The human heart is formed of four distinct chambers. This is why we fall under the category of four-chambered animals along with carnivores and other mammals.
The chambers of the heart are separated by the muscle septum. The atrium and ventricle are the different chambers of the heart separated by an interatrial and intraventricular septum.
Key Takeaways
- The atrium is an upper chamber of the heart that receives blood, while the ventricle is a lower chamber that pumps blood.
- The left atrium and ventricle pump oxygenated blood, while the right atrium and ventricle pump deoxygenated blood.
- The walls of the ventricles are thicker than the walls of the atria, reflecting their different functions.
Atrium vs Ventricle
Atria are the upper chambers of the heart, while the ventricle refers to the lower chambers of the heart. The atrium is small, while Ventricle is large. Atria have thin walls, while Ventricle has thick walls. The atrium collects blood and supplies it to the ventricles, while the ventricles supply it throughout the body.
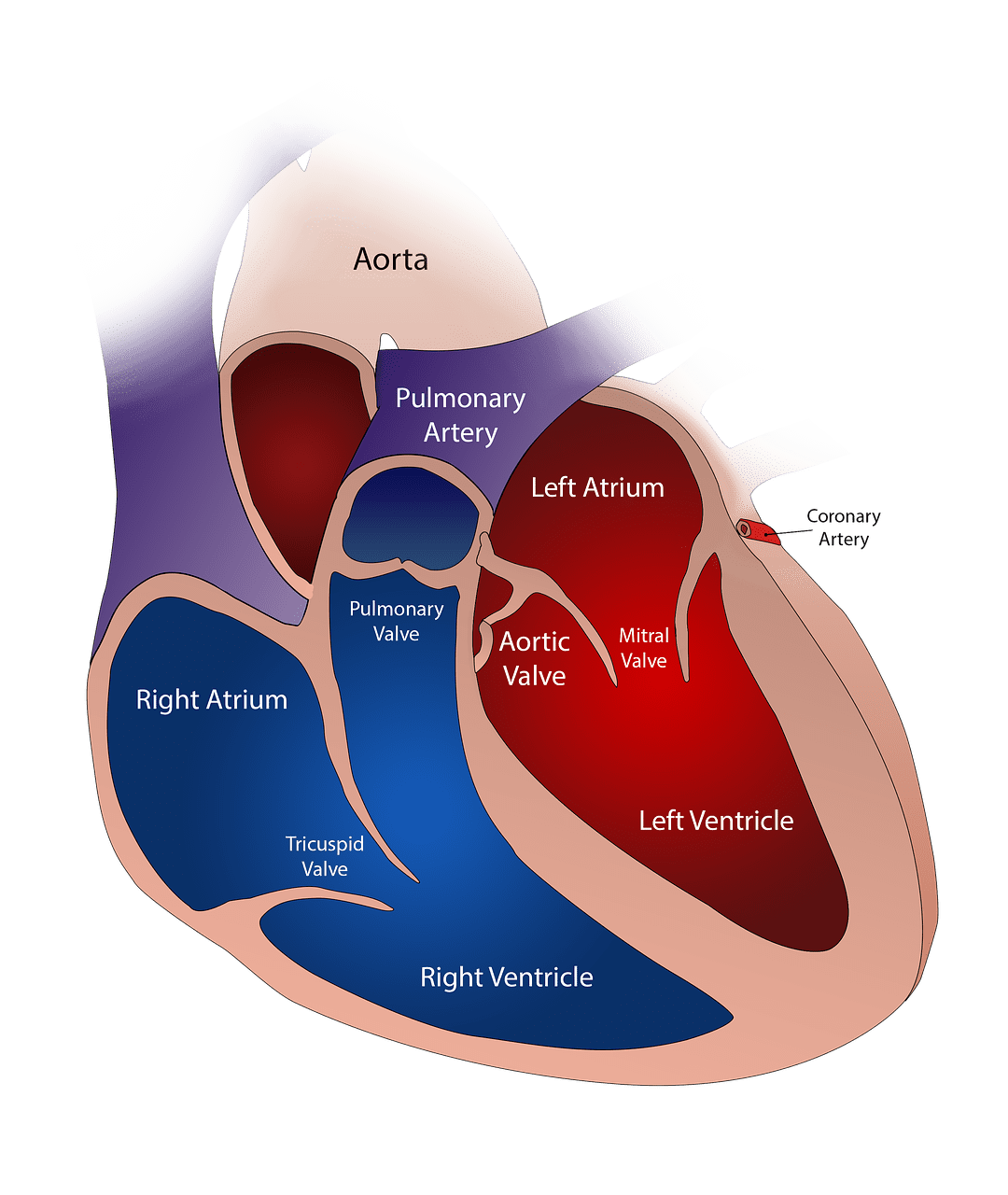
The atrium refers to the upper two divisions of the heart. There are two atria in the human heart that are separated by the interatrial septum.
