Key Takeaways
- Bruising occurs when blood vessels near the skin’s surface break, causing visible discoloration on the skin.
- Internal bleeding involves damage to blood vessels more serious within the body, which may not be immediately visible.
- Bruising is less severe and more easily identifiable than internal bleeding, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.

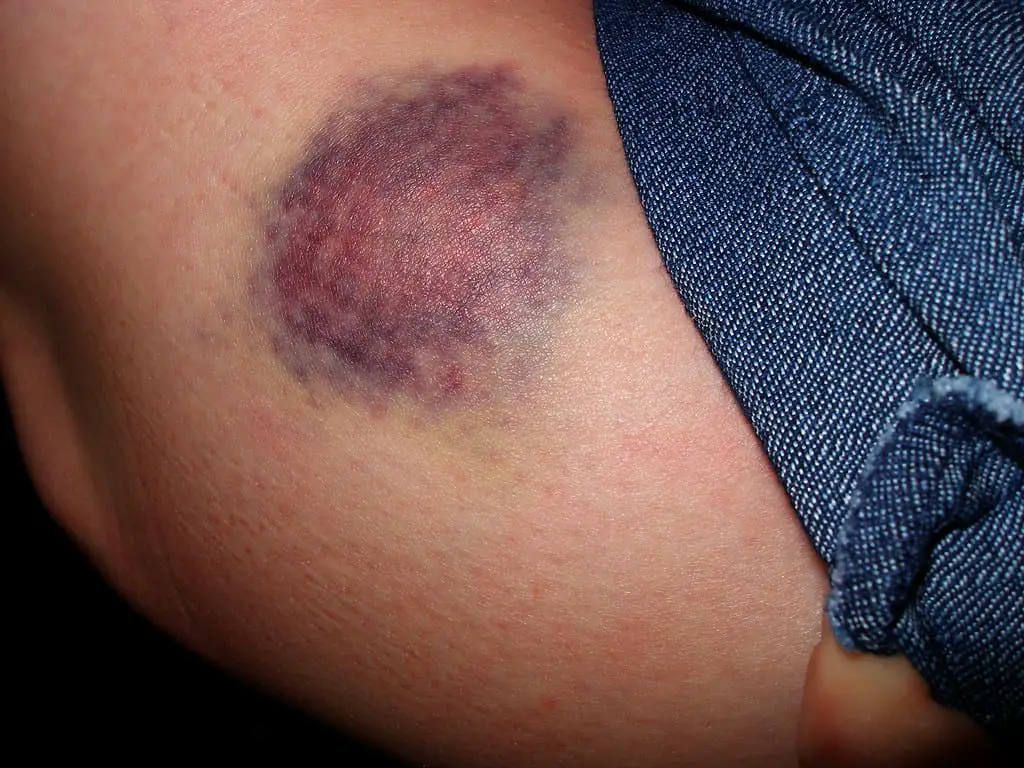
What is Bruising?
Bruising is a type of injury that occurs when damaged blood in the blood capillaries starts causing movement. The movement caused in the blood capillaries can occur due to injury or some ongoing process caused by a disease. It is caused due the formation of blood clots in the skin. The three causes of bruising are injury, ongoing anti-clotting medication, medical disorders, etc.
In many cases, a bruise only causes pain when pressure is applied to it, but in severe cases, a bruise can cause excruciating pain even by a simple movement. Some people with blood clotting medical disorders experience bruising. The inflammatory response after the occurrence of a bruise is not frequent or is not observed in many cases.
A minor bruise heals on its own. If a bruise stays longer than usual, it can cause serious complications, especially for athletes. The pigmentation caused when a body part is bruised can stay longer even if the bruise is healed. The blood will continue to pass through the injured part if proper treatment is not sought for bruising. People that lack Vitamin K are most likely to get easily bruised.
What is Internal Bleeding?
Internal bleeding occurs when blood gushes out of body part(s) due to serious injury. When internal bleeding is caused, there is less or more blood loss from the blood vessels. Internal bleeding causes injury to the body’s organs. The most common internal bleeding causes are road accidents. Many medical conditions like stomach ulcers and diseases related to the liver can also cause internal bleeding.
