Heart disease is the most common cause of death, according to statistics. It’s just so dangerous that we’ll need a special variety of systems to help us manage our pulse rate and avoid physically passing out.
This time, that’s not simply drugs and tablets because pharmacological treatments for cardiac abnormalities aren’t adequate. Patients with heart issues require stronger blessings of technology.
Key Takeaways
- Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) treat life-threatening heart arrhythmias, while pacemakers maintain a regular heartbeat for patients with slow or irregular heart rhythms.
- ICDs deliver electrical shocks to correct abnormal heart rhythms, whereas pacemakers send electrical pulses to regulate the heartbeat.
- Pacemakers are primarily preventive devices, while ICDs are life-saving devices for high-risk patients.
ICD vs Pacemaker
ICD stands for implanted cardioverter defibrillator and is a tiny electronic device linked to the heart for heart rate regulation. A pacemaker is a small gadget that is implanted in the upper chest area and beneath the skin. It detects irregular or abnormally fast heartbeats and notifies an external device.

An ICD, aka implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, is a device that requires electromagnetic stimulation to promote cardiac spasm by transmitting impulses to the atrium and ventricles.
A pacemaker, on the other hand, tries to help patients with abrupt occurrences of tachycardia and heal the abrupt pulses so that an individual with a significant drop in heart rate might get queasy or faint and then eventually pass out at which stage a ‘heart resetting’ is required.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | ICD | Pacemaker |
|---|---|---|
| Functions | When the ICD detects erratic life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias in the center of the chest, it either uses pumping to fix the rapid pulse and foster a normal rhythm, or it uses a charge (defibrillation) to restore the heart function and forestall sudden cardiac arrest. | Pacemakers assist the heart rhythm at a regular speed and cadence by sending electronically devised pulses. Pacemakers could be used to keep the valves of your heart pumping in time. |
| Invented By | Dr. Michel Mirowski, his research in the 1970s resulted in the creation of the implanted cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). | Wilson Greatbatch, an electronics engineer who was instrumental in the development of the first implanted pacemaker in 1950. |
| Appearance | An ICD is inserted beneath the epidermis right underneath the clavicle, about the size of a wristwatch. It is made up of a function generator and connections known as leads. | It’s a tiny metal coin-like gadget that’s inserted beneath your skin in the upper chest. A microprocessor in the pacemaker detects when your heart beats too quickly or irregularly. |
| Used for | For individuals at risk of cardiac collapse owing to atrial tachycardia, an ICD is required. | People with uneven rhythmic heart pumps and occasional heart failure. |
| Full Forms | Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator | Pacemaker means the device that helps in maintaining the regular pace of the heart. |
What is an ICD?
A tiny electronic device used for heart rate regulation linked to the heart is known as an implanted cardioverter defibrillator (ICD). It is used to detect and assist in managing possibly serious electromagnetic abnormalities with the heartbeat continually.
Anti-tachycardia pumping is another therapeutic option with the ICD for such rapid rhythms. This is a rapid-fire surge that is sent to adjust the rhythm.
A subsurface ICD is a kind of ICD that does not require the insertion of wiring into the ventricle. The gadget is instead placed in the left axillary area.
An ISD is planted inside your chest cavity in case the pulse of your heart’s bottom lobes, known as the ventricular contraction, is dangerously aberrant, and you may require an ICD to assist your heart rate into regular sync.
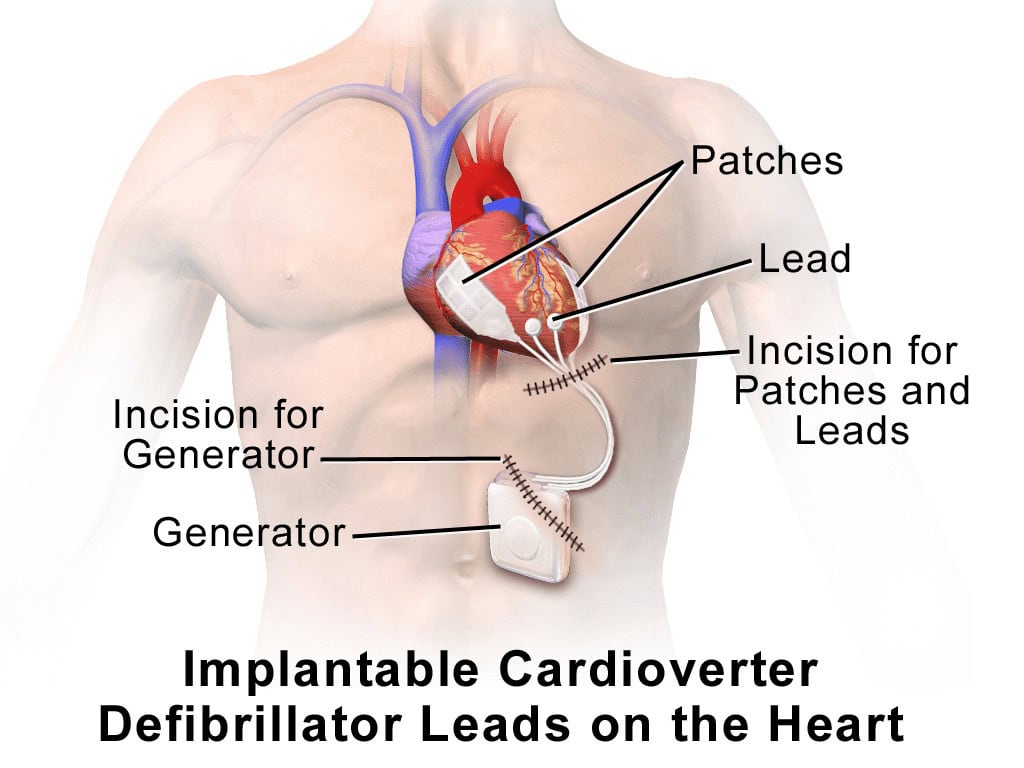
What is a Pacemaker?
A pacemaker is a gadget that can be implanted beneath the skin in the upper chest. A chip in the pacer detects whenever your heart is pumping too quickly or irregularly.
A transient or persistent pacemaker may be required according to the patient’s cardiac health and frequencies of life-threatening seizures and attacks.
Pacemakers have been used to manage irregularities in heart rates and heart failure, a disease that develops when the heart is not pumping sufficient blood to the body.
Specialized cardiologists perform the pacemaker insertion, and the surgery includes many complex steps and precautions. The pacemaker electrodes (also known as “leads”) will be threaded into the heart by your surgeon with the help of a blood artery.

