Grid computing and cloud computing are comparable but can be easily confused. The ideas are very comparative, and both offer a similar vision of offering types of assistance and services to the clients through sharing assets among a massive pool of resources.
Both Grid computing and Cloud computing depends on network technology and are fit for performing various tasks meaning clients can get to solitary or numerous application instances to perform various tasks and assignments.
Key Takeaways
- Grid computing is a distributed computing model in which multiple computers work together to solve complex problems or perform resource-intensive tasks by sharing resources and processing power.
- Cloud computing is a model that provides on-demand access to computing resources, such as storage and processing power, over the internet, without requiring the direct management of hardware and software by the user.
- The main difference between grid computing and cloud computing lies in their architecture and purpose: grid computing focuses on combining resources for problem-solving, while cloud computing aims to deliver flexible, on-demand access to computing resources.
Grid Computing vs Cloud Computing
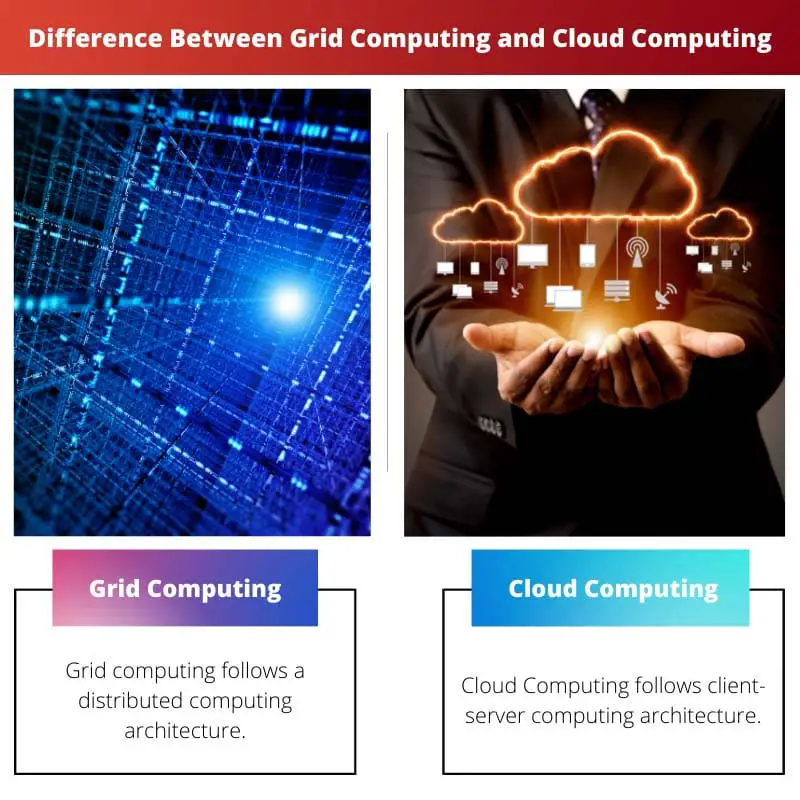
The difference between grid computing and cloud computing is that in grid computing, assets are distributed, and each site has administrative control. In Cloud computing, the resources are centrally managed.

In Grid computing, a group of computers work together and cooperate to take care of an enormous issue by parting it into a few little units, which are disseminated over computers (part of a network). While Grid computing includes virtually computing resources and assets to store enormous measures of information, Cloud computing is the place where an application does not get to assets legitimately, rather it gets to them through service over the web.
In Grid computing, assets and resources are circulated over grids, though in Cloud computing, assets are overseen midway. How about we investigate the two processing advancements?
Whereas Cloud computing ousts the need to purchase the programming software and hardware, which requires complex design and exorbitant upkeep for building and sending applications rather it conveys it as assistance or as a service over the web.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Grid Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Grid computing follows a distributed computing architecture. | Cloud Computing follows client-server computing architecture. |
| Orientation | Grid Computing is Application-oriented. | Cloud Computing is Service-oriented. |
| Flexibility | Grid Computing is less flexible than cloud computing. | Cloud Computing is a lot more flexible than grid computing. |
| Management | In Grid computing, the grids are owned and managed by the organization. | In cloud computing, the cloud servers are owned by infrastructure providers. |
| Scalability | Scalability is, as usual, normal. | Scalability is higher. |
| Service | Grid computing uses systems like distributed computing and distributed information. | Cloud computing uses services like SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. |
| Accessibility | It is accessible through grid middleware. | It is accessible through standard web protocols. |
| Operation | Grid operates as a decentralized management system. | Cloud operates as a centralized management system. |
| Function | It involves sharing a pool of computed resources on a needed basis. | It involves dealing with a common problem by a varying the number of computing resources. |
What is Grid Computing?
Grid computing is a network of computers working together to perform a task that would rather be difficult for a single machine. All machines on that particular network will work under the same protocol to act like a virtual supercomputer.
The task that they work on may include analyzing massive datasets or simulating situations which will require high computing power. Computers on the network provide resources like processing power and storage capacity to the network.
Grid Computing is a subset of distributed computing, where a virtual supercomputer encompasses machines on a network connected by some bus, mostly Ethernet, even sometimes the Internet. It can sometimes also be seen as a form of Parallel Computing where instead of many CPU cores on a single machine, it contains multiple cores spread across numerous locations.
The concept of grid computing is not new, but it is not yet perfect, as no standard rules and protocols are established, accepted and welcomed by people.

