The heart is the most important muscular part of the human body. It circulates blood through the circulatory system. The heart supplies nutrients and oxygen to tissues in the body.
It removes carbon dioxide and other wastes. The heart is divided into four chambers like Right and left ventricle and right and left atrium. The ventricle is at the below part of the ventricle.
Key Takeaways
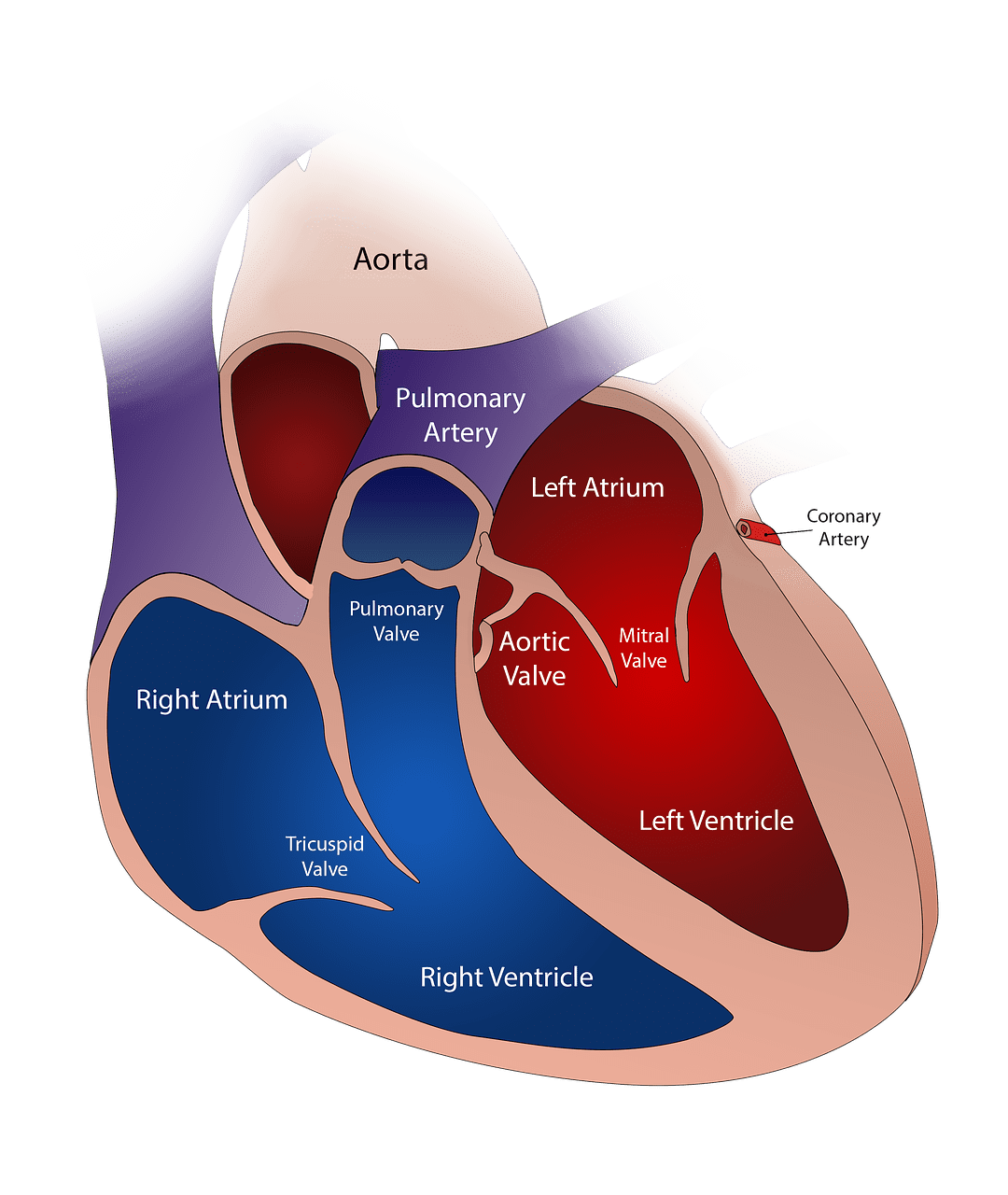
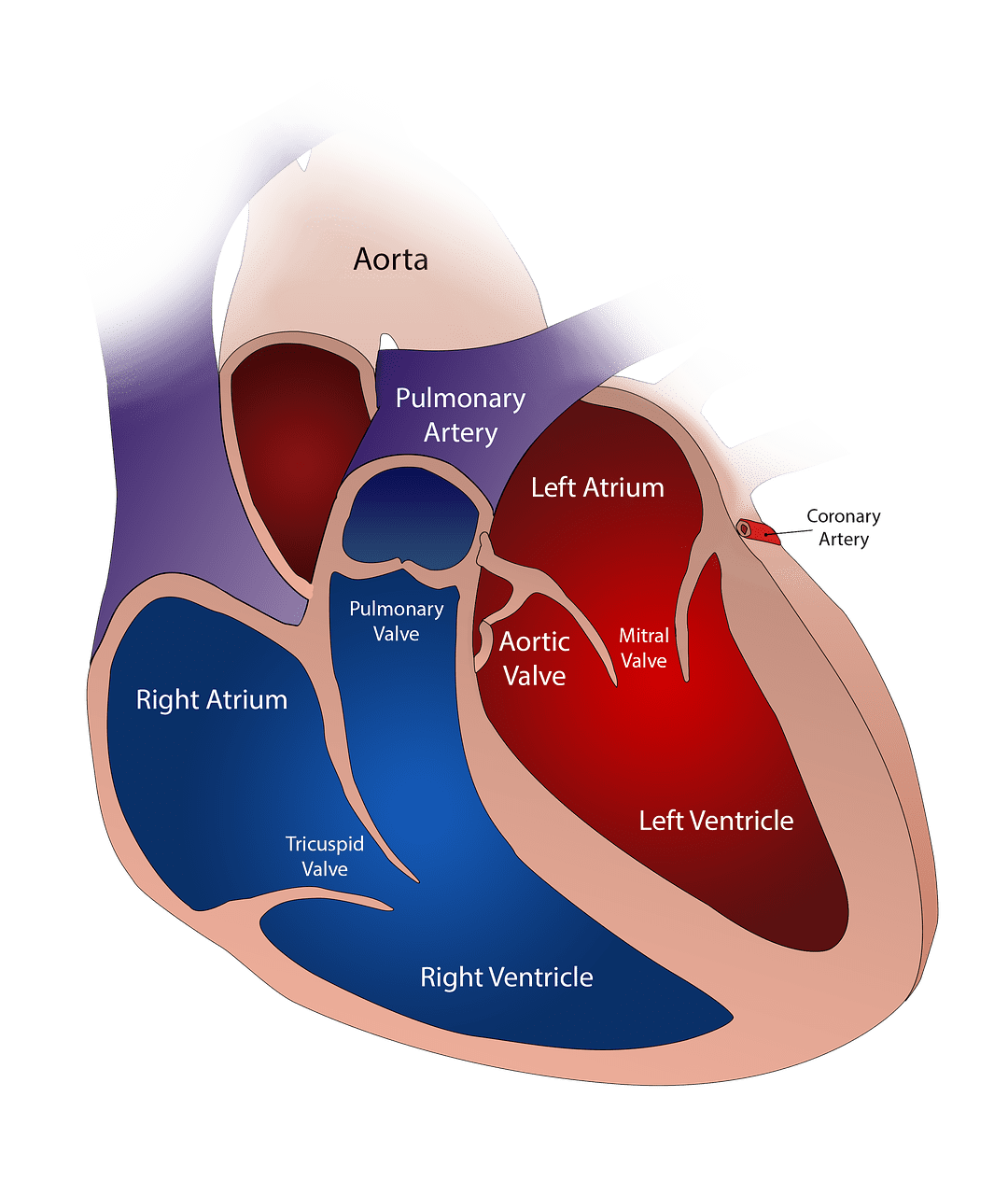
- The left ventricle pumps oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the body, while the right ventricle pumps oxygen-poor blood to the lungs.