Main Differences Between ICD and Pacemaker
- An ICD can replace a pacemaker in terms of functionality.
- ICDs are used for people who are at risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, while pacemakers are used to address sluggish heart rhythms.

- https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=85&contentid=p00234
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/pacemakers#:~:text=A%20pacemaker%20is%20a%20small,a%20normal%20rate%20and%20rhythm.

The information about ICDs and pacemakers is really clear and well-organized. It’s amazing to learn how technology can save lives by helping regulate heart rhythms.
Yes, it’s crucial for the public to have a good understanding of these devices.
Absolutely, the advancements in medical technology are truly fascinating.
The article provides a comprehensive understanding of the functionalities and significance of ICDs and pacemakers. It’s an excellent resource for individuals looking to learn more about these essential medical devices.
Certainly, the article presents valuable insights into advanced cardiac technologies.
The comprehensive overview of ICDs and pacemakers is extremely valuable. It’s essential for the public to be well-informed about advanced medical technologies.
Absolutely, educating the public about these devices can contribute to better health outcomes.
I completely agree, increasing awareness about medical innovations is crucial for public health.
The detailed description of how ICDs and pacemakers work is enlightening. It’s great to see the positive impact of technology in healthcare.
Agreed! This article provides a comprehensive overview of these life-saving devices.
The article provides a clear explanation of the main differences between ICDs and pacemakers, making it easier for readers to understand the importance of these devices in healthcare.
Absolutely, the detailed comparison helps to highlight the significance of these life-saving technologies.
The detailed descriptions of ICDs and pacemakers are very informative. It’s important for individuals to be aware of these medical technologies and their applications.
Definitely, raising awareness about health-related devices can have a positive impact on public well-being.
The information about the differences in function and appearance between ICDs and pacemakers is well presented. It’s great to see the emphasis on educating the public about these critical technologies.
Absolutely, creating awareness about medical devices is essential for public health.
I agree, the educational value of this article is commendable.
The historical background on the invention of ICDs and pacemakers provides valuable context for understanding their significance in modern medicine.
Absolutely, knowing the origins of these devices helps us appreciate the advancements in healthcare over time.
The information about the functionalities of ICDs and pacemakers is very well articulated. It’s crucial for individuals to have a good understanding of these medical devices.
Absolutely, knowledge about these devices empowers people to take charge of their health.
The comparison table really helps illustrate the differences between ICDs and pacemakers. Technological innovations in the medical field are truly remarkable.