X-ray and CT scans are imaging techniques used to diagnose internal illness. Both tests use a low ionization energy beam to detect internal defects such as bone fracture, internal swelling, and pre-surgery checkups.
Also, these tests provide clear and significant images of the internal body.
Key Takeaways
- X-rays produce two-dimensional images of body structures, while CT (Computed Tomography) scans generate detailed, cross-sectional images.
- CT scans use multiple X-ray images to create a 3D representation, providing more information than a single X-ray.
- CT scans expose patients to higher radiation doses than X-rays but offer greater diagnostic accuracy.
X-Ray vs CT Scan
The difference between an X-ray and a CT scan is that an X-ray produces a single image, whereas a CT scan produces multiple photos from different angles. X-ray has an image in a single position, whereas, in a CT scan, various images are made from different angles.
X-ray is a low ionization energy imaging test. Depending upon the density of the bones, these rays are absorbed in various portions. Denser body parts, such as bones and teeth, are represented by white colour in X-ray film.
On the other hand, lesser dense parts such as muscle and fat appear in grey and air-filled lunges are shown in black colour.
CT scan is technically known as a computerized tomography scan. Also, a separate computer program and processing are used to construct cross-sectional slides of our body’s blood vessels, bones, and soft tissues.
Moreover, CT scan images provide more detailed information than plain X-rays do.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | X-Ray | CT Scan |
|---|---|---|
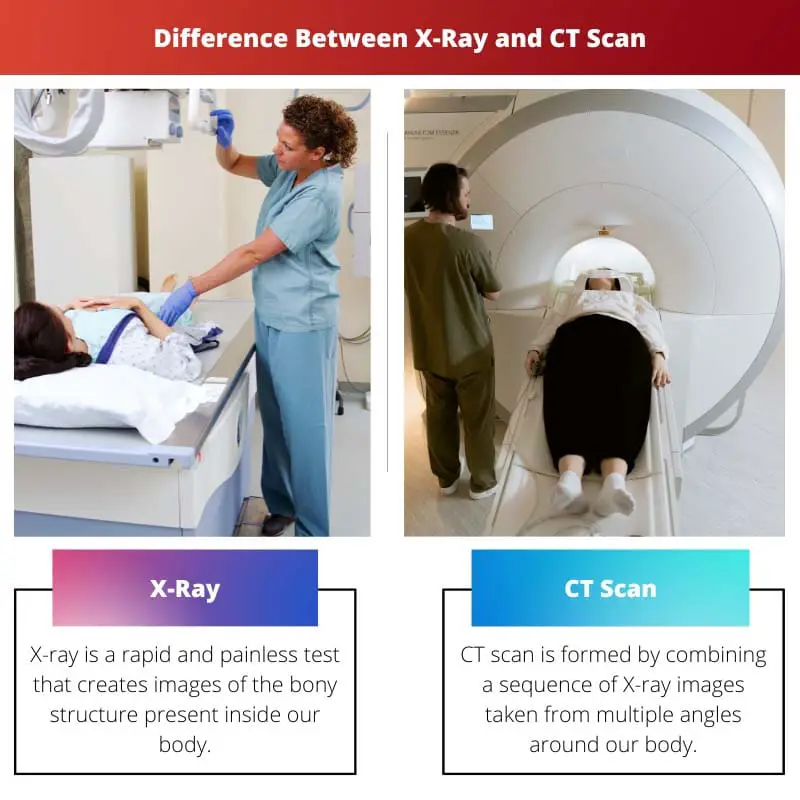
| CT scan is formed by combining X-ray images taken from multiple angles around our body. | X-ray is a rapid and painless test that creates images of the bony structure present inside our body. | X-ray is used to investigate problems in many body parts such as bones and teeth, ribs, chest, and abdomen. |
| Diagnosis | CT scan is used to construct cross-sectional slides of the blood vessels, bones, and soft tissues. | X-ray does not provide much information as X-ray is taken in a single position and one angle. |
| Details | X-ray is quite affordable and pocket friendly. | CT scan images provide more detailed information than plain X-rays do. |
| Price | CT scan is a little bit costly as compared to an X-ray. | CT scan is little bit costly as compared to an X-ray. |
| Ionisation Energy Level | X-ray uses a low ionisation energy beam. | X-ray uses a low ionization energy beam. |
What is X-Ray?
