A cell is the structural and functional unit of life. A cell is divided into three main parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm.
A cell membrane’s function is to keep the chemical reactions of a cell together. The cellular fluid in which the chemical processes of life/cells occur is the Cytoplasm.
Basically, cells are of two types – Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic cells. Both cell type differs on the basis of Mitochondria and Plastids.
Key Takeaways
- Mitochondria generate energy for cells through cellular respiration, while plastids are involved in synthesizing and storing pigments and nutrients.
- Mitochondria are found in both plant and animal cells, but plastids are exclusive to plant cells and some algae.
- Both organelles contain their DNA and reproduce independently of the cell, indicating a likely endosymbiotic origin.
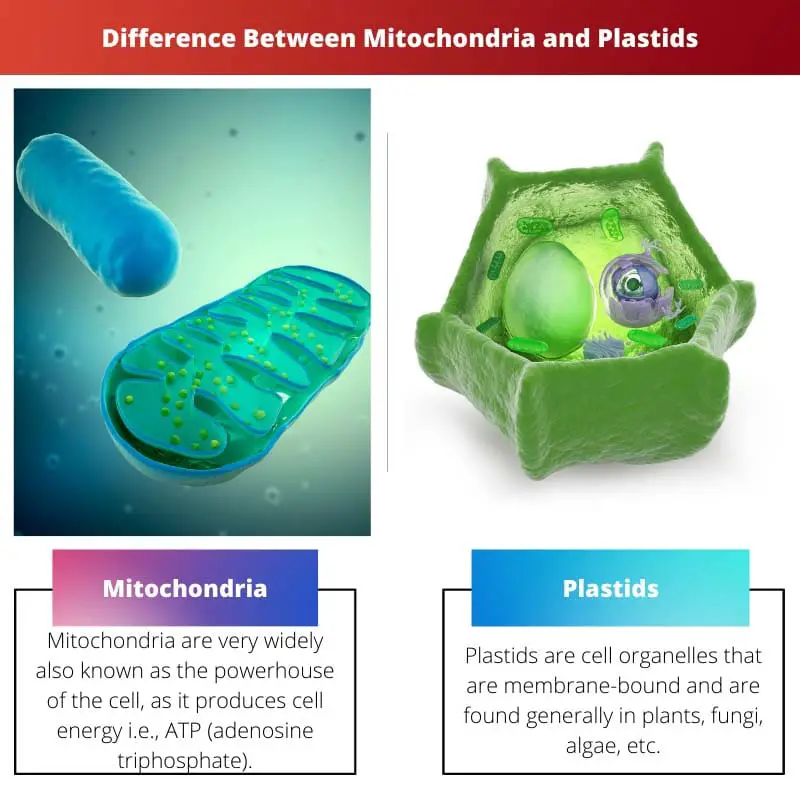
Mitochondria vs Plastids
Mitochondria are called the “powerhouses” of the cell because they are responsible for generating the majority of the cell’s energy in the form of ATP through cellular respiration. Plastids are a diverse group of organelles found in plant cells and some algae that are responsible for photosynthesis.
Mitochondria are very widely known as the cell’s powerhouse, as it produces cell energy, i.e., ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
Mitochondria are found in the cytoplasmic area of the cell and are membrane-bound. Mitochondria are said to be originated from Prokaryotic cells, but it is only found in Eukaryotic cells.
While plastids are cell organelles that are membrane-bound and are found in plants, fungi, algae, etc.
Plastids are the manufacturing as well as the storage unit of the cells of the plants that produce their food by themselves with the help of sunlight, i.e., Autotrophic.
Plastids are comprised of various plant pigments or colours too.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Mitochondria | Plastids |
|---|---|---|
| Occurrence | It is found in eukaryotic cells only. | It is found in prokaryotic and plant cells. |
| Function | Its basic function is cellular respiration in plants. | Its basic function is for the photosynthesis in the main cell organelle or in plants |
| Size | It is small in size | It is bigger in size compared to mitochondria. |
| Products | Its product is energy in the form of ATP. | Its product is glucose in the form of starch. |
| Presence of pigments | It has the presence of no pigments. | It has different types of multiple pigments present. |
What is Mitochondria?
