We are living in a world that houses more than 700 crore people. Among these 700 crores, different countries, states, religions, cultures, languages, races and several other features function together.
And to live in a world with diversity in every corner, there must be mutual respect and harmony among the people. There should be a peaceful and respectful relationship between the population to achieve harmony in the world.
For people to live together harmoniously, there must be specific rules and laws to regulate and justify proper behaviour and functioning. But, the words ‘rules’ and ‘laws’ are two concepts used interchangeably but differ in various aspects.
Both are terms that come under the legal branch of studies. Both ‘rules’ and ‘laws help properly function in a country.
Key Takeaways
- Rules are guidelines or instructions organizations, groups, or individuals set to govern behavior and maintain order within a specific context.
- Laws are formal, binding regulations enacted by a government or other authoritative body, applicable to all citizens within a jurisdiction, and enforceable legally.
- Both rules and laws regulate behavior and maintain order, but they differ in scope and enforceability, with laws carrying legal consequences and rules applying to specific contexts.
Rules vs Laws
Rules are guidelines established by organizations or groups to guide behavior within a specific setting or context. Examples of rules include workplace policies. Laws, are guidelines established by a governing body, such as a government and are designed to govern behavior in society as a whole.

Comparison Table
| Parameter of Comparison | Rules | Laws |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | A rule is a set of guidelines to regulate a practice or procedure of any activity. | A law is a system of rules that help govern the members or citizens of a country or community. |
| Applicability | Rules apply to any society, institution, association or activity. | Laws are applicable to an entire country or community. |
| Creation | Rules can be made by a secretary of the association, the headmistress of an educational institution, etc. | Laws can be made only by the Legislature of India (or any other legislative body in their respective country) |
| Consequence | Not following the rules can lead to mild consequences such as paying an amount such as a fine, suspension, etc. | Not adhering to laws can lead to strict and severe consequences such as imprisonment. |
What are Rules?
Specific guidelines must be set for a population of more than 700 crores population to exist together in harmony.
Rules help any group of people or any institution to function at ease. A rule can be placed at a level lower than a law. It acts as a set of guidelines that help regulate behaviour and functioning.
Rules can be created by the leading figure of any institution, society, association or just a group of people.
And breaking the rules lead to punishment at a much milder level. To make the concept of ‘rules’ clearer, here is a detailed example:
Consider a school or any academic institution. It is bound to have rules to maintain order in the school and function properly.
In any institution, there will always be an authority figure, leader or a person that heads the group of people within the institution.
This person has the power and right to create rules for the institution. As per the example, this person is the principal, headmaster, or headmistress.
He or she creates ‘rules’ for the betterment of the school.
Certain rules that are frequently found in academic institutions are:
- Mobile phones or any other electronic gadgets are not allowed.
- Students are expected to follow the decorum of the institution.
- Wear uniform daily.
- Sticking to the dress code listed by the school or college is mandatory.
- Students must reach the premises before 8:45 am.
These are a few rules found common in several institutions. Similarly, if you replace the academic institution with any other association or society; and the headmistress with a secretary, chairperson or president, you can find several other rules specific to the people and the group’s purpose.
And, in case of violation of any rules, there will also be the punishment of different kinds based on the broken rule.
For example, violation of any rules in an academic institution will probably result in a payment of an amount as a fine, bestowment of duties as responsibilities or, in extreme cases, suspension or rustication.
