Electrocardiography (EKG or ECG) and Echocardiography are painless, non-invasive examinations that are used to assess the heart’s function.
The physician normally orders these tests, which are then conducted by a technician or the physician himself, and the results are interpreted.
Both tests require no prior preparation and pose no dangers to the patient. The ECG and echocardiography are tests used to assess your heart’s general health.
Key Takeaways
- Electrocardiograms (ECGs) measure electrical activity in the heart, while echocardiograms use ultrasound to visualize heart structures.
- ECGs help diagnose arrhythmias and other electrical problems, while echocardiograms assess heart function, blood flow, and valve issues.
- Both tests are non-invasive and crucial for evaluating heart health but serve different diagnostic purposes.
Electrocardiogram vs Echocardiogram
Electrocardiograms are non-invasive tests that are used in the diagnosis of heart disease and arrhythmias. Echocardiograms are a type of ultrasound test that allows doctors to visualize the heart’s structure and function, including the heart’s size, shape, and pumping strength.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a waveform representation of your heart’s electrical rhythm. A healthy heart’s ECG report will have a consistent shape and will resemble the image above.
Inconsistent, irregular, or non-standard waves can indicate heart problems. An ECG is used to help your doctor understand your heart’s health and look for any anomalies.
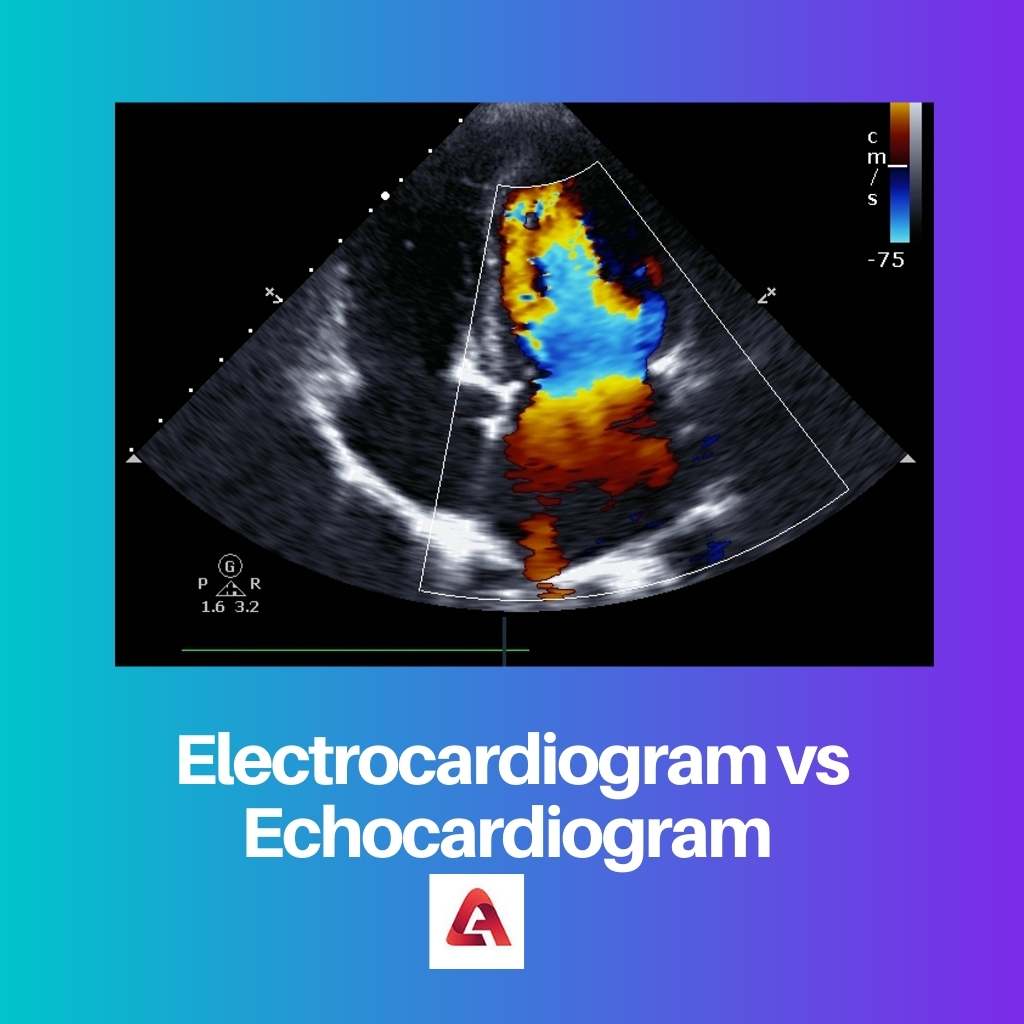
An echocardiogram is a type of live imaging test that doctors use to examine the function of your heart.
