The human body can be surprising sometimes, and you can find thousands and thousands of facts about the human body. Every second, a reaction or something else happens inside our body.
And yes, these reactions and processes are necessary for the human body in many ways.
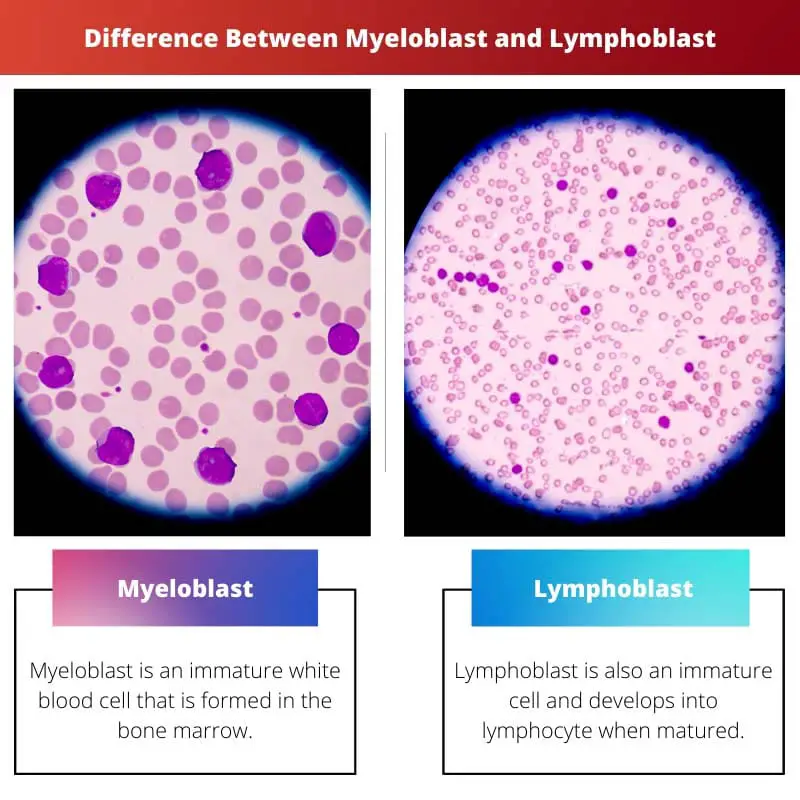
Most of you have heard the term myeloblast in your biology class. Myeloblasts are an immature type of WBC (White Blood Cell).
Myeloblast cells are formed in the bone marrow, and when these immature cells mature, they become matured white blood cells known as granulocytes.
In other words, the lymphoblast is an immature cell that further matures into a lymphocyte.
Now, if you are hearing these terms for the first time, you might think that they have almost the same meaning but are quite different.
Key Takeaways
- Myeloblasts and Lymphoblasts are immature cells found in the bone marrow, with different roles in the immune system.
- Myeloblasts differentiate into granulocytes, erythrocytes, and platelets, while Lymphoblasts differentiate into B cells, T cells, and natural killer cells.
- In terms of morphology, myeloblasts have a larger nucleus and basophilic cytoplasm, while lymphoblasts have a smaller nucleus and scant cytoplasm.
Myeloblast vs. Lymphoblast
Myeloblasts differentiate into granulocytes, Myeloblasts have granules in their cytoplasm. Lymphoblasts differentiate into lymphocytes, lymphoblasts lack these granules and have more evenly distributed chromatin in their nuclei.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Myeloblast | Lymphoblast |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Myeloblast is an immature white blood cell formed in the bone marrow. | Lymphoblast is also an immature cell and develops into a lymphocyte when matured. |
| Nucleus Shape | Curved in shape. Can be in S, C, or V shape. | Round in shape. |
