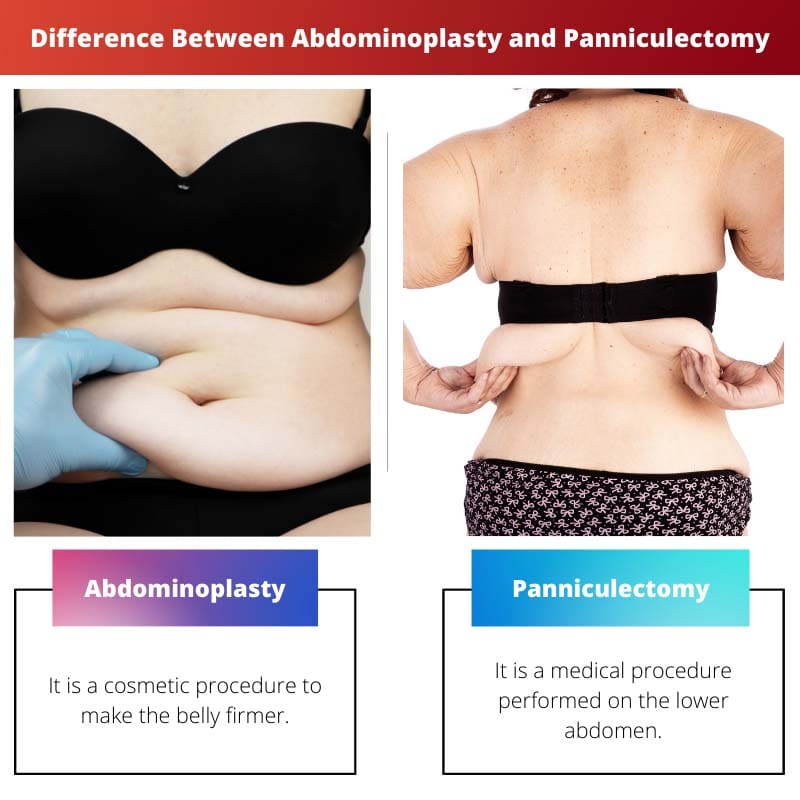
Abdominoplasty, commonly known as a tummy tuck, aims to reshape and contour the abdomen by removing excess skin and fat, often accompanied by tightening the underlying muscles for a more aesthetically pleasing appearance. On the other hand, panniculectomy specifically addresses the removal of the pannus, the overhanging apron of skin and fat typically found in individuals who have experienced significant weight loss or after pregnancy.
Key Takeaways
- Abdominoplasty is a cosmetic surgery that removes excess skin and fat from the abdominal area while tightening the muscles.
- Panniculectomy is a surgical procedure that removes only the excess skin and fat from the lower abdomen.
- The main difference between the two procedures is that abdominoplasty involves muscle tightening, while panniculectomy does not.
Abdominoplasty vs Panniculectomy
Abdominoplasty is a cosmetic surgical procedure that involves removing excess skin and fat from the abdomen and tightening the muscles of the abdominal wall to create a flatter, more toned abdomen. Panniculectomy is a surgical procedure to remove excess skin and fat from the lower abdomen to improve quality of life.
Abdominoplasty, commonly known as ‘tummy tuck’, is a cosmetic procedure that aims at making the abdomen slimmer and firm. It is done by people who have sagging skin after major weight loss or by women who have gone through pregnancy.
The muscles of the abdomen are tightened along with the removal of excess skin and fat.
Panniculectomy is a medical procedure that primarily aims at removing the panniculus. This is a thick fatty tissue that lines the walls of the lower abdomen. While abdominoplasty is an elective process, a panniculectomy is more of a medical necessity.
It is mostly done by people who have had weight loss surgery.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck) | Panniculectomy |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Restore overall abdominal contour by removing excess skin, fat, and tightening muscles | Remove excess skin and fat hanging from the lower abdomen (pannus) |
| Ideal Candidate | Moderate excess skin and fat, some separation of abdominal muscles | Significant excess skin and fat in the lower abdomen, often after massive weight loss |
| Procedure | More extensive, involving liposuction, muscle tightening (plication), skin removal, and navel repositioning (if needed) | Focuses on removing the pannus, with minimal muscle tightening |
| Incision | Horizontal incision across lower abdomen, sometimes with a vertical incision around the navel | Horizontal incision across lower abdomen |
| Recovery Time | 4-6 weeks | 6-8 weeks |
| Insurance Coverage | Usually not covered | May be covered under certain conditions (e.g., severe discomfort, hygiene issues) |
| Outcomes | Flatter, firmer abdomen with improved definition | Removal of pannus for improved comfort and mobility |
What is Abdominoplasty?
Abdominoplasty, commonly known as a “tummy tuck,” is a surgical procedure aimed at enhancing the appearance of the abdominal region. This cosmetic surgery involves the removal of excess skin and fat from the abdomen, as well as the restoration of weakened or separated muscles, resulting in a smoother and firmer abdominal profile.
Indications
1. Excess Skin and Fat:
Abdominoplasty is recommended for individuals who have significant amounts of loose skin and excess fat in the abdominal area, often caused by factors such as pregnancy, weight loss, or aging.
2. Muscle Weakness:
Women who have experienced multiple pregnancies may have weakened or separated abdominal muscles (diastasis recti), making them suitable candidates for abdominoplasty.
Procedure
1. Consultation:
A thorough consultation with a qualified plastic surgeon is essential. The surgeon evaluates the patient’s medical history, discusses expectations, and determines the most suitable abdominoplasty technique.
2. Anesthesia:
Abdominoplasty is performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient’s comfort and safety during the procedure.
