Pneumonia and Hypothermia are two medical conditions that are quite common. Both the diseases have a lot of differences and need to be taken care of by expert medical assistance as early as possible.
Also, medical instructions must be followed in order to deal with the disease and cure it before it gets out of hand. It is even more important to have the basic knowledge about the two medical conditions to be helpful at times of emergencies.
Key Takeaways
- Pneumonia is an infection that causes lung inflammation, while hypothermia is a medical emergency caused by prolonged exposure to cold temperatures.
- Pneumonia symptoms include fever, cough, and difficulty breathing, while hypothermia symptoms include shivering, confusion, and slow heart rate.
- Pneumonia is treated with antibiotics or antiviral medications, while hypothermia requires rewarming the body and managing related complications.
Pneumonia vs Hypothermia
Pneumonia is a respiratory illness that causes inflammation of the air sacs in the lungs, resulting in symptoms such as fever, coughing, and difficulty breathing. Hypothermia is a condition in which the body’s core temperature falls below normal, resulting in symptoms such as shivering, confusion, and difficulty speaking.

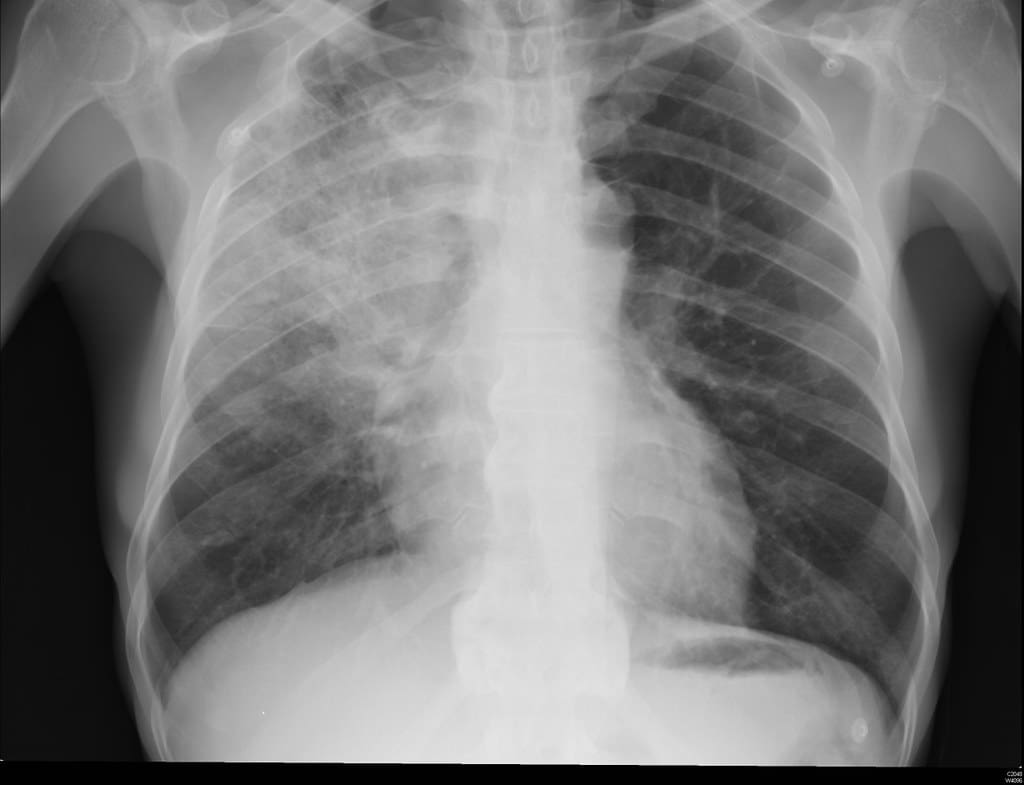
Pneumonia is an infectious disease. It is caused when any disease-causing agent or bacteria enters the lung parenchyma and solidifies the pulmonary tissues.