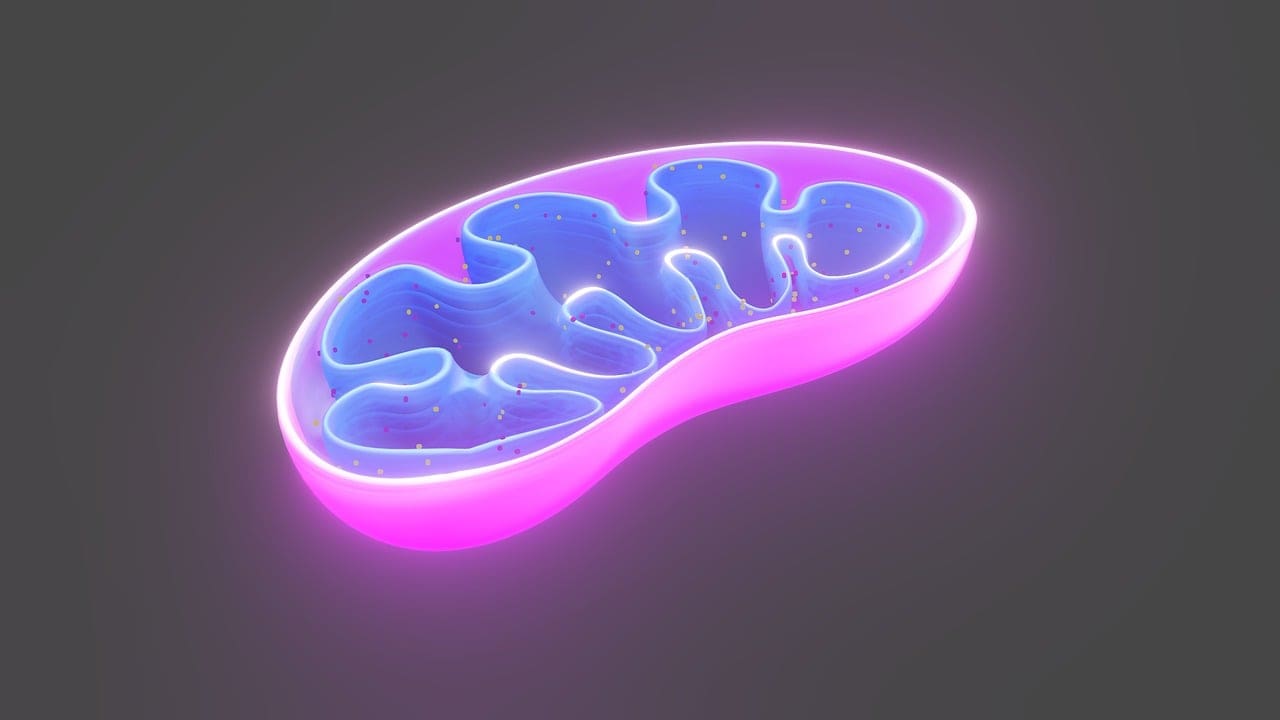
Carl Benda coined the term ‘Mitochondria’ in the year 1898. A mitochondrion is a cell organelle that is double membrane-bound. It is found in the cytoplasmic area of the Eukaryotic cells.
It is the centre of energy generation, assimilating the nutrients and liberating chemical energy in the cell as ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate).
The mitochondria also regulate the growth and death of the cells, it also indicates the cells and generates heat. Mitochondria play an important role in cellular respiration.
The process by which ATP is created in the body is called Anaerobic fermentation, and an exception is that anaerobic fermentation does not occur in the cell’s mitochondria.
The fundamental need of mitochondria to generate ATP is glucose and oxygen. The energy generated through mitochondria is more than the energy created by anaerobic fermentation.
In animals, mitochondria are oval or round in shape. Mitochondria is a double membrane and is composed of proteins and a phospholipid bilayer.
Mitochondria has Five different parts: Outer membrane, inner membrane, inner membrane space, cristae, and Matrix. The outer Membrane keeps the inner cell organelles tight/intact in place.
The inner Membrane has essential enzymes that catalyze the production process of ATP. Inner Membrane Space is the space between the inner and outer membrane of the mitochondria.
Cristae is the inner membrane of the mitochondria and has a lot of folds; those folds are known as Cristae.
Matrix is the space apart from the cristae in the inner membrane is known as the Matrix.
The function of mitochondria is to convert food into ATP/energy and elimination or remove wastes from the mitochondrial cell. Mitochondria and bacteria have a lot of common features.
RBCs do not possess any mitochondria.
What is Plastid?
Ernest Haeckel first discovered plastids; A.F.W. Schimper first proposed their basic definition.
Plastids are the manufacturing as well as the storage unit of the cells of the plants that produce their food by themselves with the help of sunlight, i.e., Autotrophic in nature.
Plastids have a lot of pigments which can be seen in plants & algae.
There are a huge number of pigments, but the basic pigments of plastids are Chloroplast, Chromoplast, leucoplasts, and proplastids.
Chloroplasts are plastids that have chlorophyll, i.e., a green pigment, which helps in the process of photosynthesis is called Chloroplast.
Chromoplasts have more coloured pigments other than green pigment. Rhodoplasts or phycoerythrin is a red pigment.
Phaeoplasts or carotenoids and Xanthoplasts or xanthophyll are yellow pigments. Leucoplasts are the colourless plastids present in the parenchyma of the cells of the plant or leaves.
It can be altered into pigmented or coloured plastids when subjected to sunlight. Proplastids have no colour and are not mature.
The meristematic cells having the minor vesicular structure are known as Proplastids. Chloroplast is filled with a liquid known as the stroma.
In the stroma, highly organized membrane structures are present and they are known as grana. Other than grana, the stromatic fluid contains a host of plastid DNA, RNAs, enzymes and 70s ribosomes.
Main Differences Between Mitochondria and Plastids
- Mitochondria are only found in eukaryotic cells, whereas plastids are present in prokaryotic and plant cells.
- The product of Mitochondria is ATP, whereas the product of Plastids is glucose, which is stored as starch.
- The function of the Mitochondria is cellular respiration, whereas the main function of plastids is for photosynthesis in the main cell organelle.
- Mitochondria are tinier in size, whereas Plastids are comparatively bigger in size.
- Mitochondria have no pigments present, whereas plastids have multiple pigments.