- The left ventricle has thicker walls to generate higher pressure for blood circulation throughout the body, whereas the right ventricle has thinner walls for pumping blood to the nearby lungs.
- The left ventricle receives blood from the left atrium through the mitral valve, while the right ventricle receives blood from the right atrium through the tricuspid valve.
Left vs Right Ventricle
The right ventricle is positioned at the lower right part of the heart. It is triangular in shape that receives deoxygenated blood from the right atria. The right ventricle has thin walls that develop low blood pressure. The left ventricle is positioned at the lower left part of the heart. It has a spherical shape with thick walls that receive oxygenated blood that passes through the aorta. Due to high blood pressure, it supplies blood all over the body.
The left ventricle is at the lower left of the heart. This receives the oxygenated blood. The blood is then passed to the tissues through the aorta. The left ventricle has thick walls. The left ventricle has a circular cavity. The left ventricle is oval.
The right ventricle is at the lower right corner of the heart. This right ventricle has thin walls. This receives the deoxygenated blood from the right atrium.
The shape of the right ventricle is crescentic. This part creates a lower pressure in the blood. This pumps the blood to the tissues with the help of the pulmonary trunk.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Left Ventricle | Right Ventricle |
|---|---|---|
| Type of blood received | Oxygen-rich blood | Deoxygenated blood |
| Composition | Thick walls | Thin walls |
| Passage for blood | Aorta | Pulmonary trunk |
| Cavity | Circular | Crescentic |
| Pressure of blood | High | Low |
| Shape | Oval | Triangular |
What is Left Ventricle?
This is at the bottom of the heart. This is situated at the bottom left of the heart. The left ventricle has the collection of oxygenated blood.
The mitral valve is the part that separates all the chambers from the left ventricle. The left ventricle is made of thick walls. The blood goes into the ventricle when there is a contraction in the heart.
The ventricle is circular, or it can also be said it has an oval shape. The blood is passed to the aortic valve, and then it is passed to the rest of the body through the aorta. This is an aortic arch that pumps blood all over the body.
The aortic arch passes the oxygenated blood to the whole body. The lungs receive pure blood from this aortic arch. The left atrium helps the blood to reach the human heart.
The blood reaches other parts of the body as it has high pressure, which helps it to move.
The oxygenated blood is under the highest pressure in this region as it is responsible for supplying blood all over the body. The oxygenated blood is taken to all types of tissues inside the body so that the body tissues can function properly.
What is Right Ventricle?
This is situated at the lower right of the heart. It is responsible for passing the blood towards the oxygen so that the blood can consume oxygen from it.
It passes the blood through the pulmonary muscles and fills the lungs with blood. It has no duty to send blood to anybody’s tissues or parts.
It has a very thin wall as compared to the left ventricle. These walls have irregular muscular columns. These columns are also known as trabeculae carnage.
This is the most anterior part of the heart. The shape of the right ventricle is semilunar. This resides around the anterolateral aspect of the left ventricle.
This has thinner walls as the left has high blood pressure. The interventricular septum stands in between the right and left ventricles. The septum is concave in shape.
The three walls inside the right ventricle are septal, anterior, and inferior. The Interior part consists of muscular ridges, which are known as trabeculae carnage.
This puts the blood move to 140 degrees from inflow to outflow tract. The blood, which is deoxygenated, flows through the inferior and superior vena cava.
The chambers help the flow of blood in proper sequence. They work as a double pump so that the circulation of the blood is smooth inside the body.
Main Differences Between Left and Right Ventricle
- The left ventricle and the right ventricle receive pure blood and deoxygenated blood, respectively.
- There are thick walls in the left ventricle but thin walls in the Right ventricle.
- The aorta helps the left ventricle to pass blood, but the pulmonary trunk helps the right ventricle to pass blood.
- The cavity in the left and right ventricle is circular and crescentic, respectively.
- The left ventricle and the right ventricle develop high pressure and lower pressure in the blood, respectively.
- The shape of the left ventricle is oval, but the shape of the right ventricle is triangular.