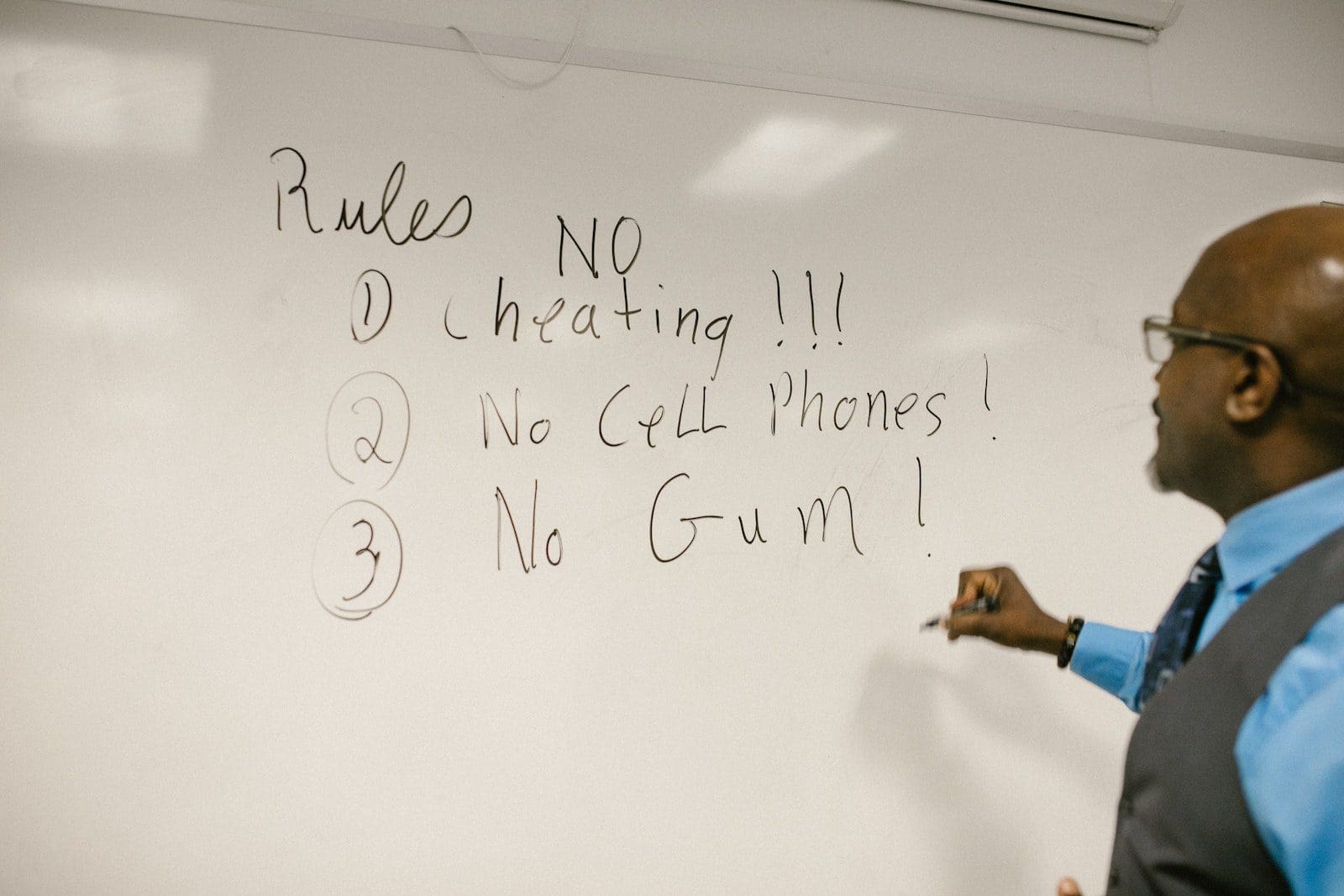
What are Laws?
Just like any institution or society requires rules to maintain order, a country or nation’s peaceful existence and functioning relies on laws. Laws make running a government and maintaining order and peace in a country easier.
A law is a system of rules that help govern the citizens of a nation.
The legislative body of a country can only create laws. Laws are made in stages.
First, a bill is presented in both houses of the Parliament. Once both houses pass the bill, it reaches the President.
If the President accepts and signs the bill, it becomes law. Violation of any laws leads to strict punishment.
For example, consider the country India. In India, the legislative body that implements laws is the Parliament.
The Parliament implements laws through the process mentioned above. And with the help of laws, it ensures that the laws are enforced and not violated.
In case of violation of any law, the punishment is severe and varies across countries and their system of governance.
The consequences of breaking the law include fines, compensations, and prison sentences, including life imprisonment, discharges, etc.
A few examples of laws are:
- Marriage laws
- Citizenship laws
- Land laws