The function of the atrium is to receive deoxygenated blood from the body that is passed on to the lungs for oxygenation and distribution to the body. It is smaller in size than the ventricles.
Ventricles refer to the lower two divisions of the heart. There are two ventricles in the human heart separated by the interventricular septum. The function of the ventricles is to pump blood to all parts of the body through the main artery called the dorsal aorta. It is bigger than the atria.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Atrium | Ventricle |
|---|---|---|
| Size | The atrium forms the smaller portion of the heart. | Ventricles form the larger portion of the heart. |
| Location | It is the upper half of the heart. | It is the lower half of the heart. |
| Walls | The walls of the atrium are thinner than the ventricles. | The walls of the ventricles are much thicker compared to the auricles. |
| Blood Pressure | It has lower blood pressure. | It has higher blood pressure. |
| Function | The main function of the atrium is to supply blood to the lungs. | The main function of the ventricles is to supply the rest of the body |
| Consists Of | It has the sinoatrial node and pacemaker cells. | It has the Purkinje fibres. |
What is Atrium?
Atrium is the singular word for auricles which refers to the upper half of the heart. These chambers of the human heart are separated by the interauricular or interatrial septum to form two auricles.
The right auricle or atrium receives deoxygenated blood from two veins blood vessels, the inferior vena cava and superior vena cava. These are essentially veins. The left auricle receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary vein coming from the lungs.
It receives deoxygenated blood and sends it to the lungs for oxygenation through the pulmonary circulation. Since the heart and lungs are close to each other, the walls of the auricles are thin as they do not have to pump blood to large distances.
This also makes the blood pressure in the auricles comparatively lower than in the ventricles.
It also sends blood to the ventricles to be distributed throughout the body. The right ventricles open into the right ventricles through the tricuspid valve, and the left auricle opens into the left ventricle through the mitral valve.
