TENS and EMS therapies are similar on a fundamental basis. Both EMS and TENS use moderate electrical impulses as a stimulant, which are delivered to the skin via electrode pads.
These two forms of electrotherapy are distinguished by their principal regions of focus, as indicated by their names. Though both are excellent pain management treatments, the use of EMS vs TENS varies.
Key Takeaways
- TENS focuses on pain relief by blocking pain signals, while EMS targets muscle strengthening and rehabilitation.
- TENS uses a higher frequency range and shorter pulse width than EMS.
- TENS and EMS devices are non-invasive and can be used for various conditions, but TENS is more widely accepted for pain management.
TENS vs EMS
TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) method uses electrical impulses to relieve pain through the transmission of low-voltage electrical currents. EMS is a type of electrotherapy in which electrical currents through electrodes on the skin to stimulate and contract muscles for strength training.
TENS (Transcutaneous Electric Nerve Stimulation) is a pain-relieving treatment that uses electrical impulses to relieve pain rather than medicines or narcotics (non-narcotic painkillers).
The electrical pulses activate nerve terminals and the skin. A TENS unit’s purpose is to stimulate sensory nerve endings.
The reasoning for this stimulation is that it prevents pain signals from reaching the brain.
Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) is a sort of electrotherapy that uses electrical impulses to stimulate muscular contractions in order to strengthen weak muscles, reduce swelling, relieve pain, and aid wound healing.
Instead of affecting pain impulses, EMS machines stimulate muscles to contract. As a result, they are more helpful for muscle development and recuperation.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | TENS | EMS |
|---|---|---|
| Full-Form | Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation | Electrical Muscle Stimulation |
| Target | Stimulates nerves | Stimulates muscle cells |
| Pain Relief | Provides pain relief | It doesn’t provide pain relief. |
| Muscles | It doesn’t affect muscles. | It helps in muscle recovery and strengthening. |
| Functional Range | A wider range is available for frequencies, pulses, and intensities. | A narrower range of functions. |
| Mechanics | It stimulates nerve endings to minimize pain. | It uses electricity to stimulate muscles by causing them to contract to help with muscle building. |
| Penetrative Values | It is low. | It is deep. |
| Results | Temporary | Permanent |
What is TENS?
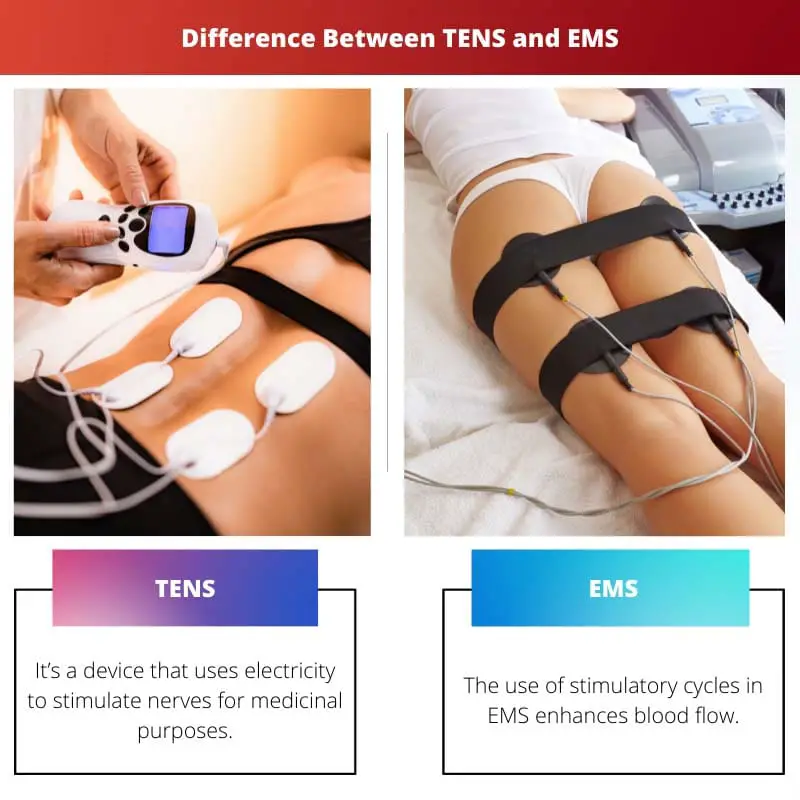
It’s a device that uses electricity to stimulate nerves for medicinal purposes. However, frequent and regular microcurrent sessions are required for the optimum effects of TENS machines and for long-term pain reduction.
At the same time, some people report that their pain relief is the most effective and lasts the longest and that the duration between sessions is getting longer.
It produces a tingling sensation rather than a tiny electric current’s painful and distressing sensation.
TENS machines are used to treat chronic pain in the nerves, muscles, and joints, such as inflammatory arthritis, back pain, foot pain, contractions during labour, and postoperative pain, along with migraines.
TENS machines function in three ways:
- They prevent pain impulses from reaching the brain.
- They encourage the release of endorphins (which are natural painkillers).
- They help to increase blood circulation.
Electronic stimulation relieves pain in a natural way, despite the fact that opinions regarding how it works disagree. These devices can also help your body release endorphins, which are natural feel-good chemicals that are important for pain relief and mood enhancement in those with chronic illnesses.
The TENS device provides unrivalled pain relief for some chronic pain sufferers. The effects of the TENS device can persist up to 24 hours after use, but they last between five minutes and 18 hours, depending on the patient.
What is EMS?
The use of stimulatory cycles in EMS enhances blood flow. It contracts and then relaxes muscles to enhance blood flow, reducing inflammation and speeding up healing and muscle growth.
An EMS unit causes muscle spasms similar to those experienced during physical exercise by stimulating the muscles.
The EMS units are used to prevent muscle atrophy or retrain muscles in persons who are paralyzed. EMS is also useful for improving the range of motion, increasing circulatory blood flow, and preventing blood clots.
The signals sent by EMS equipment treat the muscles as if they were doing a passive exercise. They function by activating the muscle first, then constricting it, which is similar to how exercise works.
This cycle has a number of advantages, including improving blood flow to the treatment area, which can help reduce inflammation and increase muscle growth. Electrical muscle stimulation can help with recovery by reducing lactic acid generation in the muscle.
Using EMS while resting perfectly fits how training works because muscle growth happens during rest. The muscle Contracts and repeatedly relaxes, which aids in blood circulation and, as a result, helps to:
- Reduce inflammation.
- Muscle atrophy.
- Increase the rate of muscle recovery.
- Encourage muscle development.
- Athlete recuperation, which includes rehabilitation.
Main Differences Between TENS and EMS
- TENS stands for Transcutaneous Electric Nerve Stimulation, and EMS stands for Electrical muscle stimulation.
- TENS stimulates nerve endings, whereas EMS stimulates muscle cells.
- The main purpose of TENS is to provide pain relief, and that of EMS is to help in muscle recovery and strengthening.
- TENS has a wider functional range with more options for frequencies, pulses, and intensities, whereas EMS has a narrower range available.
- TENS stimulates nerve endings to minimize pain. On the other hand, EMS stimulates muscle cells, causing them to contract with the help of electricity to help with muscle building and recovery.
- The penetrative value of TENS is low, and of EMS is deeper.
- The results of TENS are temporary, and the results of EMS are more permanent.