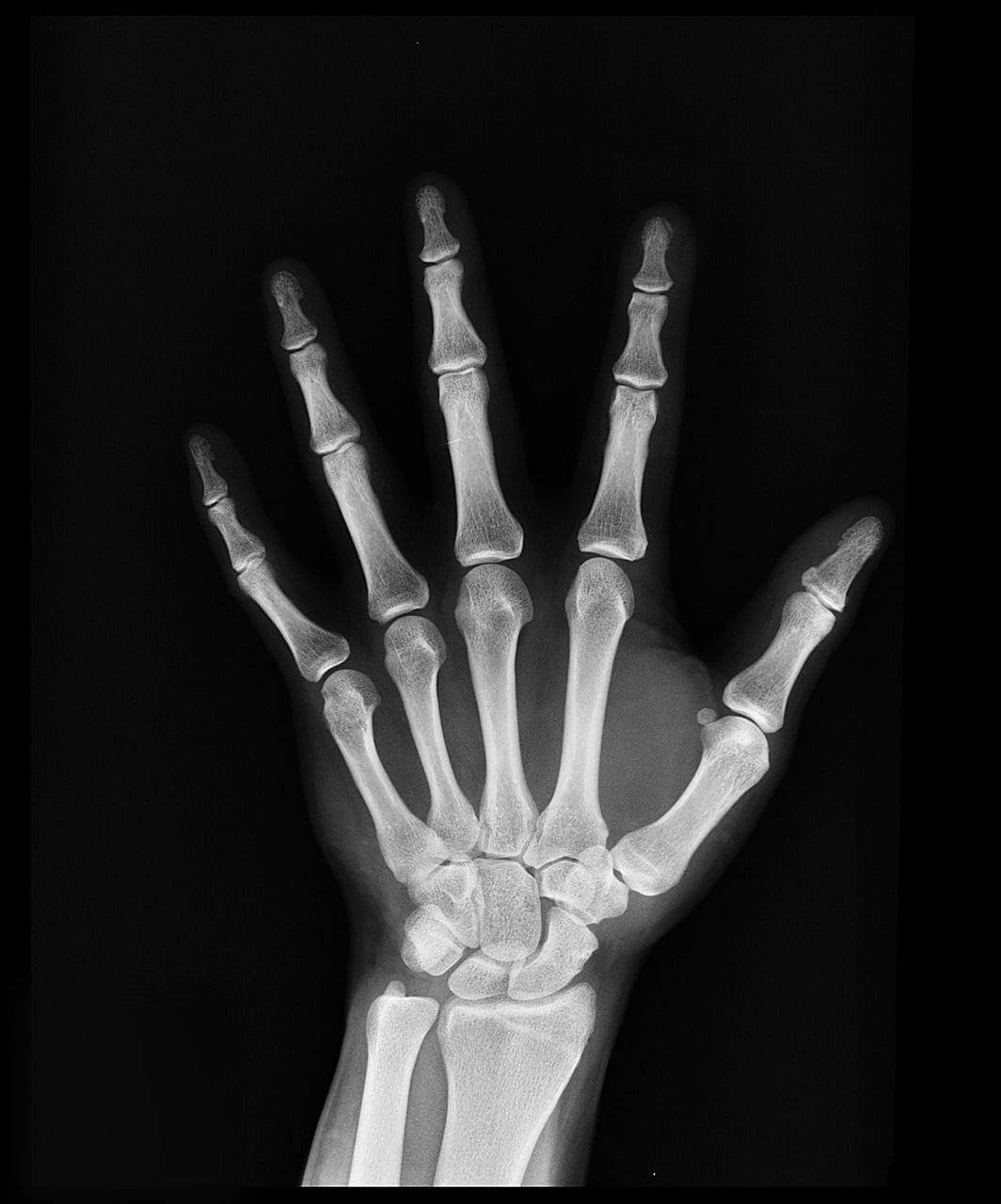
X-ray is a rapid and painless test that creates images of the bony structure present inside our body. X-ray beams are ejected through a machine, and the patient can stand in front of the device.
These beams penetrate through our bodies and are made to project an image on a screen or film.
Depending upon the density of the bones, these rays are absorbed in various portions. Furthermore, denser body parts, such as bones and teeth, are represented by white colour in X-ray film.
On the other hand, lesser dense parts such as muscle and fat appear in grey and air-filled lunges are shown in black colour.
For some particular types of X-ray tests, some non-toxic iodine or barium solutions are given to patients for drinking. These solutions provide a better and more detailed image of the affected area.
X-ray is used to investigate problems in many body parts such as bones and teeth, ribs, chest, and abdomen.
In the case of bones and teeth, an X-ray is used to detect fractures, bone cancer, arthritis, osteoporosis, and tooth decay. Whereas in the case of the chest, an X-ray is used to diagnose lung infection, enlarged heart, breast cancer, and blocked blood vessels.
However, abdominal X-rays are used to detect digestive tract infections and sometimes swollen items in the case of children.