Internal bleeding from the head, lungs, and heart trauma can result in more blood loss. Internal bleeding can be caused due to two types of traumas, namely blunt and penetrating.
In blunt trauma, a body part collides against an object at an incredible speed. In penetrating trauma, a sharp, foreign object falls on a body part, causing a hole in multiple blood vessels. A gunshot wound or a knife stab causes penetrating trauma.
A victim of internal bleeding will experience pain insidiously as the hemorrhage increases. A CT scan is performed to determine the exact place of injury, or in case of bleeding occurring in the stomach, an endoscopy is performed. The treatment involves infusion of Vitamin K, blood, or platelets intravenously, depending on the severity.
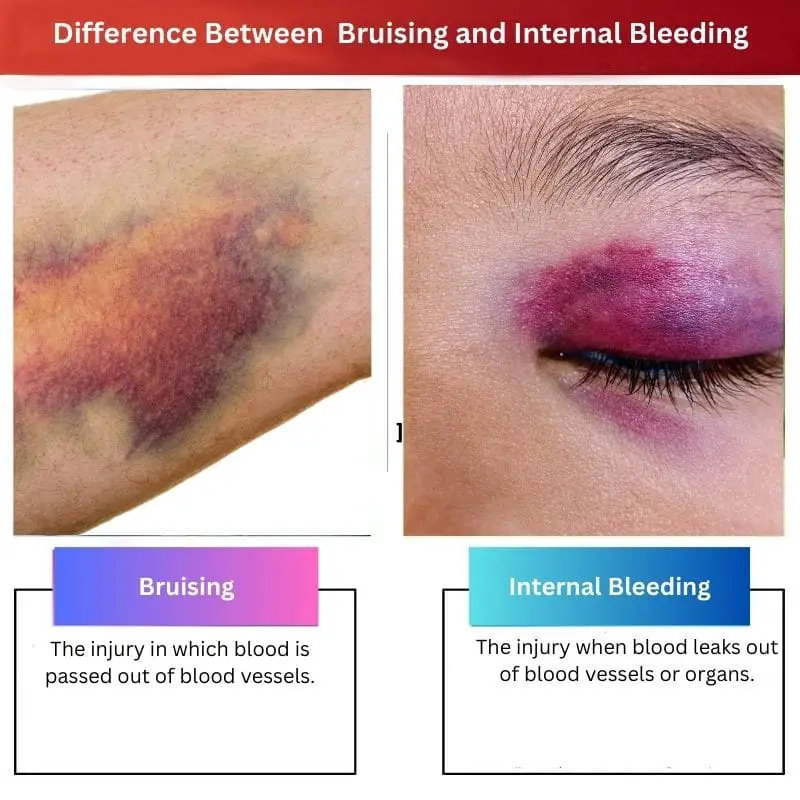
Difference Between Bruising and Internal Bleeding
- Bruising is comparatively less painful and severe. Internal bleeding is more painful and severe.
- Bruising is less life-threatening. If improper treatment is provided, internal bleeding can result in loss of life.
- In bruising, blood is moved out of blood vessels. In internal bleeding, blood is lost from blood vessels, and the person bleeds internally.
- The treatment for bruising is as simple as applying ice to the bruise. The treatment required for internal bleeding is complicated, including the intravenous infusion of Vitamin K, platelets, etc.
- The diagnosis of bruising is easy; a purple-black appearance is formed on the skin where the trauma is experienced. A CT scan and other imaging processes are used to diagnose internal bleeding.
Comparison Between Bruising and Internal Bleeding
| Parameters Of Comparison | Bruising | Internal Bleeding |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The injury in which blood is passed out of blood vessels. | The injury when blood leaks out of blood vessels or organs. |
| Causes | Bumping into an object, Hemophilia A, low platelet count. | Road accident, stomach ulcer, a broken bone. |
| Appearance | Visible | Not visible |
| Subtypes | Subcutaneous, intramuscular, periosteal etc. | Head trauma, bleeding around the heart etc. |
| Severity | Relatively less | Relatively more |