The test uses sound waves that bounce off your heart to create an image of your heart and valves, giving you a live glimpse of your heart. For this reason, it’s also known as an Echo test.
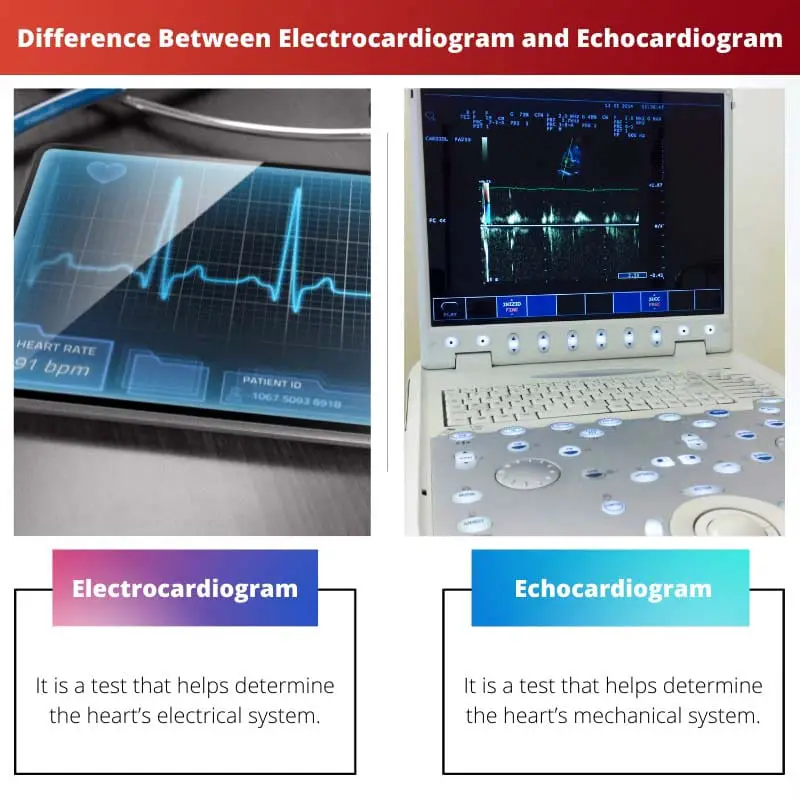
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Electrocardiogram | Echocardiogram |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It is a test that helps determine the heart’s electrical system. | It is a test that helps determine the heart’s mechanical system. |
| Test Procedure | Electrodes are attached to the patient’s chest and other places and the results are shown on a machine that is attached. | After the application of a gel, a transducer is waved which releases sound waves that echo back and show a picture of the heart. |
| Result | Results in a wave-like diagram | Results in a picture of the heart. |
| Duration | Average of 5 minutes | Average of 20 minutes |
| Commonality | Most common | Less common |
| Short Forms | EKG or ECG | Echo |
What is Electrocardiogram?
An EKG is a diagnostic test that a healthcare expert conducts to measure a person’s heart’s electrical activity.
As a person’s heart beats, electrical impulses pass through it. The heart contracts as a result of these electrical impulses, moving blood across the body.
A healthcare expert uses an EKG to measure electrical impulses and determine if a person’s heart is functioning properly.
