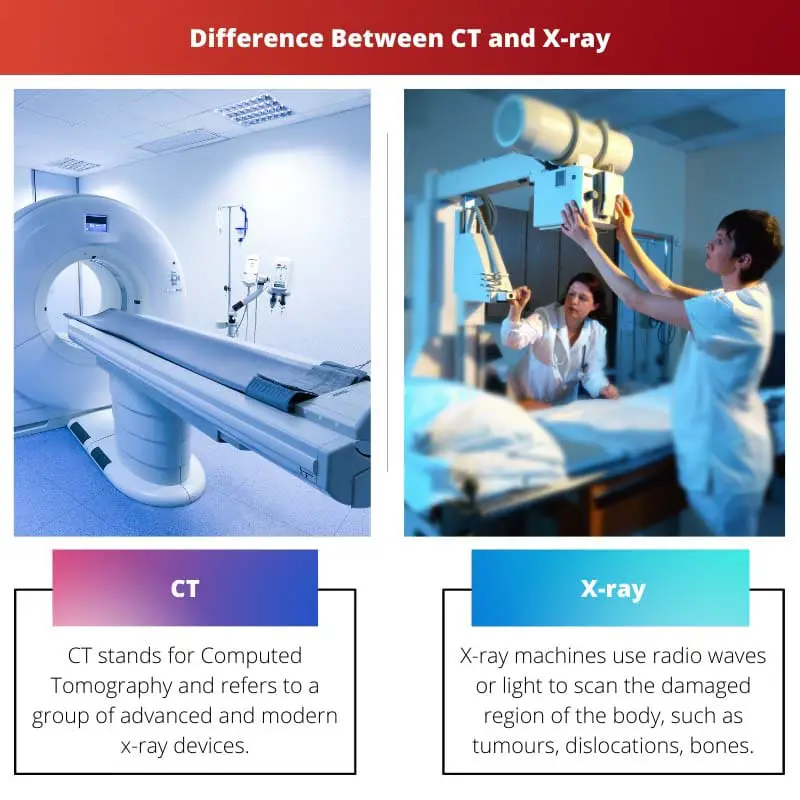
To diagnose internal body injury, several techniques are followed. Two of such as Computed Tomography scans and X-Ray machines. They spot internal injuries or small fracture that happens inside the body with the help of advanced technologies.
Key Takeaways
- CT scans generate detailed 3D images of internal structures, whereas X-rays produce 2D images with less visual information.
- CT scans expose patients to higher radiation levels than X-rays, posing a greater risk for potential long-term effects.
- X-rays are more cost-effective and readily available, making them suitable for diagnosing fractures and lung issues, while CT scans excel in detecting tumors and complex internal issues.
CT vs X-ray
The difference between CT and X-ray is that a 360° X-ray beam is used in CT scans. As a result, the images produced are crisp, strong, and easy to see on a computer screen. However, on the contrary, the X-ray images are blurry. Furthermore, the interior organ damage is not evident in detail. CT imaging yields three-dimensional images. However, on the contrary, X-ray imaging yields 2D images.
Computed Tomography, or CT, is a term for a group of advanced and modern X-ray devices. These machines create a crystal clear image of internal organs and soft tissues, as well as clear and precise anatomy of any damaged place on the body.
The success and invention of Computed Tomography, or the CT machine, are credited to Allan Cormack and Godfrey Hounsfield. In 1972, they came up with the idea.
X-ray machines use radio waves or light to scan the damaged area of the body, such as tumours, dislocations, fractures, pneumonia, and lung infection. Wilhelm Rontgen assumed charge in 1895 and was eventually credited with developing X-ray methods.
The X-ray creates two-dimensional images. Tumours, pneumonia, dislocations, and fractures of the bones are all diagnosed with X-ray machines and methods.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | CT | X-ray |
|---|---|---|
| Inventor | Allan Cormack, Godfrey Hounsfield | Wilhelm Rontgen |
| Type of images | 3D | 2D |
| Diagnosis | Soft tissues and internal organs, blood vessels. | Pneumonia, tumours, dislocation and fracture of bones. |
| Quality of Image | High quality, deep. | Not clear. |
| Cost | Expensive | Inexpensive |
| Availability | Not available widely. | Widely available. |
What is CT?
CT stands for Computed Tomography and refers to a group of advanced and modern X-ray devices. These scanners produce a crystal clear image of internal organs and soft tissues, as well as clear and detailed anatomy of any damaged place on the body.
The success and invention of Computed Tomography, or the CT machine, are credited to Allan Cormack and Godfrey Hounsfield.
In 1972, they came up with the idea together. CT scans provide images that are three-dimensional in appearance. CT scans are utilised to diagnose blood vessels, soft tissues, and internal organs in particular.
The scanned images obtained from CT are of great quality and depth. CT scans are frequently more expensive than other types of scans.
CT scans are designed to use a 360-degree X-ray beam. As a result, the images obtained are clear, strong, and easy to perceive on a computer screen.
Because computed tomography is a sophisticated method, it is only available in large, well-equipped hospitals in cities, not in small rural healthcare systems.

What is X-ray?
