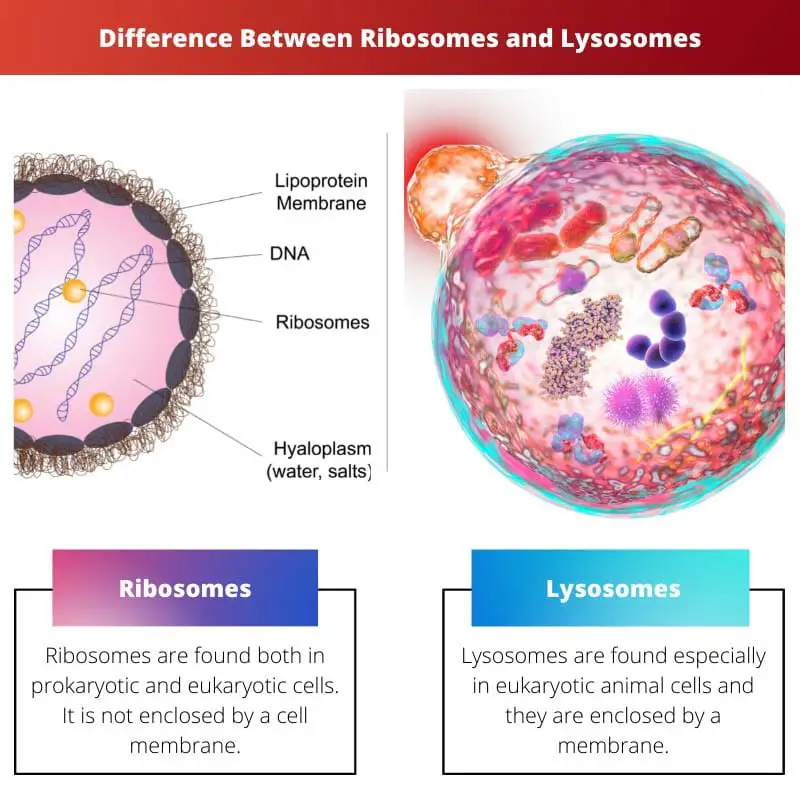
A cell primarily consists of cell organelles that serve various functions in a cell. Both organelles possess distinct functions. Ribosomes are found within the cellular structure and are responsible for protein synthesis.
Lysosomes are bounded by the membrane, and they eliminate the pathogens entering the cell.
Key Takeaways
- Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis, while lysosomes break down waste materials and cellular debris.
- Ribosomes are found in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, while lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles.
- Ribosomes consist of RNA and proteins, while lysosomes contain enzymes.
Ribosomes vs Lysosomes
The difference between ribosomes and lysosomes is that they vary in function specificity. Lysosomes are found only in animal cells, whereas ribosomes can be found both in plant and animal cells. Ribosomes that are present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are responsible for translation in cells. Lysosomes are organelles performing autolysis and are responsible for breaking down several foreign factors.

Ribosomes can be found suspended in the cytoplasm of the cell, and it is composed of two different sub-units i.e., a small and a larger sub-unit. These two subunits are found locked together.
These ribosomes are also termed ‘protein synthesizers’ in a cell. They help in synthesizing an amino acid chain for protein synthesis.
Lysosomes that are found in animal cells are evenly and freely distributed in the cytoplasm of a cell. They resemble a bag-like structure carrying hydrolytic enzymes. Lysosomes are comparatively larger and possess about sixty enzymes responsible for digestion.
These enzymes are produced by the rough endoplasmic reticulum and transferred to the Golgi complex present in the cell. These lysosomes are quite gigantic and possess a size of up to 1.2 µm.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Ribosomes | Lysosomes |
|---|---|---|
| Organelle location | Ribosomes are found both in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. It is not enclosed by a cell membrane. | Lysosomes are found especially in eukaryotic animal cells and they are enclosed by a membrane. |
| Organelle composition | They contain two sub-units namely the large and small sub-unit. Where both consists of ribosomal RNA and proteins. | They are composed of lipids and proteins with a single membrane coat. |
| Function | Protein synthesis through a process called translation. | They degrade by engulfing the foreign pathogens found in cytoplasm and they are useful in intracellular digestion. |
| Cellular size | They are comparatively smaller and the size differs from 20-30nm. | They are larger and they vary from 0.1-1.2 µm in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| Segmentation of the organelle | Expansion segments are found as enigmatic insertions in ribosomes of eukaryotes. | Lysosomes do not possess segmentation like ribosomes. |
What are Ribosomes?
Ribosomes are present as the larger population in all cells, and they are responsible for protein synthesis. It was first founded and explained by George E. Palade in the year 1955.
He found that ribosomes were closely related to endoplasmic reticulum structures present in the cell. There are abundant ribosomes scattered in the cytoplasm. They almost take one-fourth of the total cell composition.
The E. coli ribosome measures about 20nm. They possess both ribosomal proteins and ribosomal RNA. The sub-units of ribosomes, namely the smaller and larger sub-units, are scaled by the Svedberg unit or S.
Ribosomes are the locality in a cell where genetic code is coded to protein molecules. Ribosomal molecules of mRNA code for the transfer of RNA.
They are made up of up to 80 different ribosomal proteins. The sub-units are named the 40S and 60S in eukaryotes. In contrast, prokaryotes possess the 30S and 50S subunits. The ribosome reads the messenger RNA and translates it into a sequence of amino acids.
The sub-unit structure acts as a suitable position of docking for tRNA that will again be a part of a polypeptide chain which turns into a protein. The codon in the mRNA that possesses tRNA requires an anti-codon.
The mitochondrial ribosomes of eukaryotes have functional likeliness with the features of bacteria.
What are Lysosomes?
Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes and are involved with different cellular mechanisms. Lysosomes facilitate the self-destruction of damaged cells. Lysosomes are very acidic since it has to digest foreign particles and cells that are beyond the capacity of repair.
They are also called suicidal bags. They are spherical and contain a pH of about approximately 4.5 to 5.
Besides degradation, the lysosomes play a vital role in secretion and energy metabolism. Lysosomes even recycle the intracellular components. The lysosome also carries out the endocytosis process, where hydrolytic enzymes finally digest the food particles.
Lysosomes engulf several bio-molecules, including carbs, nucleic acids, and fatty substances.
The enzymes that are responsible for hydrolysis require an acidic environment. The lysosomal membrane boundaries the cytosol in the cell. Lysosomes are involved in a clinical condition called lysosomal storage disease.
It was later discovered that in 2009, lysosomal enzymes and membrane proteins were manipulated by TFEB. This TFEB refers to the transcription factor EB.
In the hydrolytic enzymes present within the lysosomes, cathepsins are the major class enzyme. The enzymes are clumped together as a vesicle to establish a lysosome.
Lysosomal activity triggers a significant elevation in viral pathogenicity. Lysosomes can also be fused with the plasma membrane.
Main Differences Between Ribosomes and Lysosomes
- Lysosomes are only present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotes, whereas ribosomes can be found in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
- Lysosomes are suicidal bags and engulf foreign substances, whereas ribosomes are a combination of two sub-units.
- Ribosomes do not contain enzymes, whereas lysosomes contain hydrolase enzymes to degrade cell debris.
- The lysosomes are up to 0.1µm, whereas the ribosomes in the cytoplasm are 20-30nm. The ribosomes are smaller when compared to the larger lysosomes.
- Ribosomes are the organelles that are responsible for protein synthesis, whereas lysosomes are responsible for the hydrolysis of foreign bio-molecules in the cell.