| Nucleus Size | The nucleus is smaller in size as compared to the lymphoblast. | On the other hand, Lymphoblast is larger and has thick chromatin pigments. |
| Chromatin | Myeloblast contains less condensed chromatin. | Lymphoblast, on the other hand, has more condensed chromatin. |
| Diameter | 20 um | 15 um. |
| Differentiated into | Myeloblast is differentiated into basophils, eosinophils, and neutrophils. | Lymphoblast, on the other hand, can be differentiated into T and B lymphocytes. |
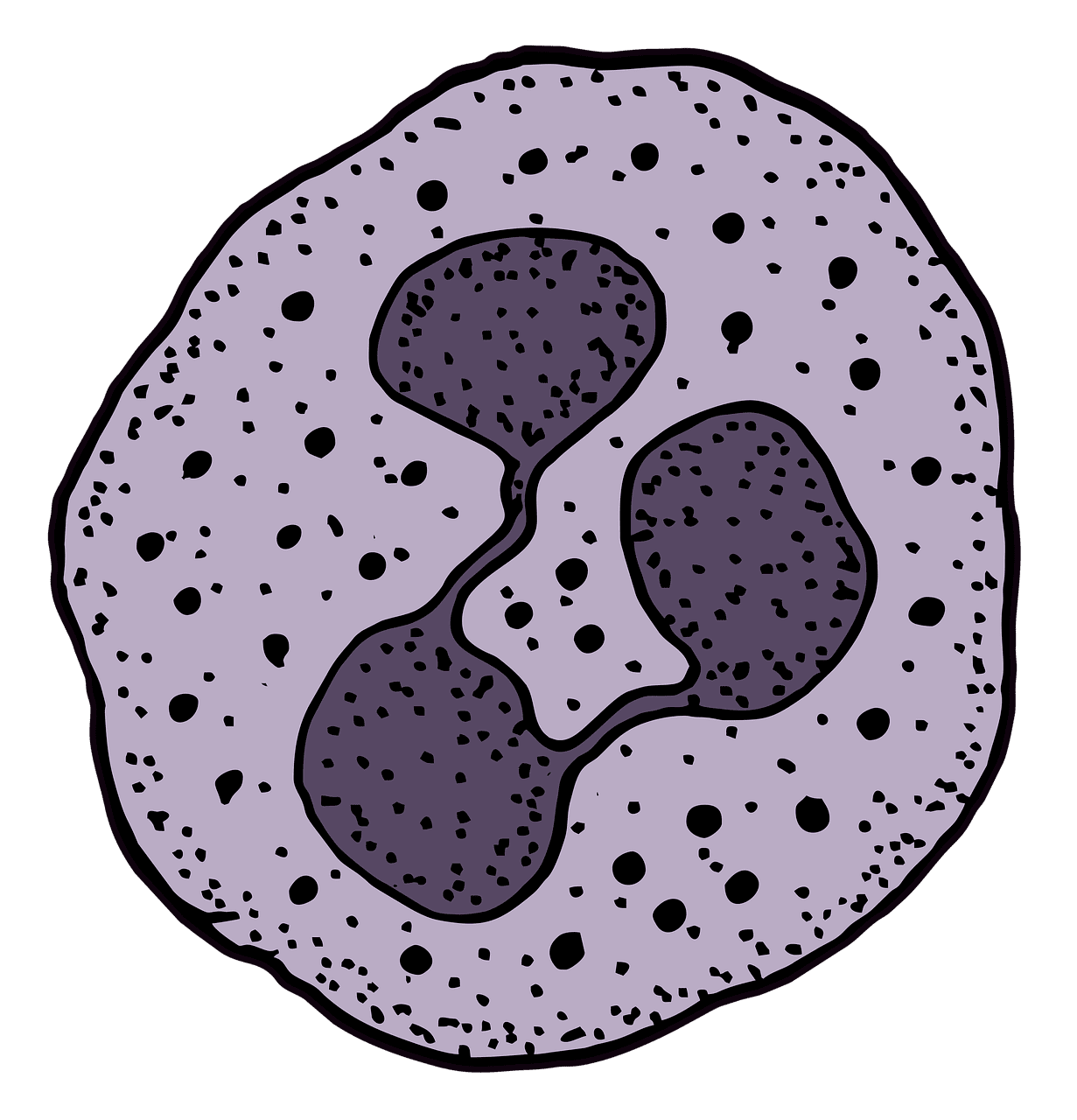
What is Myeloblast?
Myeloblast is nothing, but they are called immature white blood cells formed in the bone marrow, and further, when they mature, they form granulocytes. You might be wondering why these cells are necessary for the human body.
Well, the myeloblast, though found in the bone marrow, triggers maturation, differentiation, proliferation, and for survival of the cell. Myeloblast differs from the lymphoblast in many ways and functions differently in the human body.
These cells are also called band cells, where the nucleus of these cells has shapes as they can be in S, C, or V shape, unlike the shape of a Lymphoblast’s nucleus, which is round.
Since these cells are immature and take time to mature, they take time to process.
Myeloblasts undergo a process, and ultimately they form into the band cells mentioned above (basophils, eosinophils, and neutrophils).
Now, when malfunctioning occurs, then it leads to myeloblast leukemia. This is the condition where all the immature myelocytes get collected into the peripheral blood.
Yes, this is where we should know the difference between myeloblast and lymphoblast because everything is based on the diagnostic point of view.
Unfortunately, leukemia has no cure, but having a healthy diet and avoiding tobacco consumption might help.