What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is storing and accessing the data and programs on remote servers hosted on the internet instead of the computer’s hard drive or local server. Cloud computing is also commonly referred to as Internet-based computing.
Cloud computing is the delivery of different services through the help of the Internet. These resources include applications and tools like data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software.
Cloud-based storage allows them to be saved to a remote database rather than keeping files on a proprietary hard drive or local storage device. As long as an electronic device can access the web, it can access the data and the software programs to run it.
Cloud computing is a popular option for businesses and people for numerous reasons, including cost savings, increased productivity, speed and efficiency, performance, and security.
Main Differences Between Grid Computing and Cloud Computing
- Grid computing uses a well-distributed computing architecture; on the other hand, Cloud computing uses a client-server architecture.
- Grid computing infrastructure can quickly deal with interoperability, whereas Cloud computing doesn’t support interoperability.
- In Grid computing infrastructure, the assets and resources are very much limited, while in Cloud computing, there is an enormous pool of assets and resources. Sometimes grids can be made using cloud computing.
- Resources and assets are always used in a decentralized manner in grid computing. On the other hand, resources and assets are pooled in a centralized or seldom in a decentralized manner in Cloud computing.
- The applications expanded on the cloud are explicit business applications, for example, online applications regularly utilized by meagre customers or for handheld gadgets. On the other hand, Grid centres around the research-based application with the assistance of distributed independent administrative units working inside and out to take care of a more significant figuring issue.
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/4738445/
- https://www.dcc.fc.up.pt/~ines/aulas/1314/CG/Presentations/Goncalo/papers/06028683.pdf

The article presents a detailed comparison between grid and cloud computing, providing valuable insights into their functionalities.
I found it to be an excellent source of information on this topic.
Indeed, it’s well-researched and informative.
The article effectively showcases the advantages and distinctions of grid computing and cloud computing.
Exactly, it’s very educational.
It’s a great resource for anyone wanting to delve into this topic.
This article provides a comprehensive and clear comparison between grid computing and cloud computing, highlighting their differences and similarities.
I completely agree, it’s a very informative read.
Yes, the key takeaways are very well presented.
The explanation of distributed computing and its relationship to grid computing is well-researched and insightful.
Absolutely, it provides a solid understanding of the technology.
This article offers a comprehensive understanding of grid and cloud computing, making it an excellent read for anyone interested in the subject.
I find the distinction between decentralized and centralized management systems in grid and cloud computing very compelling.
Yes, it’s a critical aspect of the comparison.
It really highlights the varied approaches to resource management.
This article does a fantastic job of clarifying the nuanced differences and applications of grid computing and cloud computing.
Absolutely, it’s written in very understandable terms.
The detailed comparison table makes it easier to understand the architectural and functional distinctions between the two computing models.
Absolutely, it’s a great reference for anyone wanting to learn about these technologies.
Agreed, this article is a valuable resource for the topic.
The comparison between grid computing and cloud computing is presented in an easily digestible manner, suited for both technical and non-technical readers.
Yes, it’s an excellent piece for anyone interested in the subject.
The descriptions of grid computing and cloud computing are quite clear and straightforward, making it easy to grasp the concepts.
Agreed, it’s very well articulated.