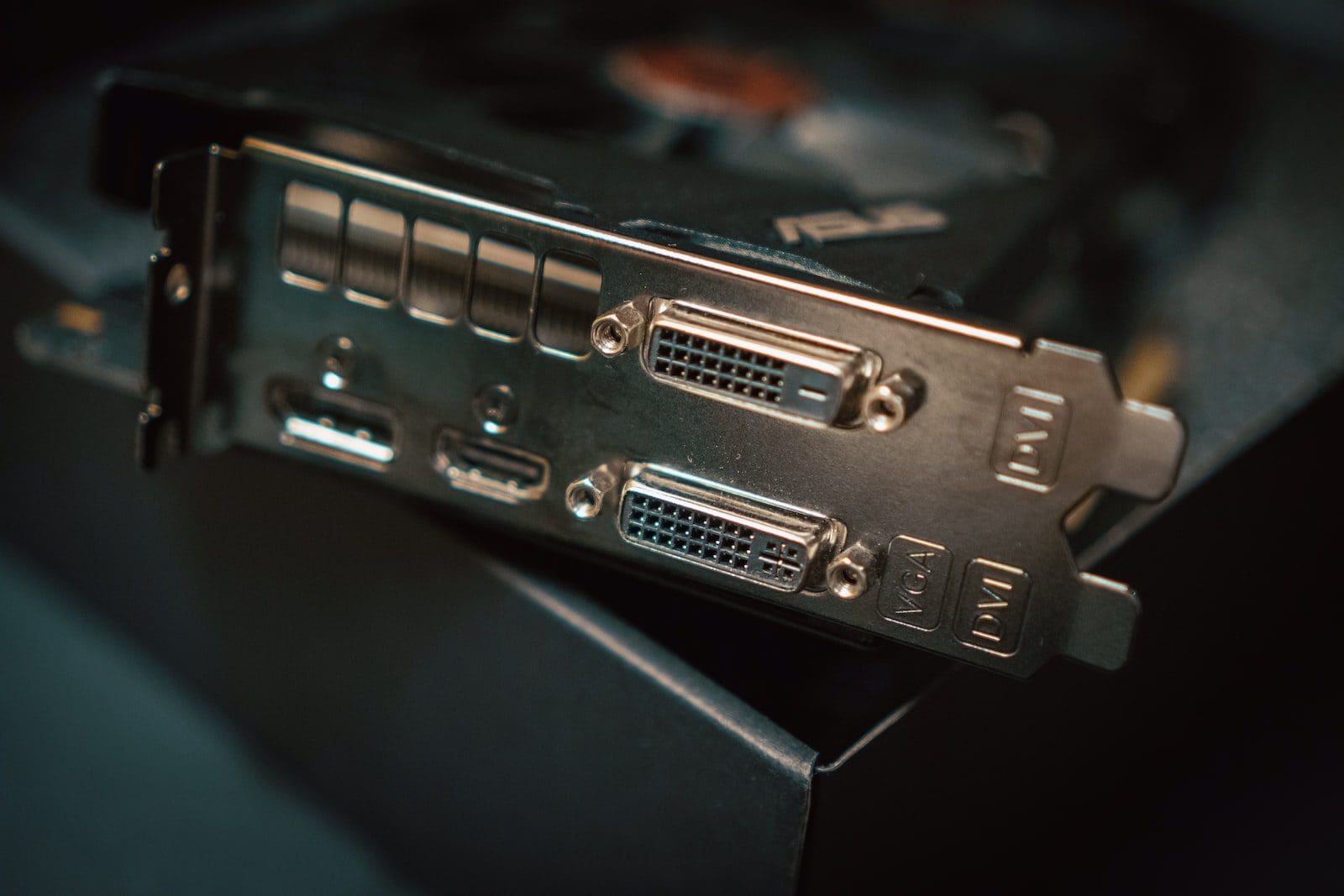
What is DVI?
DVI was introduced in 1999 for commercial use and was made explicitly to support visual displays of higher resolution. DVI was curetted to transmit digital and analogue signals and was known for its more precise and crisper video quality.
There are three main types of DVI, which are:
- DVI-A: transmits only analogue signals
- DVI-D: transmits only digital signals
- DVI-I: transmits both analogue and digital signals
DVI-A, which uses analogue signals, is predominantly out of use. In contrast, digital-only DVI-D and DVI-I, which supports digital and analogue signals, are still heavily used in LCD monitors.
The DVI-I standard was widely used due to its compatibility with analogue and digital signals. Thus, its rapport with VGA cables allowed it to connect input and output devices with both plug-in types.
DVI, or Digital Visual Interface, is a hot-pluggable cable mainly used for computers and laptops. DVI is a D-shaped shell that also uses pins to connect to the channel, which forms the basis for the confusion of DVI and VGA cables.
DVI with the dual signal link can support video images of 2560 × 1600 at 60Hz, whereas a single signal link DVI can stream 1920 × 1200 at 60 Hz resolution.

What is D-Sub?
D-Sub, a short form of D-Sub miniature, is an electronic cable introduced for multipurpose use in 1957 that is mostly obsolete in the present times. When used for transmitting video signals, it is also known as VGA.
VGA standard only uses analogue signals; however, other D-Sub cables, such as serial ports, are also designed for transmitting digital signals. VGA, also known as D-Sub 15-pin, or mini D-Sub 15-pin, has a D-shaped shell with 15 pins arranged in 3 rows.
Other D-Sub applications, such as parallel ports and serial ports, mice, and gaming pads, have subsequently been replaced by USB cables.
The only D-Sub still in use is DB9 and DB15 connectors; however, VGAs are now widely applicable in LCD monitors and other visual display interfaces.
D-Subs have a robust build and supposedly can screen against electromagnetic radiation. Their D structure gives enhanced support and correct orientation to the cable, while its metal shield protects it from radiation.
Main Differences Between DVI and D-Sub
- The main difference between DVI and D-Sub is that DVI can transmit analogue and digital signals. At the same time, the D-Sub equivalent can support only analogue signals for video streaming.
- Thus DVI subsequently replaced D-Sub because it could transmit higher-resolution images and produce more explicit pictures.
- In DVD-R, you can only write it once, while The next notable difference between the two cables is that DVI was made explicitly for visual display. In contrast, D-Sub cable is multipurpose with various uses such as VGA, serial and parallel port cables, mice, gaming pads, etc.
- DVI is of 3 types, DVI-A, DVI-D, and DVI-I, whereas D-Sub has 5 shell sizes with various configurations.
- More recently developed DVI mainly applies to visual displays such as LCD monitors. At the same time, D-Sub, now almost obsolete, was used as a standard computer connector.