3. Incision and Tissue Removal:
The surgeon makes an incision typically from hip to hip, low on the abdomen. Excess skin and fat are then removed, and the underlying muscles are tightened to create a more contoured appearance.
4. Navel Adjustment:
In some cases, the navel may need to be repositioned to maintain a natural look after excess skin removal.
5. Closure:
The incisions are meticulously closed with sutures, and drains may be placed to prevent fluid accumulation.
Recovery
1. Postoperative Care:
Patients are advised to follow postoperative care instructions, which may include wearing compression garments, taking prescribed medications, and avoiding strenuous activities during the initial recovery period.
2. Healing Time:
Complete recovery may take several weeks, during which patients gradually resume normal activities. Strenuous exercise is typically restricted for a more extended period.
Risks and Complications
1. Infection:
Though rare, infection is a potential complication post-surgery. Antibiotics may be prescribed to mitigate this risk.
2. Scarring:
Scarring is inevitable, but surgeons aim to place incisions strategically to minimize visibility. Scars often fade over time.
3. Numbness:
Some patients may experience temporary numbness in the treated area, which usually improves with time.
Results
Abdominoplasty can yield dramatic and long-lasting results, providing patients with a flatter, more toned abdomen. However, individual outcomes may vary, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for preserving the benefits of the surgery.
What is Panniculectomy?
Panniculectomy is a surgical procedure designed to remove excess skin and fat from the lower abdomen, particularly the apron of skin known as the pannus. This surgical intervention is distinct from abdominoplasty (tummy tuck) as it primarily focuses on addressing the overhanging pannus rather than tightening the abdominal muscles. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into various aspects of panniculectomy.
Indications
1. Massive Weight Loss
Panniculectomy is often recommended for individuals who have undergone significant weight loss, either through bariatric surgery or lifestyle changes. The excess skin left behind after substantial weight loss can lead to functional impairments and hygiene issues, making panniculectomy a valuable solution.
2. Postpartum Changes
Women who have experienced multiple pregnancies may develop a pannus due to stretched abdominal skin. Panniculectomy can help address the cosmetic and functional concerns associated with postpartum changes.
3. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as dermatitis and recurrent infections within the pannus, may necessitate panniculectomy for therapeutic reasons.
Surgical Procedure
1. Patient Evaluation
Before undergoing panniculectomy, patients undergo a thorough evaluation by a plastic surgeon. This evaluation includes assessing the patient’s overall health, medical history, and specific concerns related to the pannus.
2. Anesthesia
Panniculectomy is typically performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient’s comfort throughout the procedure.
3. Incision and Tissue Removal
The surgeon makes an incision in the lower abdominal area, strategically hidden to minimize visible scarring. The excess skin and fat are then carefully excised, and the remaining tissue is reshaped to achieve a more natural contour.
Recovery and Aftercare
1. Hospital Stay
Patients usually spend a day or two in the hospital following panniculectomy to monitor their initial recovery and manage postoperative pain.
2. Postoperative Care
After discharge, patients are provided with detailed instructions for wound care, pain management, and gradual resumption of daily activities. Compression garments may be recommended to support the healing process and reduce swelling.
Risks and Complications
1. Infection
As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection. Proper hygiene and adherence to postoperative care instructions help mitigate this risk.
2. Hematoma and Seroma
Collection of blood (hematoma) or fluid (seroma) may occur, requiring drainage or additional medical attention.
3. Scarring
While efforts are made to minimize scarring, some degree of scarring is inevitable. However, scars typically fade over time.
Main Differences Between Abdominoplasty and Panniculectomy
- Purpose:
- Abdominoplasty: Primarily performed for cosmetic reasons, aiming to improve the appearance of the abdomen by removing excess skin and fat. It often includes muscle tightening for a more toned result.
- Panniculectomy: Typically performed for medical reasons, addressing the removal of the pannus (excess skin and fat) that hangs down over the lower abdomen. It is often done to alleviate medical issues such as infections or skin irritation.
- Muscle Repair:
- Abdominoplasty: Involves the repair and tightening of the abdominal muscles (rectus muscles) to enhance abdominal contour and provide a flatter appearance.
- Panniculectomy: Does not typically include muscle repair unless medically necessary. It mainly focuses on the removal of excess skin and fat.
- Cosmetic vs. Medical Indications:
- Abdominoplasty: Primarily an elective cosmetic procedure chosen by individuals seeking aesthetic improvement in the abdominal area.
- Panniculectomy: Generally considered a medical necessity and is often covered by insurance when performed to address health issues related to the excess skin and fat.
- Extent of Tissue Removal:
- Abdominoplasty: Targets not only excess skin and fat but also includes reshaping of the abdominal muscles, creating a more sculpted appearance.
- Panniculectomy: Mainly focuses on the removal of the pannus, with less emphasis on muscle contouring.
- Recovery and Downtime:
- Abdominoplasty: Typically involves a longer recovery period due to muscle repair. Patients may need to limit physical activities for an extended period.
- Panniculectomy: Generally has a shorter recovery time, as it primarily addresses the removal of excess skin and fat without extensive muscle work.
- Insurance Coverage:
- Abdominoplasty: Usually not covered by insurance, as it is considered a cosmetic procedure performed for aesthetic reasons.
- Panniculectomy: Often covered by insurance when deemed medically necessary to address health issues associated with the pannus.
- Patient Profile:
- Abdominoplasty: Suited for individuals seeking aesthetic improvement in the abdominal area, often after weight loss, pregnancy, or aging.
- Panniculectomy: Recommended for patients with medical conditions or discomfort caused by the excess skin and fat in the lower abdominal region.