Earth is a fantastic place where all kinds of minerals and substances can be found even with the same composition but still have different characteristics.
Earth is full of elements like copper, carbons, hydrogen, etc., and elements that lead to the formation of the substances found on Earth.
Carbon is a fantastic element as a diamond, the hardest substance on earth, is made out of carbon, whereas graphite, also made out of carbon, is used in our pencils, which is easily breakable.
Similarly, oil and wax have the same composition.
Still, they show different characteristics from the lipid molecule design composed of the hydrocarbons that make these substances non-soluble in water, even being imposed out of the same hydrocarbon; both the products show a lot of difference in the characteristics.
Key Takeaways
- The oil penetrates the material’s surface and provides a natural and matte finish, while wax sits on top and creates a glossy and protective layer.
- Oil is more suited for porous materials like wood and leather, while the wax is better for non-porous surfaces like metal and stone.
- Oil and wax offer protection against moisture and wear, but the choice depends on the type of material and desired outcome.
Oil vs. Wax
Oil derived from plants is a form of vegetable oil that is used in cooking, as a lubricant, and in the manufacture of a variety of items such as cosmetics and biodiesel fuel, etc. Wax is a natural or synthetic substance that can be used for coating, proofing, and making candles or other items.

Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Oil | Wax |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | These are the substances produced naturally extracted from fossil fuels; these oils are lipids and are converted to a usable form when the long fatty chain is composed while doing electrolysis. | These are the organic and human-made substances imposed out of the lipids. The wax is a semi-solid substance at room temperature. |
| State at Room Temperature | The oil is and always liquids at room temperature and can be heated a little for better uses, like hair oils. | The wax is hard and semi-solid at room temperature and has a minimum of 45 degrees Celsius melting point. |
| Exceptions | No oils are liquid at room temperature; domestic coconut oil becomes a solid during winter. | Not all wax is human-made. Beeswax is a naturally made wax and is then produced synthetically. |
| Chemical Formula | The formula is C8H18, representing that all carbon atoms are bonded with 3 or 4 hydrogen atoms. | The chemical formula for wax is Cn H2n+2, where C is the no of carbon atoms, H is the no of hydrogen atoms, and n is no molecules. |
| Uses | Wax is used in many products like hair wax and shoe wax. | It is used for cooking. |
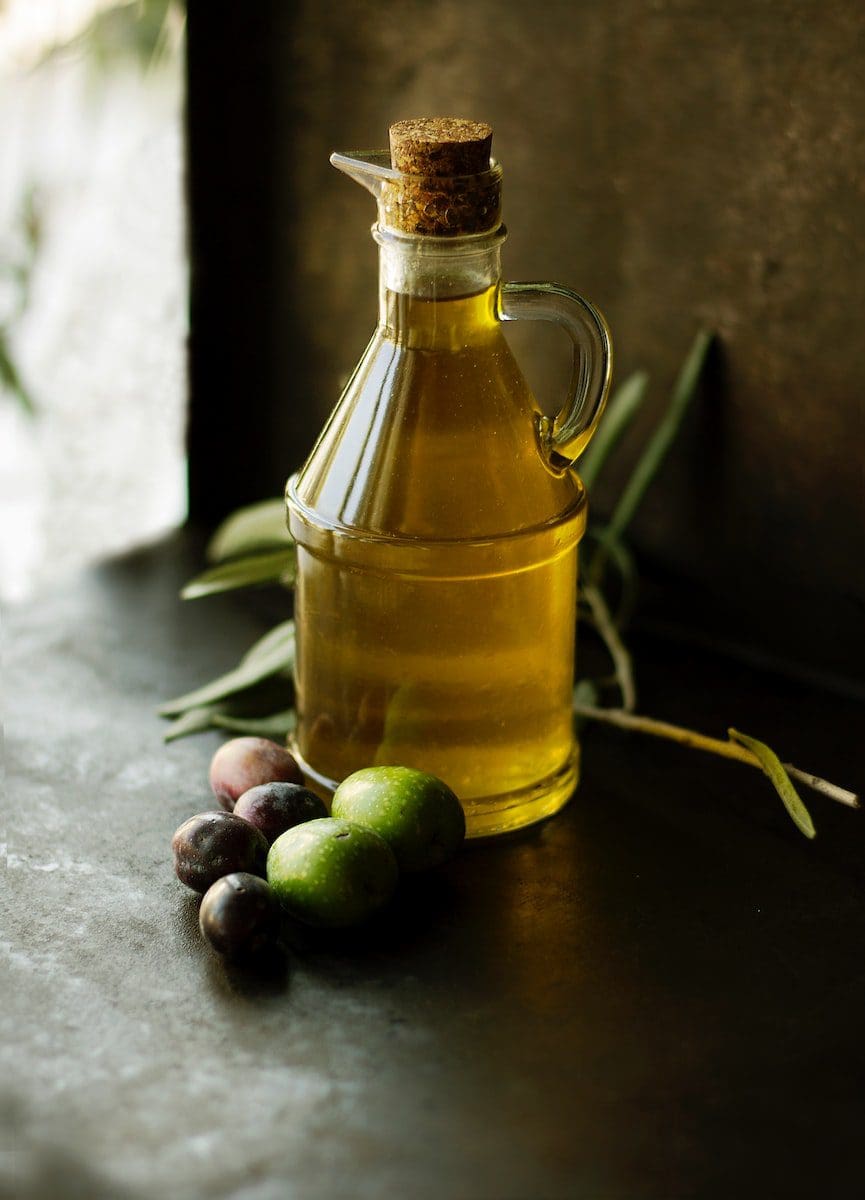
What is Oil?
Oil is a substance that shows very different properties, but it is essential for humanity, sometimes even leading to wars.
Oil can be easily classified into two parts depending on the extraction. Organic oil is produced and extracted from plants and animals through different metabolic processes.
The second type of oil is the mineral oils classified as crude oil and petroleum, extracted from fossil fuels that are the remains of dead plants and animals deep down in the earth; this oil contains high levels of hydrogen and carbon that result in long chemical chains.
Oil has many uses, such as cooking and painting. Oil paints help create beautiful paintings worldwide, and oil plays a significant role in many religions.
Oil may seem to be a simple substance, but its formation is quite complicated. The pure oil is extracted and then undergoes electrolysis resulting in the shape of domestic oil.
The chemical formula is C18H8, a long carbon chain forming an ester.