There are some specialized cells in the auricular region called the sinoatrial node and the pacemaker cells.
The sinoatrial node generates impulses that set a normal rhythm and rate of the heart. That is why it is also called the natural pacemaker of the heart.
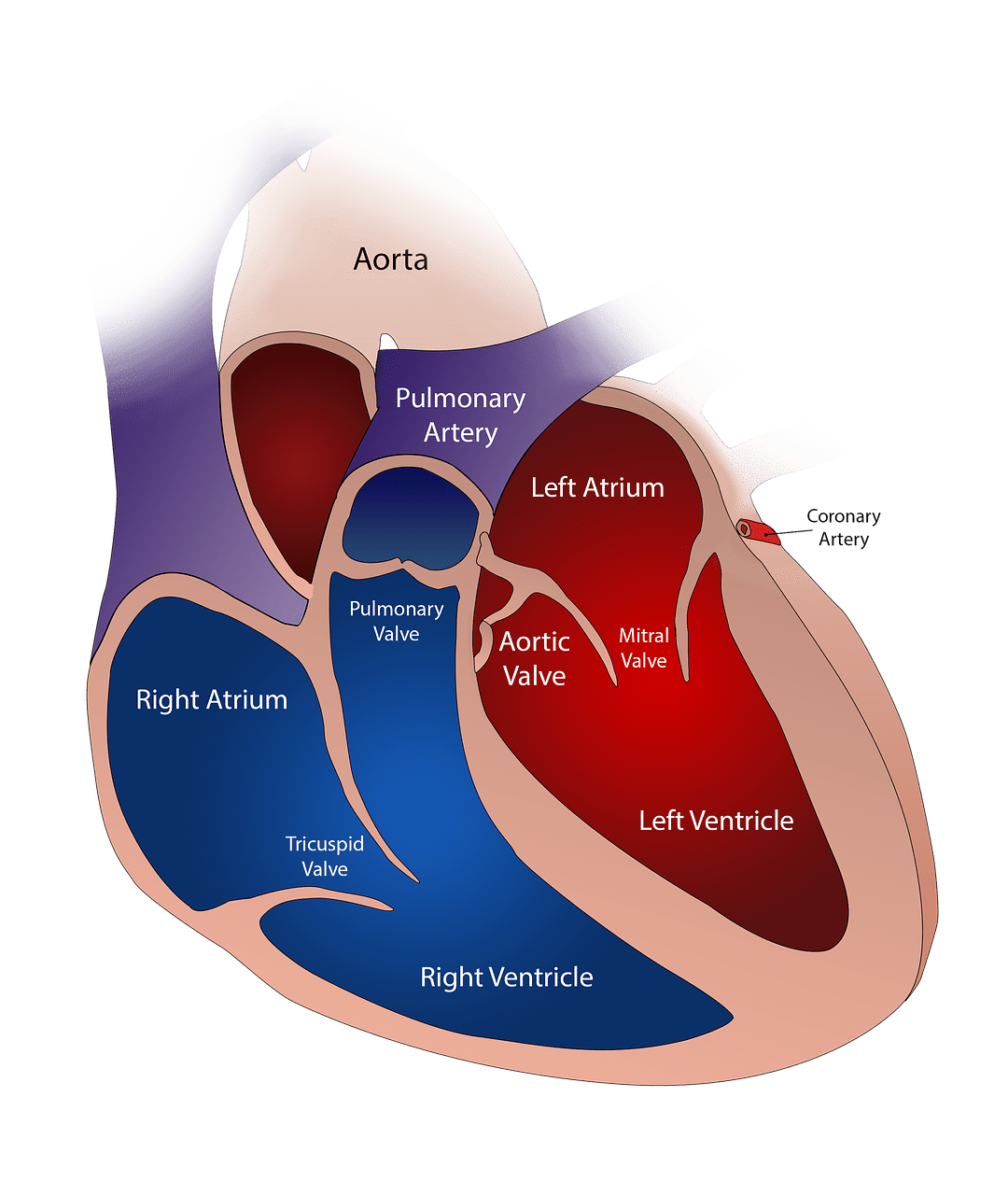
What is Ventricle?
The ventricle is the singular for the ventricles that refers to the lower half of the heart. The lower divisions of the heart are separated by the interventricular septum.
The left ventricle receives fresh blood from the auricles, and it pumps it to the rest of the body from the right ventricle through the aorta.
Oxygenated blood from the heart is transported to all parts of the body from the heart through various arteries and systems.
Since the distance of blood flow is large from the heart to the lower portion of the body or the kings the blood pressure in this chamber is high, and its walls are highly muscular and thick.
Because the ventricle uses a large amount of pressure to pump blood hence, we can feel our heartbeat slightly towards the left, where the pumping is the hardest.
The right ventricle opens into the pulmonary artery through the semilunar valve, and the left ventricle opens into the aorta through the aortic valve.
Due to more function and power required, it is also bigger. It has special fibres called Purkinje fibres that conduct electrical impulses throughout the ventricles.
Main Differences Between Atrium and Ventricle
- The atrium is smaller and narrower than the larger, broader ventricles.
- The atrium supplies the heart and the lungs, whereas the ventricles supply the whole body.
- The atrium contains deoxygenated blood, whereas the ventricles always contain oxygenated blood.
- The walls of the atrium are thinner, whereas the walls of the ventricles are thicker.
- The atrium is drained by the ventricles, and the ventricles are drained by the aorta.
- The atrium is supplied by the vena cava, whereas the ventricles are supplied by the pulmonary vein.
- The atrium is responsible for the rhythm of the heart, whereas the ventricles are responsible for helping the heart keep up the rhythm.
