The cell is the basic building unit in the human body, and it is a self-reliant unit. Tissues are the second layer after the skin layer, and skin protects tissues because these are very sensitive and can easily be damaged by sun rays.
Dysplasia and Metaplasia are associated with the cells that are present in the human body. These cells need very much good care because their rapid growth can lead to organ cancer and less quantity can lead to diseases like anaemia, red cell membrane disorder, red cell membrane disorder, etc.
Key Takeaways
- Dysplasia is an abnormal growth of cells characterized by varying cell size, shape, and architectural organization.
- Metaplasia is a reversible change in which another mature cell type replaces one mature cell type.
- Both dysplasia and metaplasia are considered precancerous conditions and may progress to cancer if left untreated.
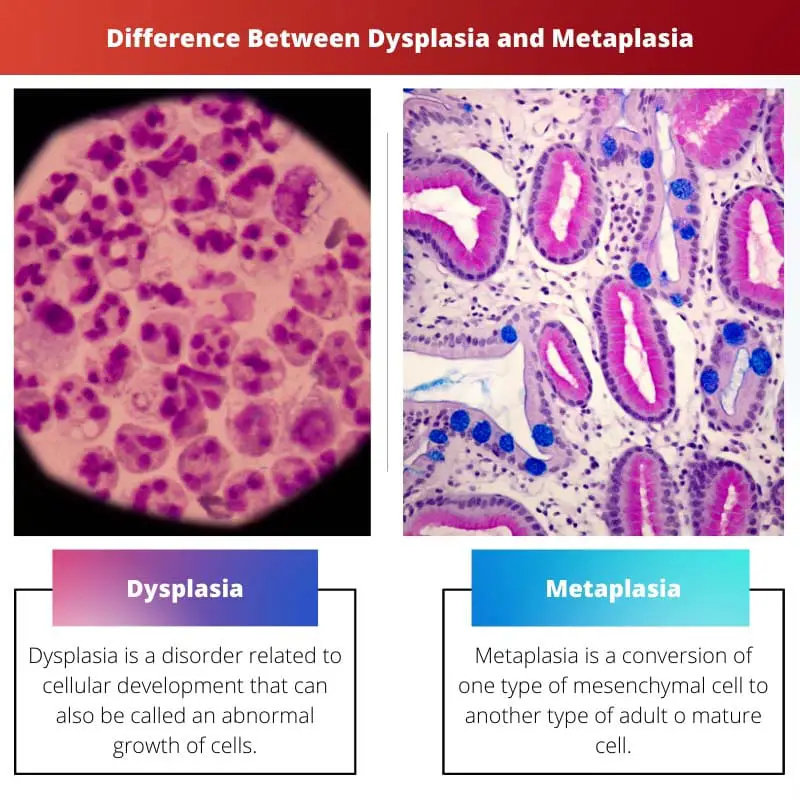
Dysplasia vs Metaplasia
Dysplasia refers to the abnormal growth of cells within a tissue, characterized by changes in the size, shape, and organization of cells within a tissue. Metaplasia is the replacement of one type of cell with another type of cell and can occur in response to injury, and is a reversible process.

His condition is associated with uncommon cell development. The cells are gone through a microscopic checkup, where their size and shapes are observed or analyzed, and then after this, the report is made.
Metaplasia is a condition related to somatic cells. In this, a somatic cell is divided into another somatic cell which means a cell is differentiated into another new cell.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Dysplasia | Metaplasia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dysplasia is a disorder related to cellular development that can also be called an abnormal growth of cells. | Metaplasia is a conversion of one type of mesenchymal cell to another type of adult o mature cell. |
Types and Tissues affected | This is mostly caused in epithelial cells only and tissues affected by this are the uterine cervix and bronchial mucosa. | This is mainly caused in epithelial and mesenchymal cells and commonly affects bronchial mucosa, uterine endocervix, etc. |
| Changes in a cellular pattern | Dysplasia is a condition associated with cellular development therefore it changes the shape and size of the cell. | Metaplasia leads a cell to its maturity state. Which means one division of the cell gets matured. |
| Medication | Dysplasia can be treated with cryosurgery, laser therapy, and electrosurgical process, etc. | Metaplasia can be treated with chemotherapy and electrosurgical process etc. |
| Nature of process | This process is irreversible and cannot be changed if not treated properly or in time. | This process is reversible and can lead a cell to its normal state. |
| Cancer-causing | Dysplasia comes under one of the symptoms of cancer and may lead to cancer. | Metaplasia does not form cancer cells but if not treated on time this may lead to the generation of cancer cells. |
What is Dysplasia?
Dysplasia is a disorder that contributes to unusual cell growth, which is not good for health and can lead to many chronic or long-term diseases.
This disorder causes cysts in the cells, which develop with time and increase the cell’s size, leading to hormonal imbalances in the body that causes improper functioning of the body’s organs.
Dysplasia in its very early stage can be treated and does not lead to cancer, but when it reaches its maturity, it may cause cancer in specific organs, therefore, proper surgery or electrical treatment is required.