EKGs are used to detect problems with a person’s cardiac rhythm. Healthcare workers can also use EKGs to screen heart attacks that have already occurred or silent heart attacks.
An EKG can be obtained in a variety of settings, including a healthcare professional’s office or a hospital. Before having an EKG, a person does not need to do anything to prepare.
EKGs are quick and easy to do. An EKG takes a healthcare professional about 5 minutes to complete.
Around ten adhesive pads will be attached to various spots around your chest by your doctor, which will lead to the machine.
The gadget will then start tracking your heart’s electrical activity and producing an electrocardiogram of your heart rhythm.
The printed lines depict the heartbeat, regularity of rhythm, cardiac tissue issues, and the thickness of the heart muscle wall.
An EKG may be required to look for irregular heartbeats, chemical or electrolyte imbalances, cardiac muscle or tissue damage, and changes in the thickness of the heart’s walls.

What is Echocardiogram?
An echocardiogram is heart ultrasound imaging. It can aid doctors in the diagnosis of a variety of heart conditions.
An echocardiogram produces a live image of your heart in the same way that an ultrasound machine does.
Physicians can use echocardiograms to watch live feeds of a beating heart and obtain vital functional information about your heart’s health.
It’s a more advanced, non-invasive diagnostic medical test for detecting heart structure and function problems.
Echocardiography is a 20-minute treatment that examines the heart (5 minutes of preparation time and 15 minutes for the procedure).
The doctor will apply an ultrasound conductive gel to your body before running the ultrasound probe over your chest to collect the appropriate photographs.
Echocardiography may be performed for a variety of reasons. When compared to other imaging modalities, echocardiography is a very affordable procedure.
Another non-invasive test is the echocardiogram, which, when combined with its inexpensive cost, makes it a favourite choice among doctors for ruling out heart disease and other heart-related issues.
An echo may be required to check for any blood clots in the heart, tumours, heart valve problems, infections, and damage from past heart attacks, among other things.
Echocardiography is a type of heart ultrasonography. High-frequency sound waves are transmitted into the body and ‘echo’ back, allowing us to observe the heart and all its structures in real time.

Main Differences Between Electrocardiogram and Echocardiogram
- An electrocardiogram is a test that helps determine the heart’s electrical system, whereas an echocardiogram helps determine the mechanical system of the heart.
- In an electrocardiogram, electrodes are attached to the patient’s chest and other places and the results are shown on a machine that is attached. In an echocardiogram, ultrasound waves are used to show pictures of the heart.
- The results of an electrocardiogram are in the form of a wave-like diagram. On the other hand, the results of an echocardiogram are in the form of pictures of the heart.
- An electrocardiogram takes an average of 5 minutes. An echocardiogram takes an average of 20 minutes.
- An electrocardiogram is the most common test for heart rhythms, whereas an echocardiogram is less common.
- The short form of the electrocardiogram is EKG or ECG, and the short form of an echocardiogram is an echo.
- https://beva.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.2042-3306.1984.tb01939.x
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0002914911014172

Absolutely, the article’s explanation of the main differences between electrocardiogram and echocardiogram is excellent.
These tests are crucial for evaluating heart health, I already had an EKG but after reading this article I’m considering doing an echocardiogram too.
The importance of EKGs and echocardiograms for the diagnostic purposes is well emphasized, and it’s clear that both tests are non-invasive and crucial for evaluating heart health.
EKGs and echocardiograms are essential for assessing overall heart health, and this article serves as an informative guide for understanding the utility and differences between these tests.
The benefits of EKGs and echocardiograms are well explained and this article provides valuable information for understanding how they work and what they are used for.
The comparison table is very enlightening, it underscores the main differences between an electrocardiogram and an echocardiogram in a clear way.
The clear description of what an EKG and an echocardiogram are and the procedures involved, facilitates a better understanding of these non-invasive tests.
I completely agree, this article provides a valuable explanation of the differences between EKG and echocardiogram, and the importance of each test.
I agree, these tests are essential and understanding the differences between them is important in order to grasp their diagnostic purposes.