- https://academic.oup.com/ejcts/article-abstract/27/2/191/475859
- https://rupress.org/jcb/article/36/3/497/17138

This article offers a comprehensive overview of the atrium and ventricle, delineating their anatomical differences and physiological functions. The informative content enhances our knowledge of cardiac anatomy and physiology.
I was particularly intrigued by the comparison table, which succinctly outlines the distinctions between the atrium and ventricle. It aids in clarifying the intricate details of cardiac chamber dynamics.
The explanation of the atrium’s function in receiving deoxygenated blood and the ventricle’s role in pumping oxygenated blood to the body is both informative and engaging. It offers a holistic view of the heart’s circulatory processes.
The detailed description of the ventricle’s anatomy and its muscular walls, which contribute to the pumping of blood throughout the body, is particularly fascinating.
The expansion on the specialized cells within the atrium and ventricle, as well as their contributions to cardiac rhythm regulation, provides a deeper understanding of the heart’s functionality.
The comprehensive nature of the article’s content, which delves into the anatomical and functional aspects of the atrium and ventricle, enriches our understanding of the human heart’s chambers. The informative details serve to enhance awareness of cardiac physiology.
The detailed description of the atrium and ventricle’s functions and anatomical features provides a comprehensive understanding of the heart’s circulatory dynamics. It’s a valuable source of knowledge on cardiac physiology.
The elucidation of the atrium and ventricle’s functions in oxygenating and pumping blood throughout the body is both informative and enlightening. The article serves as an excellent reference for studying cardiac anatomy and physiology.
The elucidation of the atrium and ventricle’s roles in oxygenating and distributing blood throughout the body is enlightening. It provides a deeper understanding of how the heart functions in maintaining circulation.
The explanation of the specialized cells within the atrium and ventricle underscores the intricate nature of cardiac regulation. It’s a testament to the heart’s remarkable physiology.
The detailed explanation of the atrium and ventricle’s functions in the human heart provides valuable insights into cardiac physiology. Understanding the structures and roles of these chambers is essential in comprehending the circulation process.
Indeed, the atrium and ventricle play crucial roles in the circulatory system, and the explanation provided here enhances our knowledge of their significance.
The specialized cells in the atrial and ventricular regions, such as the sinoatrial node and pacemaker cells, are particularly noteworthy. They contribute to the regulation of the heart’s rhythm and are vital components of its functioning.
The distinction between the atrium and ventricle, as well as their respective functions, is elucidated with clarity in this article. It emphasizes the anatomical and physiological differences between these two chambers in the human heart.
The comparative analysis of the atrium and ventricle, along with the functions and pressure differentials, provides a comprehensive perspective on the heart’s circulatory dynamics.
I was particularly intrigued by the detailed description of the atrium’s role in receiving deoxygenated blood and subsequently supplying it to the lungs for oxygenation. The physiological intricacies are impressive.
The human heart is a fascinating organ with its four distinct chambers. Each chamber has its own unique function in providing oxygenated and deoxygenated blood to the body. The differences in pressure and wall thickness between the atria and ventricles are particularly interesting.
The comparison table provided offers a clear and concise understanding of the differences between the atrium and ventricle. It’s crucial to comprehend these distinctions.
I completely agree. The complexities of the heart’s chambers and their roles in blood circulation are truly remarkable.
The detailed comparison and contrasting of the atrium and ventricle’s characteristics and functions offer a comprehensive insight into the complexities of the human heart’s chambers.
Indeed, the intricate details regarding the size, location, and blood pressure differences between the atrium and ventricle underscore the complexity of cardiac anatomy and physiology.
The detailed explanation of the atrium’s role in receiving deoxygenated blood and the ventricle’s function in pumping blood throughout the body provides valuable insights into the heart’s circulatory processes. It’s a commendable resource for understanding cardiac physiology.
I agree. The physiological intricacies of the atrium and ventricle, as well as the pressure differentials and structural variances, are elucidated with clarity.
The complexities of the atrium and ventricle, as well as their distinct characteristics, are expounded upon with precision. This article serves as a valuable resource in understanding the intricate workings of the human heart.
I concur. The article’s detailed explanation of the atrium and ventricle’s anatomical features and their physiological functions is commendable.