With the evolution of technology, new techniques are used in today’s world to cure various diseases. One such technique is the use of radiation therapy or radiotherapy to treat cancer or tumours.
These techniques help reduce various side effects. The beams are adjusted in a way to match the shape of the tumours.
Key Takeaways
- Gamma Knife uses multiple focused gamma radiation beams for precise, non-invasive brain surgery.
- CyberKnife combines robotics and image guidance to deliver radiation therapy to tumors throughout the body.
- Both technologies minimize damage to surrounding healthy tissue and offer treatment options for inoperable or difficult-to-reach tumors.
Gamma Knife vs CyberKnife
The difference between Gamma Knife and CyberKnife is that the flexibility offered by CyberKnife is much more than that of Gamma Knife. It can treat tumours throughout the body, unlike Gamma Knife, which only treats tumours in the head and brain area. Unlike a Gamma Knife, no headframe and anaesthesia are required while using a CyberKnife.

Gamma Knife is a radiation therapy in which focused beams of high-dose radiation are used on a highly specific area. Side effects are much less compared to traditional radiation techniques as there isn’t much effect on surrounding tissues.
The recovery period and post-procedural pain are the least when a Gamma Knife is used.
CyberKnife is also a radiation therapy in which photons are focused on the tumour. Using this, the tumour is reduced or eliminated in a few sessions only. Its machine comprises a robotic arm that moves around the patient to find the affected area.
This prevents the chances of radiation being used in affected areas.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Gamma Knife | CyberKnife |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy enabled by | The accuracy is achieved by making the patient immobile throughout the treatment | Uses real-time imaging and enhanced tumor tracking technology to achieve accuracy |