What is Wax?
Wax and oil may seem to have the same formation and forming out of the same element, but wax shows many different characteristics.
Waxes are organic compounds that are formed by long hydrocarbon chains. Some wax may contain different items like aromas added later, leading to scented candles.
All kinds of wax are found in terms of extraction; many are extracted from plants, which is seen when plants pull material onto their tips through evaporation that contains esters, fatty acids, etc.
Wax is also extracted from animals, out of beeswax, which is removed naturally—used by bees in honeycomb construction. These waxes consist of esters that are formed by hydroxy acids.
Esters show a property of non-dissolving water; the wax is also extracted during the purification of the crude oil, which results in Vaseline being used for many purposes.
The chemical composition is Cn H2n+2, where C is the no of carbon atoms, H is the no of hydrogen atoms, and n is no molecules.

Main Differences Between Oil and Wax
- Oil is a substance found everywhere; for example, the oils are extracted from the ground made from fossil fuels used in cars and machinery; oil is also found in the human body, the oil reserves to the food we eat. In contrast, wax is an item that is made by man and is not used in many products. It is used for making candles or hair wax.
- Wax and oil share a common substitute which is hydro-carbon. They are extracted using hydrolyses, which results in a long carbon chain consisting of elongated hydrogen and carbon elements, wax and oil consisting of esters.
- They are chemical compounds in which an alkyl replaces one hydroxyl group -OH and the resin comprises one ester in its chain.
- In contrast, the oil consists of three esters in its chain.
- The oil contains lipids, whereas the wax includes a minimal number of lipids that make wax thicker than the oils; lipids are a term from micro-biology which states that all the insoluble materials (non-mixable) in the water and the same characteristics are found in oil and wax.
- All oils have a minimum melting point of 30 degrees Celsius and a melting point of 300 degrees Celsius. In contrast, the wax, which is semi-solid at room temperature, has a minimum melting point of 45 degrees Celsius and a boiling point of 370 degrees Celsius.
- All terms present an exceptional case in chemistry same goes for oil and wax; not all are found to be thick liquid at room temperature.
- The coconut oil that becomes a hard solid during winter has to be heated to use, whereas not all the wax is human-made. The resin, called beeswax, is extracted naturally.