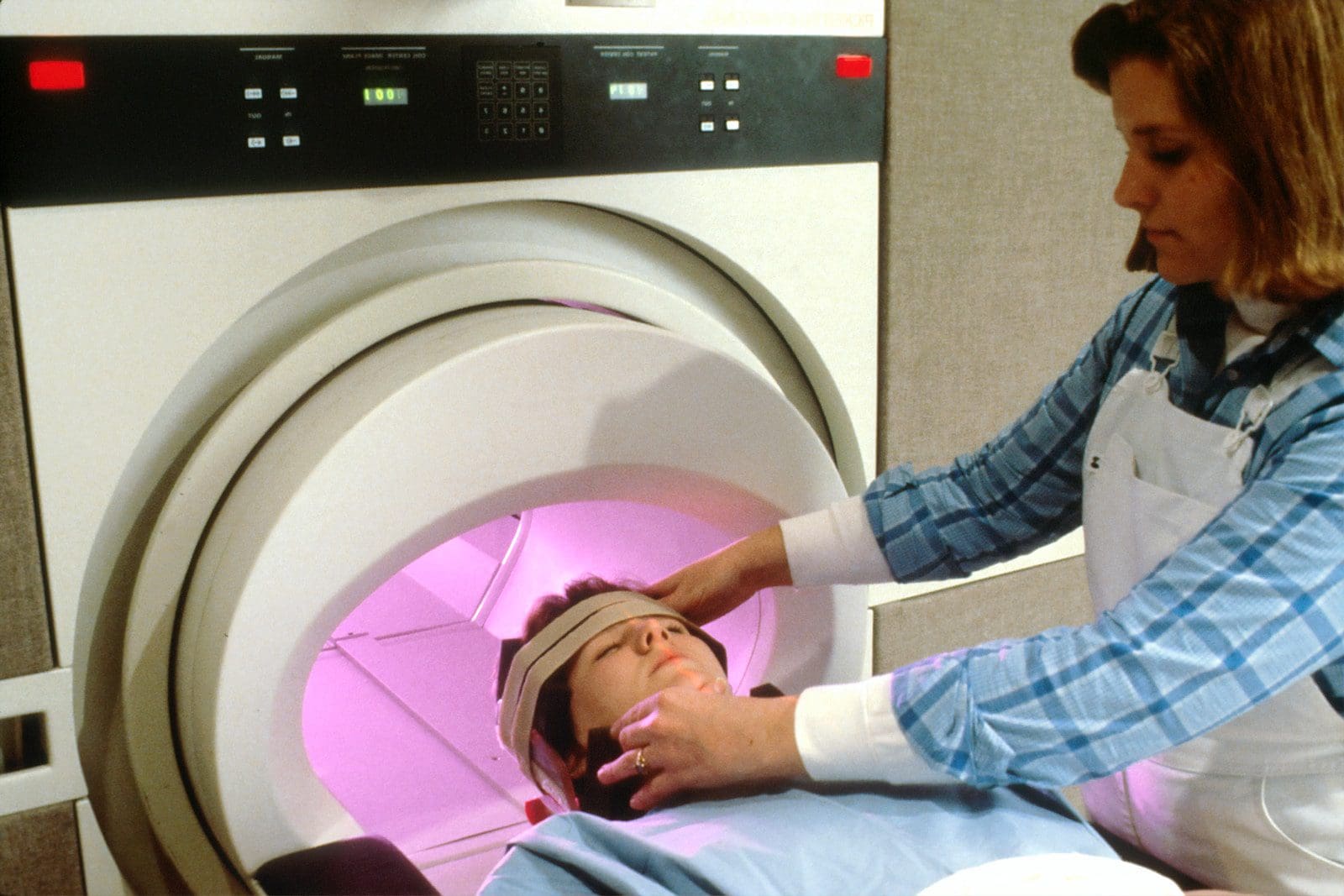
What is CT Scan?
A CT scan is technically known as a computerized tomography scan. It is formed by combining a sequence of X-ray images taken from multiple angles around our body.
Furthermore, a separate computer program and processing are used to construct cross-sectional slides of our body’s blood vessels, bones, and soft tissues. Moreover, CT scan images provide more detailed information than plain X-rays do.
CT scan is used to diagnose internal injuries from any accident or any other trauma. Also, a CT scan is preferably used to schedule surgery or medical therapy and analyze an injury or a disease.
Furthermore, a CT scan is used to detect bone and muscle disorders, infections, tumors, internal blood clots or injuries, and internal bleeding. Since a CT scan captures more details than an X-ray, the amount of radiation is also more than a plain X-ray.
In a particular type of CT scan, a particular non-toxic chemical known as contrast material is inserted into the patient’s body through injection or oral.
If the oesophagus or stomach is being scanned, contrast material is given orally. If the gallbladder, urinary tract, liver, or blood vessels are being observed, then contrast material is provided through injection.

Main Differences Between X-Ray and CT Scan
- X-ray displayed only a single film for an affected part. A CT scan displays a film by combining multiple X-rays from different angles.
- X-ray is used to detect fractures, bone cancer, arthritis, osteoporosis, tooth decay, lung infection, enlarged heart, breast cancer, and blocked blood vessels. On the other hand, a CT scan is used to diagnose any bone and muscle disorders, infections, tumours, internal blood clots or injuries, and internal bleeding.
- In some special kinds of X-rays, some non-toxic iodine or barium solutions are provided to patients for drinking. Whereas in CT scans, some non-toxic contrast material is given to the patients.
- The price for an X-ray is quite low and is affordable. On the contrary, a CT scan is quite expensive and is not easy to afford.
- X-ray uses a low ionization energy beam of rays whereas CT scan uses a bit higher ionization energy beam than X-ray.
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/1594876/
- https://academic.oup.com/mnras/article-abstract/424/3/1991/976957
- https://aapm.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1118/1.598470
- https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/psychological-medicine/article/neuropsychological-deficits-and-ct-scan-changes-in-elderly-depressives/0FE5FBFF1B1EA8B3E5AE4B5EE52F966A