| Invasive | Treatment is invasive; a large, metalhead frame bolted into the skin of the patient | Treatment is non-invasive; a soft, mesh mask is worn by the patient during treatment |
| Part of the body treated | In the skull and several cases in the cervical spine | Throughout the body |
| Anesthesia | Required | Not required |
| First used in the U.S. | First used in the U.S.A. in 1979. | First used in 2001 in U.S. |
| Radioactive material used | Radioactive cobalt is used | Makes use of electrically generated photons |
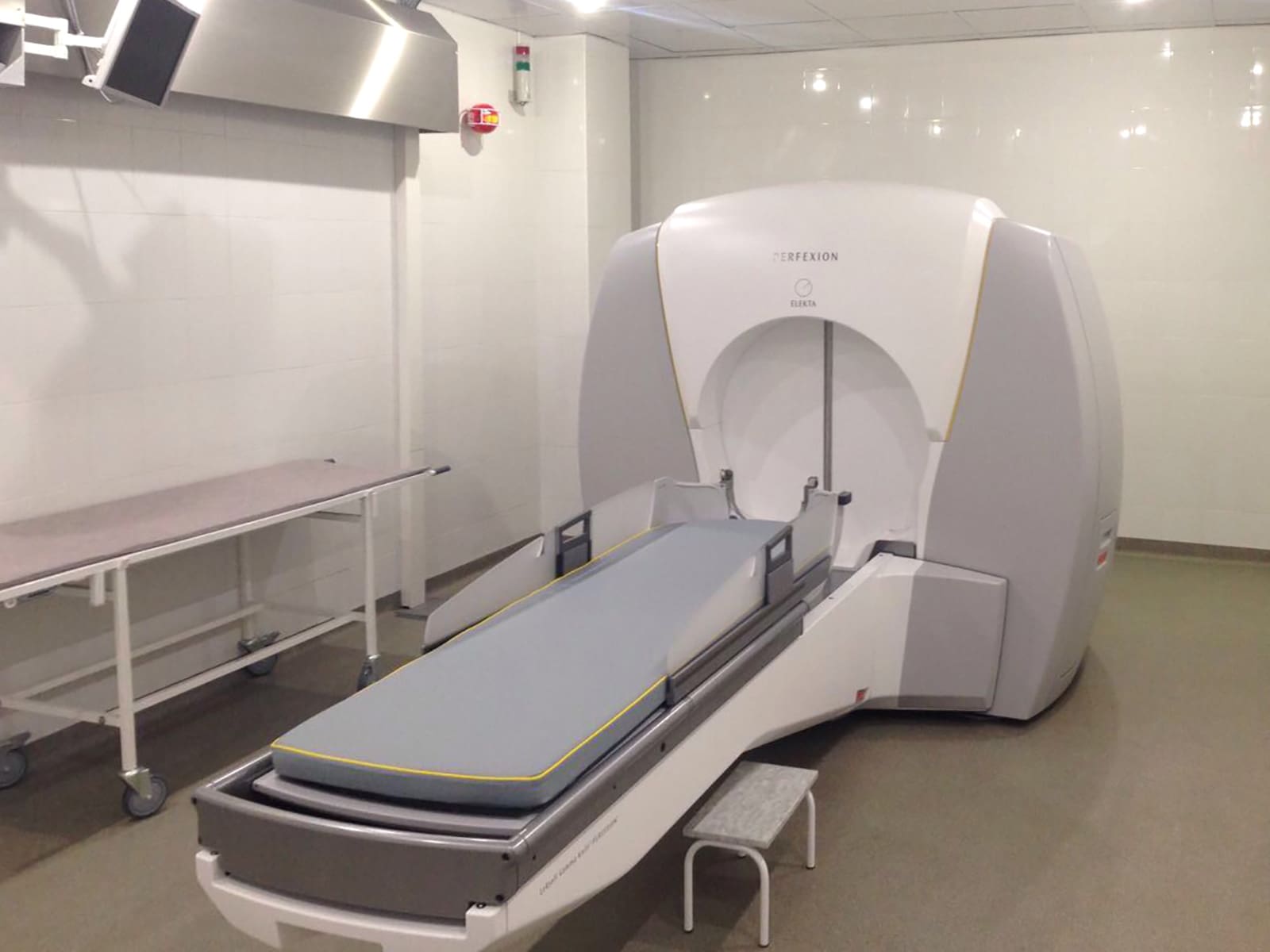
What is Gamma Knife?
Gamma Knife is a radiation therapy that makes use of computerized treatment planning software. It assists physicians in locating and removing small affected regions within the brain and head with sub-millimeter accuracy.
In this, intense radiation doses are delivered to the affected while leaving the unaffected areas alone.
A medical physicist, radiation oncologist, and neurosurgeon are involved in this radiation therapy.
They are known as a multidisciplinary team. It is also a requirement laid down by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission, which states the presence of an authorized user for the treatment.
Highly trained professionals are needed to operate for the same. Any discrepancy can cause major issues.
Shaping the volume of tissue to be treated, ensuring that the head frame is properly attached, and the accuracy of the imaging studies are all essential for precise treatment.
A medical physicist ensures safety by testing all the types of equipment and software involved.
The Gamma Knife is used to treat a variety of problems. It can be used to treat benign brain tumours, blood vessel defects, select malignant tumours, and functional problems.
Future use for epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease are also being evaluated. The risk involved in this therapy is less and has a minimum recovery period, so it is preferred in the treatment of various problems.
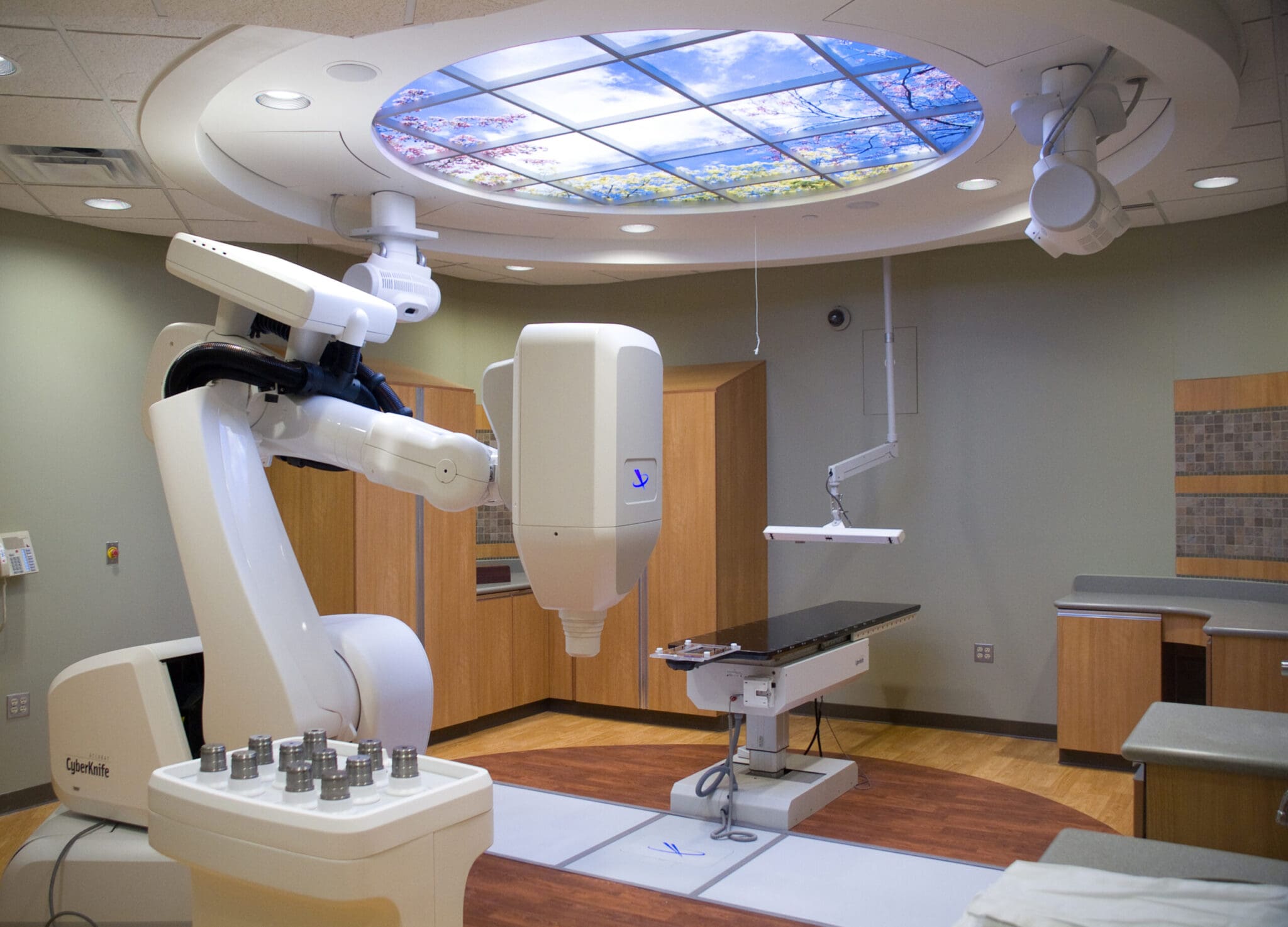
What is CyberKnife?
