The Internet of Things or IoT has surrounded us completely, and Fog Computing and Edge Computing are part of it. These two mitigate the latency time; however, both share some security and privacy issues.
Edge Computing does not work with the cloud, and that is where Fog Computing wins as it is competent in working with the cloud.
Key Takeaways
- Fog computing distributes computing resources across a network, enhancing data processing closer to the source, while edging computing processes data at the network’s periphery or near the data-generating device.
- Fog computing covers a broader area, serving multiple edge devices and users, whereas edge computing focuses on individual devices.
- Fog computing allows for better scalability and handles more data than edge computing.
Fog Computing vs Edge Computing
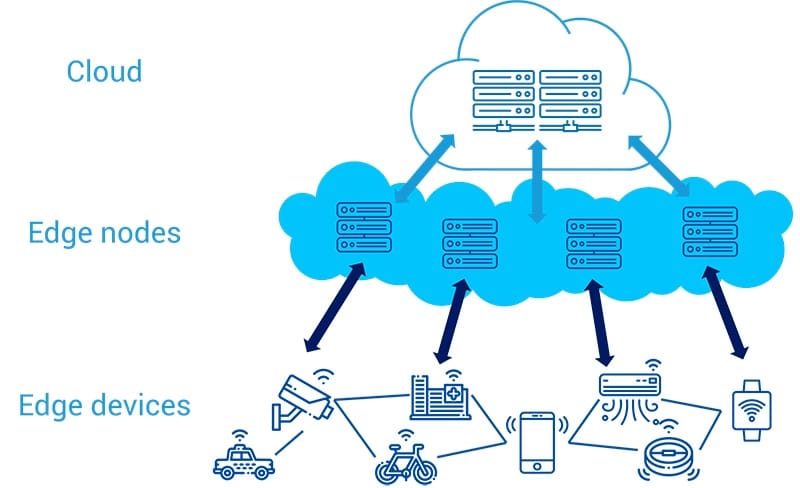
Fog computing is a decentralized computing infrastructure that produces data located between the data source and the cloud. It takes place further away from sensors that generate data. Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that processes data closer to where it is being generated.

You can interpret Fog Computing as an extension of cloud computing. It decides if to deliver a set of data through a cloud or personal resources.
It is more focused on the infrastructure level. Fog Computing confirms that cyber-physical systems perform their duties well.
Edge Computing can be defined as an architect that is required in the IoT. Data communication with Edge computing devices is very simple.
For building Edge computing, one can not take the help of already existing system elements. Instead, new components are required. It is focused on things level in IoT.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Fog Computing | Edge Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Data process | Fog Computing decides if to send data through a cloud or personal resources. | Edge Computing processes data manually instead of sending it to the cloud. |
| Cloud | It is capable of working with the cloud. | It does not work with the cloud. |
| Handling multiple IoT application | It supports handling multiple IoT applications. | It does not support dealing with multiple IoT applications. |
| Focus | Its focus is on the infrastructure level. | Its focus is on the things level. |
| Formation | It can be adapted from already existing system elements. | This needs to be built as a new system. |
What is Fog Computing?
Fog Computing can be defined as an extension of cloud computing. It is spread from the core of the network to the edge of the network.
Cisco came up with this term. It is an intermediate layer.
It is enlarged from the cloud layer, and this way, it makes the computing networks get closer to storage devices. As a result, the end-nodes in IoT also come closer.
The devices that reside at the edge are known by the name fog nodes. These are able to be deployed anywhere with network connectivity.
It is used in railway tracks, traffic controllers, parking meters etc. Fog Computing should not be regarded as an alternative to cloud computing; rather, it should be seen as an extended form of cloud computing.
The delay in sending data to the cloud gets decreased with the help of Fog Computing. The security issues that occur during the transmitting of data to the cloud also gets settled by Fog Computing.
So we can say the overall system efficiency is maintained and improved by Fog Computing. In the end, Fog Computing makes sure the operations under critical cyber-physical systems are reinforced and up to the mark.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge Computing can be defined as an architect. This architecture employs end-user clients.
It is also known to use one or more near-user edge devices. Edge Computing collaborates and then pushes computational facilities towards several data sources.
These resources are sensors, mobile devices and others.
Edge Computing can expand the quality of the performance conducted by the overall system. Edge Computing can not be made with the help of existing components.
It requires a new system in order to get formed. When it comes to data communication, Edge Computing is very simple.
We can undoubtedly say it is simpler than Fog Computing.
Edge Computing also has lesser chances to fail. The intelligence and power of the edge gateway get placed by Edge Computing, and it places them in various devices, for instance, programmable automation controllers.
However, privacy issues are a concern in the matter of Edge Computing.
In the case of wireless network security, it does not have very decent protection to offer. Authentication of it can not be trusted as well.
Main Differences Between Fog Computing and Edge Computing
- Fog Computing is responsible to decides the mode of sending data. It can be done through a cloud or even personal resources, whereas Edge Computing processes data manually directly. It does not wait for the cloud.
- Fog Computing can easily work with the cloud, but Edge Computing can not function with the cloud.
- Fog Computing can support and handle multiple applications of IoT, while Edge Computing, on the other side, is not capable of supporting multiple IoT applications.
- Fog Computing focuses its concentration on the infrastructure level, but Edge Computing, on the contrary, gives all its focus on the things level.
- Fog Computing can be adapted from already existing system elements, but Edge Computing needs to be built as a whole new system. It is like a mini cloud data centre.
- Fog Computing might not get controlled by network operators, but Edge Computing allows mobile network operators to improve existing services.
- Fog Computing consists of a hierarchical and flat architecture that possess several layers, and these layers are responsible for constructing a Network. On the other side, Edge Computing holds several nodes that are not capable of forming any Network.




