Electronics is the field of study that deals with the physics and applications of the movement of electrons.
With electronics comes electronic communication and electronic devices that work under the principle of the flow of electrons from one point/ terminal to another.
For those starting to familiarize themselves with electronics, the most common and confusing terms they come across are microprocessor and microcontroller.
It is important to differentiate them since they come with different hardware and perform different tasks.
Key Takeaways
- Microprocessors are single-chip CPUs that only process data, while microcontrollers have CPUs and additional components like RAM, ROM, and input/output peripherals.
- Microprocessors are used in devices that require high processing power, while microcontrollers are used in devices that require both processing power and input/output control.
- Microprocessors are more expensive than microcontrollers, requiring additional external components to function properly.
Microprocessor vs. Microcontroller
A microprocessor is a tiny processor chip inside a microcomputer that performs Arithmetic and logic operations. Microcontroller is a computer system designed for embedded systems to control different functions. Microcontroller can perform various tasks simultaneously as it has multiple chips embedded.

The processing unit of a computer is called the microprocessor. They are mainly used in computers as they help in the functioning of general and complex tasks.
They have high power consumption and consume energy even in their idle state. Microprocessors also have a high clock speed of 1 GHz.
The processing unit of an embedded system is called a microcontroller. Their applications are mainly seen in the ones that handle a specific task. This is when the output depends on the input of the system.
They have minimal external components as they have all the necessary components in a single chip.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Microprocessor | Microcontroller |
|---|---|---|
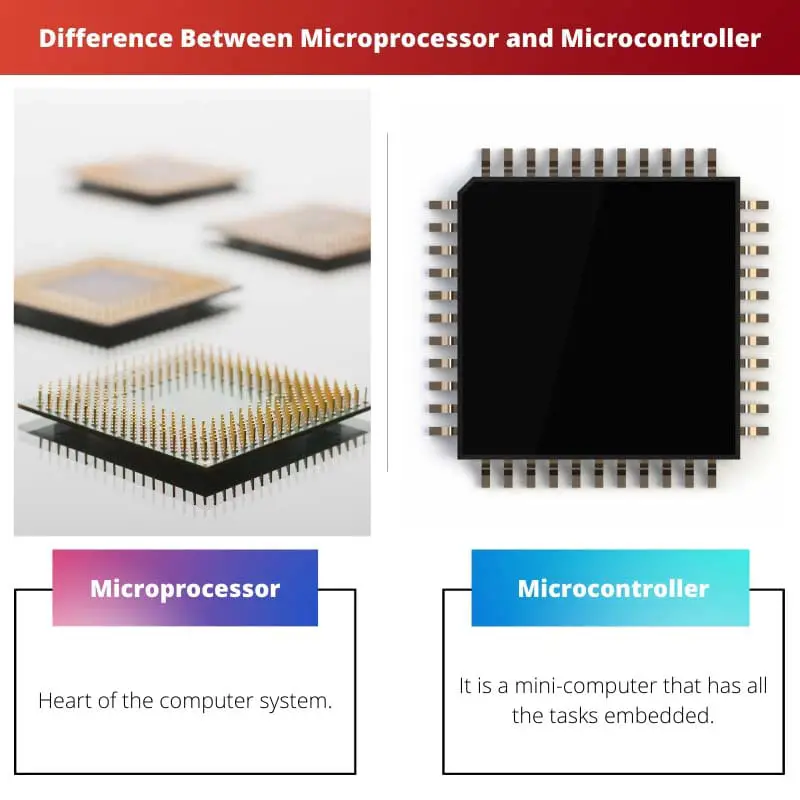
| Meaning | Heart of the computer system | It is a mini-computer that has all the tasks embedded |
| Components | Only CPU | CPU along with internal memory and I/O components |
| Application | It is used in computers | It is used in embedded systems for performing specific tasks |
| Tasks performed | They perform unspecific and general tasks | They perform specific tasks |
| Clock speed | 1Ghz | 8Mhz to 50 Mhz. |
| Memory | Variable | Fixed |
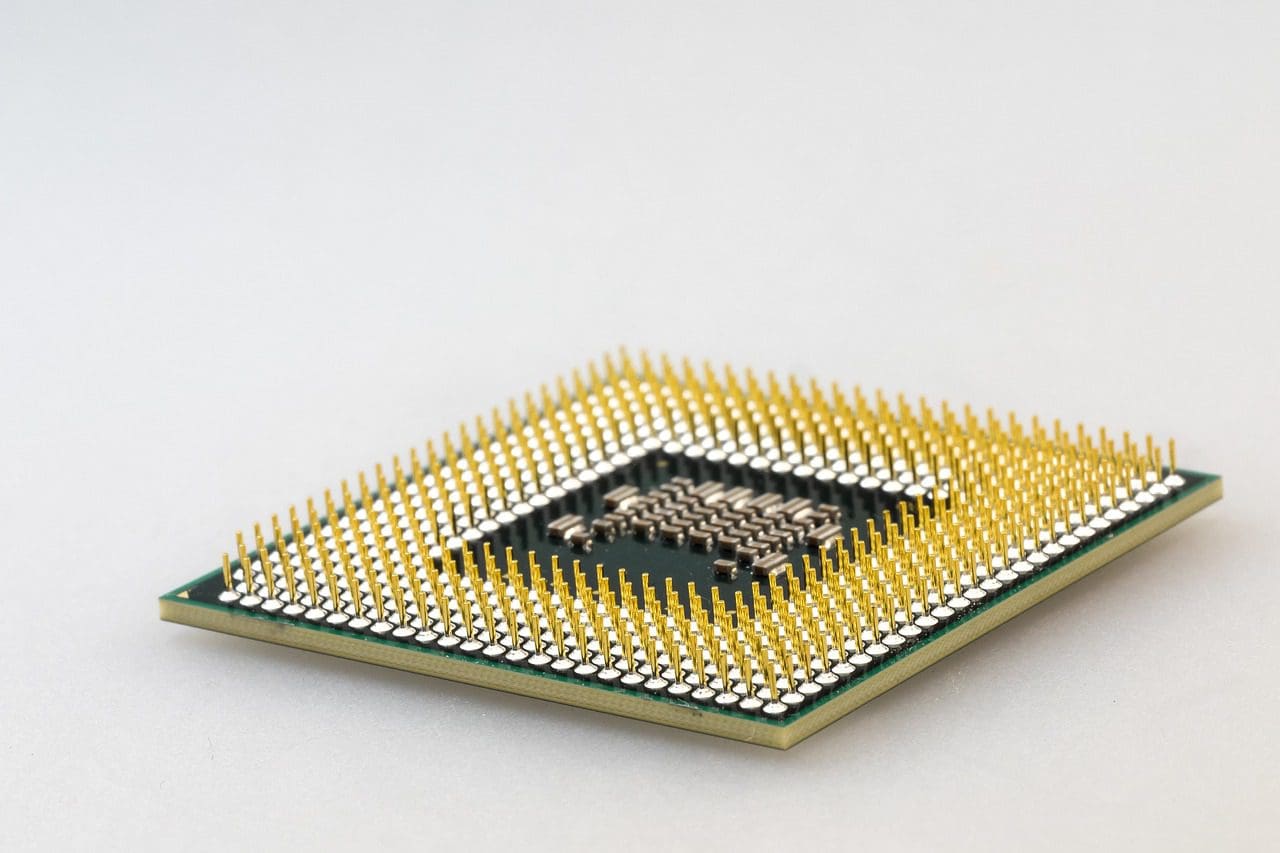
What is a Microprocessor?
A microprocessor can be considered the heart or the controlling unit of a computer system. They do not come with internal components other than the processing unit and therefore require a high power load.
They are only attached to an internal controller, and all the other components have to be externally attached for them to function. Therefore, they are made bulkier than a microcontroller.
They are expensive and consume high power, but this makes them perfect for complex tasks.
They function in general tasks such as images, editing, etc., which do not have any relation between the input and output. Therefore they also require only small amounts of external RAM and ROM.
Since they have less quantity of registers, they are memory-based and function on their tasks with their memory. They are also coined inefficient because they cannot be used in compact systems.
