OVPO and MCVD stand for Outside Vapor Phase Oxidation and Modified Chemical Vapor Deposition, respectively.
The OVPO and MCVD processes are fibre fabrication processes used to build and produce optical fibres. Optical fibres use the technology of light and are made as strands to transfer data.
Key Takeaways
- The OVPO (outside vapor phase oxidation) process is a technique for fabricating optical fibers by depositing soot particles onto a substrate. In contrast, the MCVD (modified chemical vapor deposition) process involves depositing glass layers inside a hollow glass tube.
- The OVPO process produces high-quality, low-loss fibers more efficiently than the MCVD process.
- The MCVD process is more widely used due to its compatibility with various fiber types and ease of scaling up for mass production.
OVPO Process vs MCVD Process
OVPO (Outside Vapor Phase Oxidation) process is an optical fibre fabrication method. It is a complicated procedure but plays a great role in the development of technology using optical fibres. This process consists of four steps. MCVD (Modified Chemical Vapor Deposition) is an optical fibre fabrication process. The structure of this process is complex.

The OVPO process is one of the very initial methods used to fabricate optical fibres. In this process, a traversing burner is used to heat a bait rod consisting of metal halide vapours and glass material, on the other hand.
It was a busy and inconvenient process.
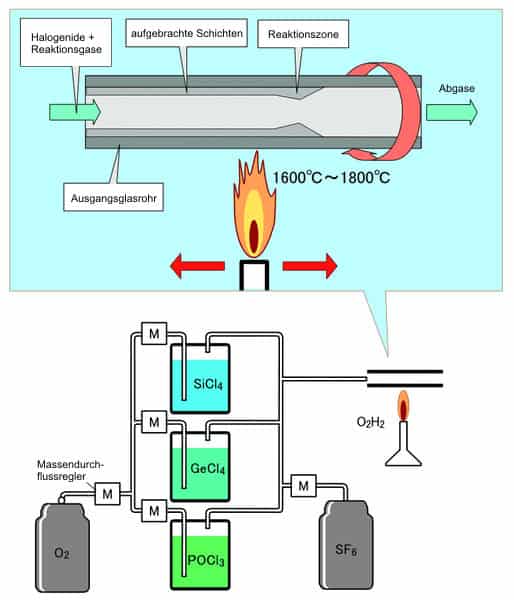
MCVD process is a modified version of the fabrication of optical fibres. It uses a traversing burner that can move to any side to provide heat to a substrate tube of metal halide vapours.
It also involves a gas mixture passing through the tube and finally exhausting after sufficient heating.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | OVPO Process | MCVD Process |
|---|---|---|
| Output | The OVPO process makes a loss of about 20 decibels per kilometer for the optical fiber. | MCVD process is used for producing low loss graded-index optical fibers. |
| Deposition | The OVPO process does the layer deposition of the content outside the fiber. | The MCVD process does layer deposition inside the optical fiber. |
| Chemical Reaction | OVPO method makes use of chemical hydrolysis reaction through the flame. | The MCVD process uses the vapor dimension reaction for fabrication. |
| Steps | OVPO method has four basic steps of soot deposition, its preform, perform sintering, and fiber drawing. | The MCVD method is very convenient and quick enough with small steps. |
| Influence | The OVPO process for fabricating optical fibers was used in the initial stages and is a tough one. | MCVD process is a modified method that has several advantages for convenience. |
What is the OVPO Process?
The OVPO process is abbreviated as the Outside Vapor Phase Oxidation method and is one of the four used methods for fabricating optical fibres. Optical fibres are fabricated through this process.
However, it is a strict and tough process, but it is a very popular method that has a big influence in the initial stages of developing technology through optical fibres.
When the process was implemented initially, it was found that the OVPO method has less than 20 decibels of loss of data per kilometre within the fibre.
The basics of the OVPO process are simple and direct though tough and very strict. It requires a mixture of silicon dioxide compounds. These compound particles are togetherly called soot.
There is a traversing flame burner used in the process that can move and heat a bait rod which is called a Mandel.
This rod has the deposition of the soot through the heat of the flame. Once the deposition starts, the soot is increased substantially layer by layer on the ceramic Mandel.
Then, glass halide vapours are introduced to form the optical fibre’s core and cladding. At about 1400 degrees Celsius, the optical fibres are fabricated by removing the glass rod.
What is the MCVD Process?
MCVD process is abbreviated as the Modified Chemical Vapor Deposition process. It is regarded as a more convenient method. This is because the MCVD method is a more modified version of normal processes for the fabrication of optical fibres.
MCVD is a more advantageous process to fabricate graded-index optical fibres of very low loss.
This process has a more complex structure. It involves a substrate tube that is made up of glass silica and a traversing burner to put the flame on sufficient regions of the substrate tube.
Besides the soot mixture of silicon dioxide compounds, a gas mixture is also passed within the substrate tube with the presence of soot particles. These are then exhausted out of the tube at a suitable time.
Likewise, the substrate tube also has the capability of rotating like the bait rod.
The gas mixture introduced in the tube is a mixture of vapour halide gasses to react with soot. Now the soot is sintered on the glass rod using an oxyhydrogen torch.
When the glass rod becomes sufficient enough for fabricating optical fibres, the vapour flow and suit deposition gets stopped manually, and a high temperature is used with the glass rod to fabricate fibre.
Main Differences Between OVPO Process and MCVD Process
- The OVPO process uses the glass halide gasses only to form the core and the cladding of the fibre. On the other hand, the MCVD process uses the core as a gas halide vapour and cladding as the material of the soot.
- OVPO method does not involve the use of oxyhydrogen flame for sintering soot over glass rods. On the other hand, the MCVD process uses.
- The OVPO process uses soot as silicon dioxide. On the other hand, the MCVD process can also make use of phosphorus or germanium material.
- The OVPO process uses 1400 degrees Celsius temperature. On the other hand, the MCVD process uses 250 degrees Celsius only.
- The OVPO method has a flame hydrolysis reaction. On the other hand, the MCVD method uses a vapour deposition reaction.