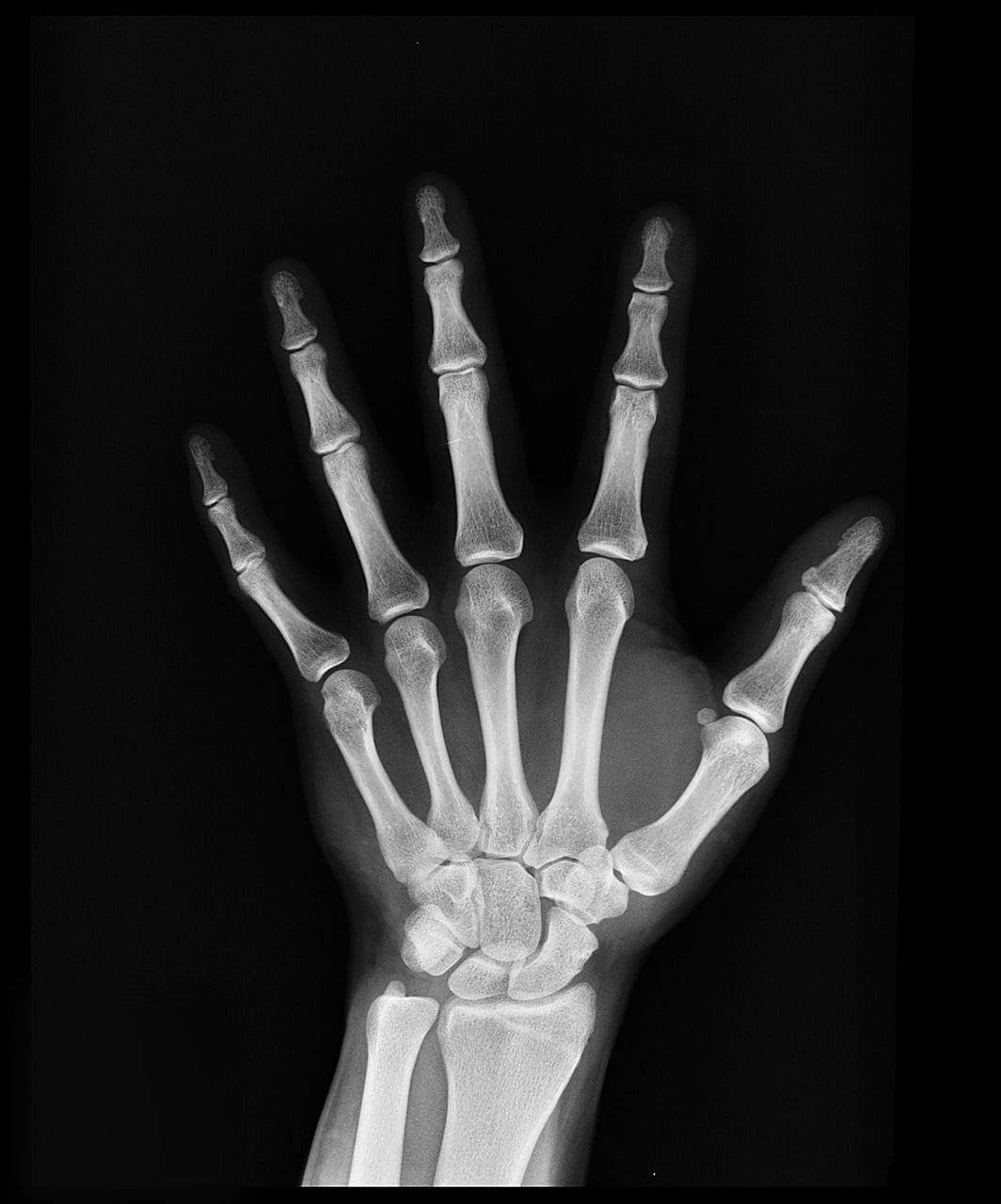
X-ray machines use radio waves or light to scan the damaged region of the body, such as tumours, dislocations, bones, fractures, pneumonia, and lung infection.
Wilhelm Rontgen assumed responsibilities in 1895 and eventually came up with a novel X-ray method.
X-rays produce two-dimensional images. Tumours, pneumonia, dislocations, and fractures of bones are all diagnosed using X-ray machines and methods. The images produced from the X-ray are not particularly clear. Furthermore, the lesions to the interior organs are not evident in detail.
X-ray techniques are not particularly costly. They are, nevertheless, very inexpensive. X-ray images are created using radio wave radiation, which can be extremely damaging to the body if proper and timely safeguards are not taken.
X-ray is readily available, as it has grown commonplace in recent years.
Main Differences Between CT and X-ray
- CT or also known as Computed Tomography, is a variety of advanced and modern X-ray machines. These machines produce a clear and detailed structure of any affected area on the body with a crystal-clear image of internal organs and soft tissues. On the other hand, X-ray machines are designed to use radio waves or light radiation, which scans the affected part of the body, like tumours, dislocations, bones, fractures, pneumonia, and lung infection.
- Allan Cormack and Godfrey Hounsfield are the people behind the success and invention of Computed Tomography, or the CT machine. They invented it together in 1972. On the other hand, in 1895, Wilhelm Rontgen took responsibility and finally came up with a new invention of X-ray procedures.
- CT produces pictures of images that are three-dimensional in characteristic. On the other hand, X-ray produces pictures of images which are two-dimensional in characteristic.
- CT is specifically used in the diagnosis of blood vessels, soft tissues and internal organs. On the other hand, X-ray machines and procedures are used in the diagnosis of tumours, pneumonia, dislocation and fracture of bones.
- The scanned pictures obtained from CT are high-quality images, and they are deep as well. On the other hand, the pictures obtained from the X-ray are not much clear. Moreover, the details of the injuries in the internal organs are not visible.
- CT scans cost higher and are expensive. On the other hand, X-ray procedures are not much expensive. However, they are easily affordable.
- CT scans are designed in such a way that they use a 360° X-ray beam. Thus, images obtained are clear, powerful and can easily be seen on the screen of the computer. On the other hand, Images produced in X-rays are done with the help of radiations of radio waves, which can be highly harmful to the body if correct and timely precautions are not taken.
- As Computed Tomography is an advanced technique, therefore it is only available in urban and well-equipped hospitals and not in small healthcare systems in rural areas. On the other hand, X-ray is available easily as it has become common nowadays.