The CyberKnife comprises a lightweight linear accelerator that is put on a robotic arm. It is a non-invasive treatment used to treat both non-cancerous and cancerous tumours and several other conditions involving radiation therapy.
Unlike a Gamma Knife, it treats conditions in all parts of the body, including the lungs, liver, kidney, pancreas, and others.
The treatment is completed in 1 to 5 sessions and has less recovery. The precision is high as it involves the latest technology.
In this, the robot examines the patient, and radiation is provided to the exact affected area reducing doses to the healthy tissues.
Two treatment types of CyberKnife system are as follows:
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS)
- Stereostatic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT)
It uses real-time X-rays to note the patient’s position while treatment and then aligns the radiation beam accordingly. Every move of the patient is taken into consideration by the machine and accommodated during treatment.
Each beam of this machine is independent of the other.
It is also approved by the FDA to perform radiosurgery. It is also the only system with live motion synchronization, improving its precision. A moving tumour is also recorded by it.
Main Differences Between Gamma Knife and CyberKnife
- Gamma Knife is invasive, wherein the patient wears a large metalhead frame. On the other hand, a CyberKnife is non-invasive, wherein the patient wears a soft mesh mask.
- Gamma Knife achieves precision by immobilizing the patient, whereas live motion synchronization is used in CyberKnife.
- Treatment options are more flexible when using a CyberKnife than a Gamma Knife. The patient has to opt for a single treatment while a Gamma Knife is in use, whereas the patient can opt for single or multiple treatments while a CyberKnife is used.
- Anaesthesia and radioactive cobalt are used in Gamma Knife treatment, while electrically generated photons are used in CyberKnife treatment. No anaesthesia is required for CyberKnife treatment.
- Gamma Knife was first used in the U.S. in 1979, whereas CyberKnife was used in 2001.