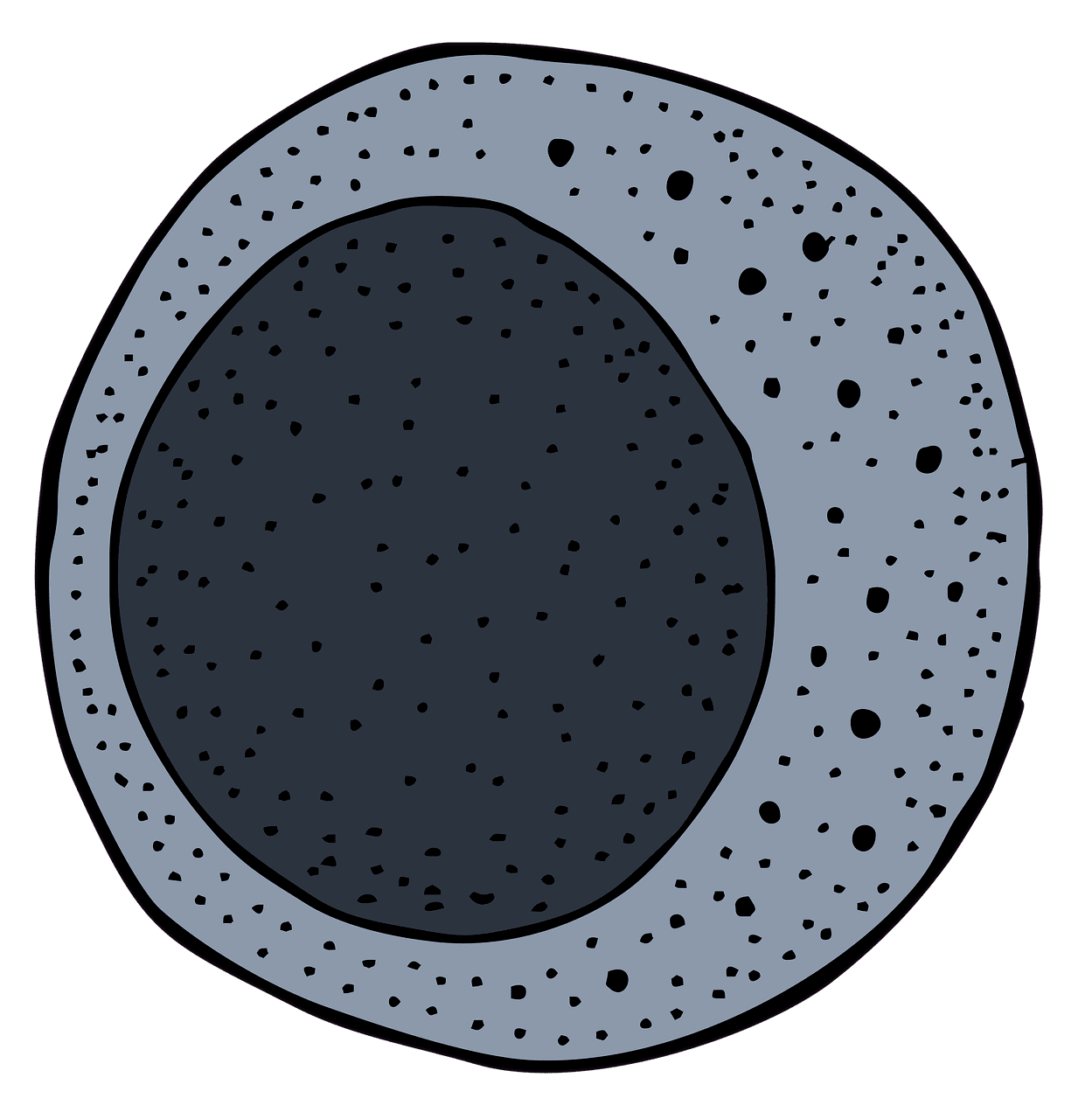
What is Lymphoblast?
Lymphoblast or lymphocyte becomes larger when they get stimulated with an antigen. These cells are also immature and, when matured, get develop into mature lymphocytes. These cells to are found or formed in the bone marrow.
Now, these cells have important functions in the human body to perform. These cells play a significant role in developing blood cells in the human body.
Blood cells are important, and yes, blood cells must be healthy, too, because the blood cells carry all the oxygen and nutrients to the other cells of the body.
Other than that, blood cells also help fight against any infection and regulate bleeding. Now, you can imagine how lymphoblasts play a significant part in the survival of human beings.
Myeloblast and lymphoblast are found in the bone marrow, but the cells do not look alike.
The nucleus of the lymphoblast cells is round, and they are larger and have thick chromatin pigments in them. Altogether the size of a lymphoblast is much bigger than myeloblast.
Main Differences Between Myeloblast and Lymphoblast
- Myeloblast and lymphoblast cells are found in the bone marrow, and both perform an important function.
- Lymphoblast is responsible for the development of red blood cells inside our body.
- The nucleus inside the myeloblast cell is S, V, or C shaped, whereas the nucleus of the lymphoblast is round-shaped.
- Myeloblast cells have less condensed chromatin, whereas lymphoblast is said to have more condensed chromatin.
- A myeloblast cell’s diameter is estimated to be 20 micrometers, whereas a lymphoblast’s diameter is 15 micrometers.
- Myeloblast can be differentiated into basophils, eosinophils, and neutrophils, whereas lymphoblast can be differentiated into T and B lymphocytes.