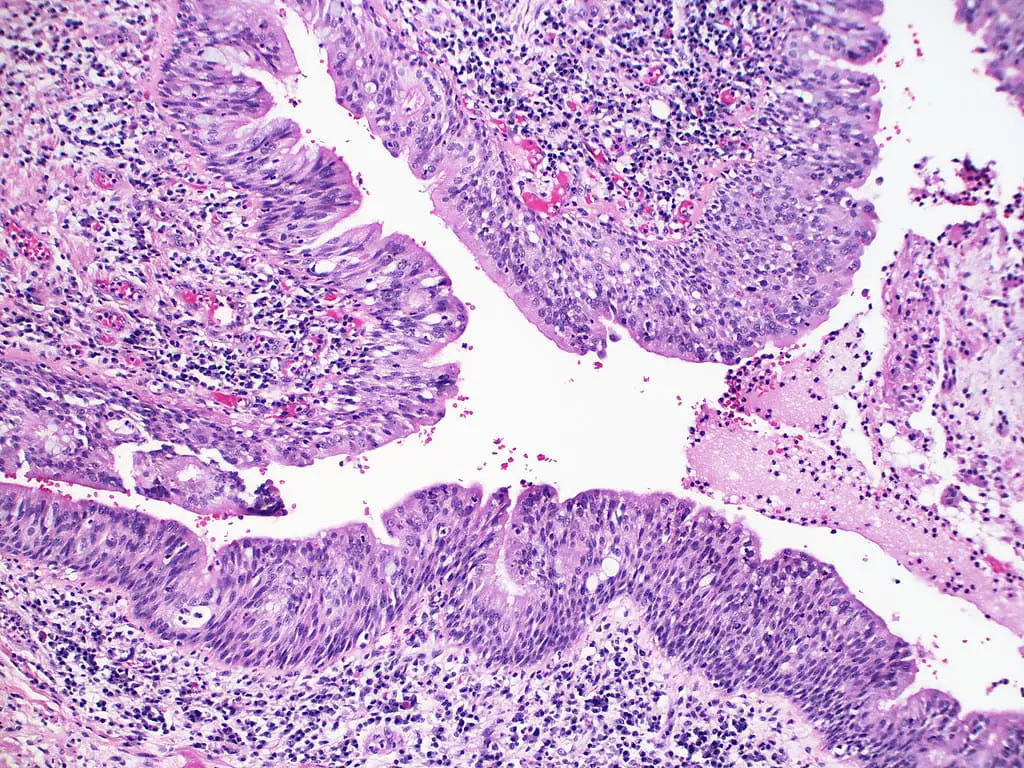
What is Metaplasia?
Metaplasia changes the state of the body cell, which means that the cells get divided into a new mature cells. And this mature cell is an unknown cell that can be harmful to other body organs and other cells of the body.
This disorder is mainly caused due to changes in the surroundings or environment of the cells. And these changes in the environment of the cells cause them to adapt to a new habitat and lead to the formation of the new cell.
There are many examples of these changes, and some of them are smoking cigarettes, chewing tobacco, and drinking alcohol, which causes irritations in the cell and forces them to adapt to a new environment.
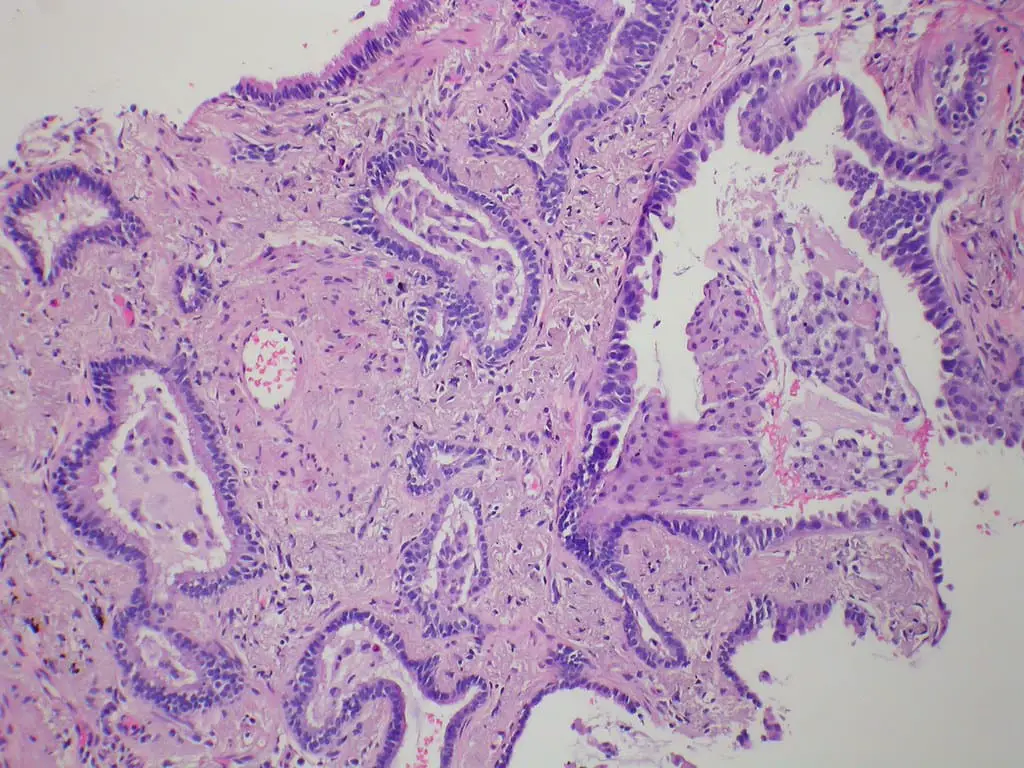
Main Differences Between Dysplasia and Metaplasia
- Metaplasia does not form cancer cells, but if not treated on time, this may lead to the generation of cancer cells. Whereas, Dysplasia comes under one of the symptoms of cancer and may lead to cancer.
- The process of Dysplasia is irreversible and cannot be changed if not treated properly or in time. While the process of Metaplasia is reversible and can lead a cell to its normal state.