There are also many classifications of pneumonia based on different aspects like a causative agent and host reaction.
Hypothermia is briefly described as a medical condition in which the temperature of the patient’s body falls below 35 degrees celsius.
This happens due to the failure of the body’s thermoregulatory system to maintain the core temperature of the body. It is quite a serious condition, and if medical assistance is not provided on time, it can also result in fatality.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Pneumonia | Hypothermia |
|---|---|---|
| About | It is the solidification of pulmonary tissues due to invasive bacteria. | It is the falling of body temperature below 35 degrees celsius. |
| Charge | It is categorised as an infectious condition. | It is categorised as a physiological derangement. |
| Cause | It is caused due to foreign bacteria | It is caused due to failure of the body’s thermoregulatory system. |
| Symptom | Cough, fever, and chest pain. | Cold, shivering, confusion, and dehydration. |
| Treatment | Antibiotics and Penicillin are useful in the treatment of pneumonia. | Rewarming, electrolyte balance correction, resuscitation. |
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is characterised as an infectious disease that is caused due to the invasion of a disease-causing agent, most commonly bacteria that enters the lung parenchyma and evokes solidification of the pulmonary tissue.
There is a lot of classification of pneumonia which is based on several different aspects. Pneumonia classified on the basis of causative agents is viral, bacterial, or fungal.
On the basis of the nature of the host, it is fibrinous and suppurative. On the basis of gross and atomic distribution, it can be bronchopneumonia and lobar pneumonia.
The large classification is based on the place from where pneumonia was acquired, which categorises it into hospital-acquired or community-acquired.
The lungs and the respiratory tract have a lot of defence mechanisms whose sole purpose is to prevent the entry of any foreign agents that can cause disease.
These include nasal clearance, which helps in the removal of any dirt or particles deposited on the airway by sneezing and coughing, alveolar clearance and tracheobronchial clearance.
The indications for pneumonia are chest pain, acute fever, cough, friction rub, dyspnea and effusion.
Pneumonia can be treated with the help of antibiotics, and there is its own vaccine known as penicillin.
There are also some complications related to pneumonia-like Abscess, which is the result of tissue destruction and Empyema, which is a result of the spread of infection to the pleural cavity.
What is Hypothermia?
Hyperthermia is a medical condition in which the body temperature of a person falls down below 35 degrees celsius. This results in rapid cooling of the body below the temperature that a human body needs to maintain for survival.
This happens because of the failure or inability of the thermal regulatory system of the body, which is in charge of maintaining the core temperature of the body at a constant level.
It is a serious condition, and if assistance is not provided on time, it can even result in fatality. The core temperature after the body needs to be maintained at all times for the proper functioning of the body.
Old people, as well as infants, are the two most affected by hypothermia. The reason for hypothermia in infants can be a poorly developed thermoregulatory system for a high surface area to weight ratio.
The reason for hyperthermia in old people can be a damaged thermoregulator system. Other causes of hyperthermia include stroke, hypothyroidism, hyperglycemia, corticosteroid insufficiency, hepatic failure, or even alcohol and drug use.
It can be treated by rewarming the person correcting the electrolytic balance of the body, treating cardiovascular abnormality and also resuscitation.
Main Differences Between Pneumonia and Hypothermia
- Pneumonia is an infectious disease, while hypothermia is a result of the body’s thermoregulatory system failure.
- Pneumonia results in the solidification of pulmonary tissues whereas, in hypothermia, the temperature of the body falls down below 35 degrees celsius.
- Pneumonia is caused due to invasion of disease-causing bacteria in the lung, while hypothermia is caused due to failure of the thermoregulatory system of the body.
- Symptoms of pneumonia include cough, fever, and chest pain. On the other hand, the common symptoms of hypothermia are cold, shivers and dehydration.
- Pneumonia can be treated with antibiotics and vaccination (penicillin). Hypothermia can be treated by rewarming the body, correcting the electrolytic balance, and resuscitation.