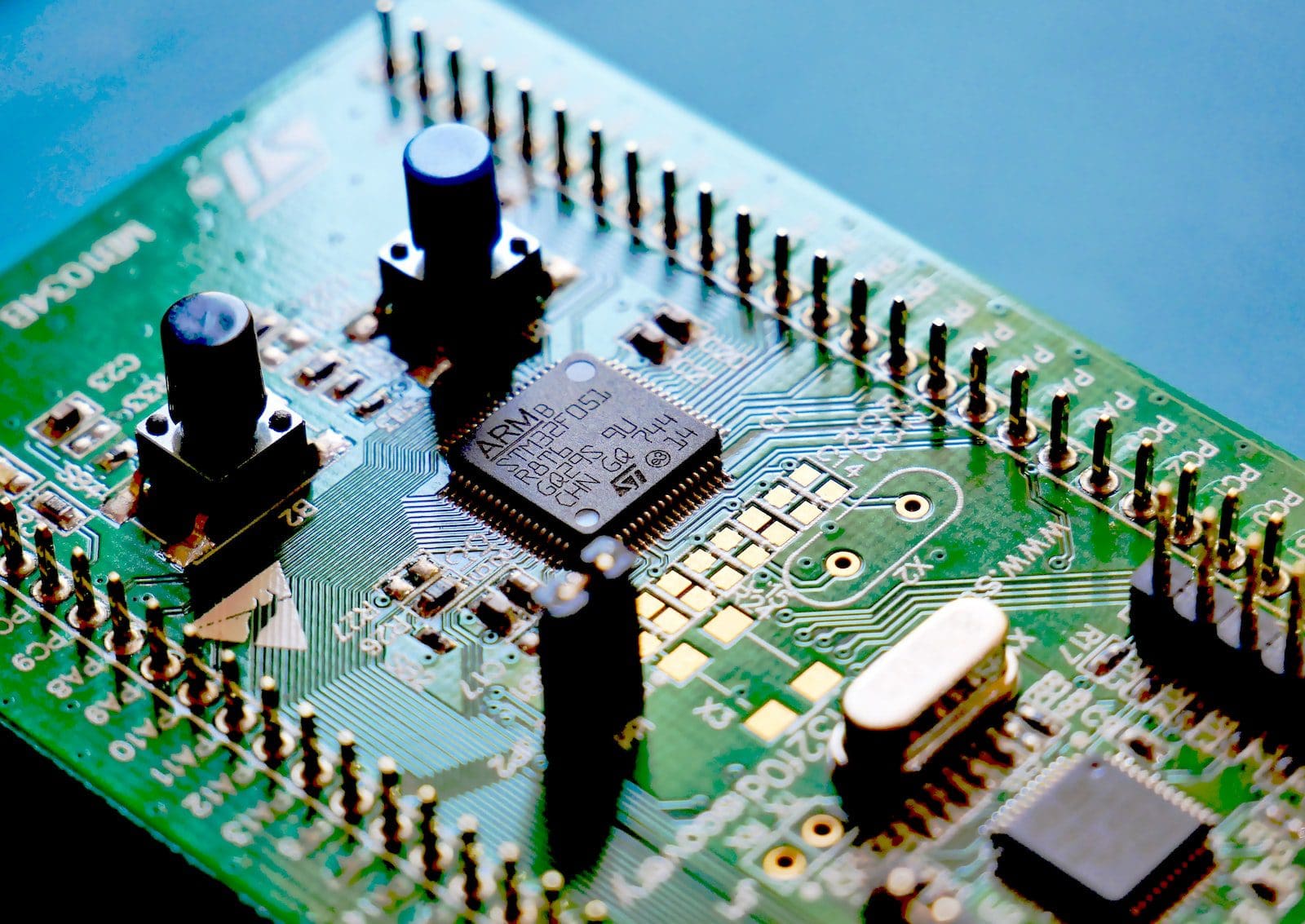
What is Microcontroller?
Microcontrollers are the processing unit of an embedded system. They also have high speed in loading instructions because of their on-flash memory and existing internal memory.
The microcontrollers come with a power-saving system and therefore do not consume power in idle mode. Thus, it uses less power than microcontrollers. They are also cheaper than microprocessors but cannot be used for complex tasks.
They have a CPU and small or limited amounts of RAM, ROM, and other necessary peripherals in one single chip. So they are also termed mini-computers.
They can also be used with compact systems, unlike microprocessors. Writing a program in a microcontroller is also comparatively easier because they have more registers.
Microcontrollers have few external components, so their power consumption is naturally low. Therefore they can be used with batteries.
They are seen to be used in a washing machine, digicam, etc. So, one can also say that microcontrollers are used in projects and other applications that require a direct user interface.
Main Differences Between Microprocessor and Microcontroller
- A microprocessor is the heart of a computer system, and a microcontroller is a mini-computer embedded to perform specific tasks.
- They vary even in components. The microprocessor only has an internal controlling unit, and all the memory and I/O components must be installed externally. The microcontroller has an internal controlling unit, memory, and I/O components.
- Since the microprocessor is the processing unit of a computer, they are used in a computer. In contrast, the mini-computer microcontroller uses an embedded system for performing specific functions.
- The microprocessor performs general tasks like editing, games, and websites where the output and the input are not relative. The microcontrollers perform specific tasks in which the output depends on the inputs.
- The clock speed of both these components varies greatly. The microprocessor has a clock speed of 1 GHz and can perform complex tasks. Whereas the clock speed of the microcontroller, being in the range of 8 to 50 MHz, does not let it perform complex tasks.
- Since the microprocessor has external memory, adding this memory is possible. But since microcontrollers have fixed internal memory, it is impossible to extend a microcontroller’s memory.