Melanomas and Carcinomas are two kinds of skin cancers. These terms refer to skin cancer but are two different kinds of skin cancer.
Though these two grow similarly, i.e. growing the cell in an unusual way that causes tumours, the detailed function or working structure is very different.
Melanomas and Carcinomas arrive from two different cells, leading to cancer. Melanomas come from Melanocytes.
These cells in the skin protect it from sunlight and determine its colour. These cells release or produce melanin, the main compound that helps in this function.
Conversely, Carcinomas come from two different kinds of cells: Basal cells and Squamous cells. Basal cells are present in the lower level of the epidermis.
These cells help produce new cells or reproduce to create new cells for the skin. On the other hand, Squamous cells form the outer layer of the skin.
Melanomas vs Carcinomas
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer, caused by sun exposure or genetic factors. Carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that develops in epithelial cells, which are the cells that make up the skin’s outermost layer. It is more common than melanoma and less aggressive, but can still be dangerous if left untreated.

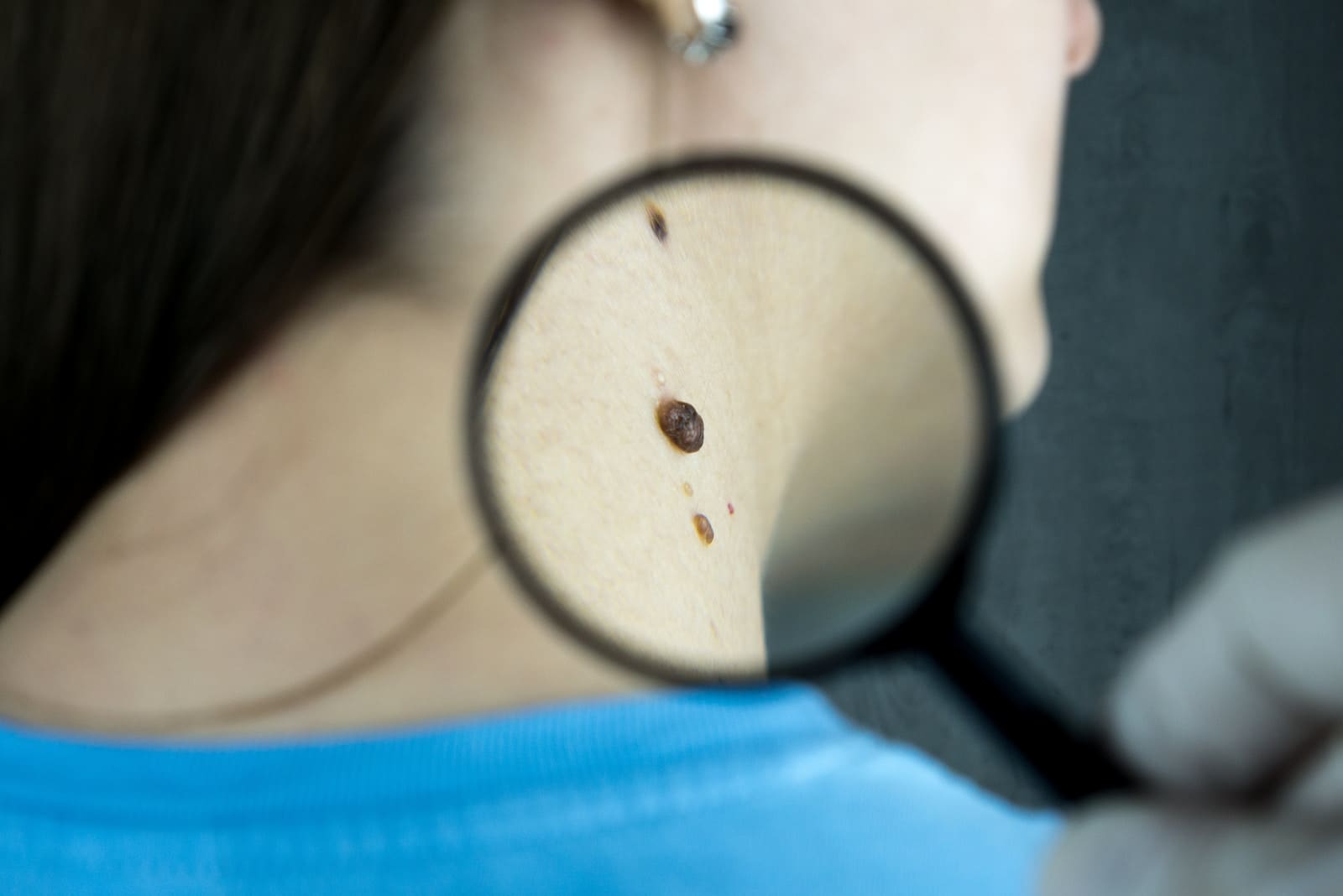
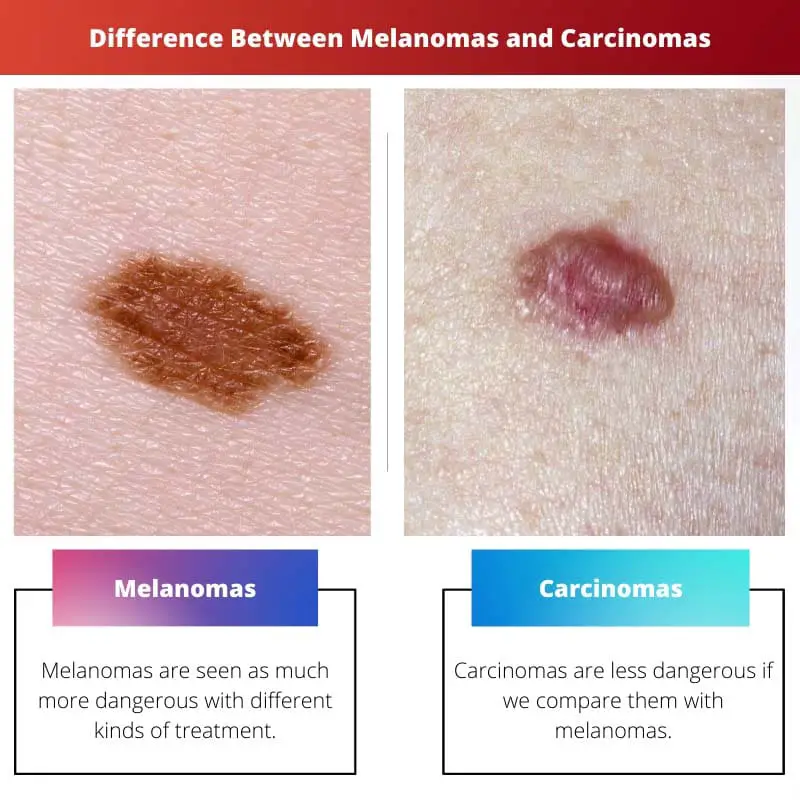
Melanomas are seen as much more dangerous with different kinds of treatment. These types of cancers show a little bump or growth on the skin.
The colour of these bumps can also signify which type of cancer it is. Colours like shades of blue, bright red, or purple represent melanomas.
Carcinomas, on the other hand, are less dangerous if we compare them with melanomas. These skin cancers also manifest as small growth or bump on the skin.
The colour of this bump differs from that of Melanomas. Mainly pink or reddish colour represents the occurrence of Carcinomas.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Melanomas | Carcinomas |
|---|---|---|
| Occurrence | Melanocytes cells | Basal and Squamous skin cells |
| Survival rates | Stage 4 is 50%, decreases with age and for men | 100% survival due to high medical technology |
| Treatment | Removal of the mass or sometimes radiation | Different kinds of treatment, from surgery in stage 1 to radiation |
| Appearance | This firstly appears like a reddish or pinky bump or growth | This firstly seems like a bright red or purple or bluish lump or growth |
| Spreading rate | It can proliferate, spread, and become life-threatening in about a month and a half | It is not life-threatening nowadays but can be very aggressive and cause death if ignored for a long time |
What are Melanomas?
Melanomas are not a common type of skin cancer, making a relief as it is a dangerous form of skin cancer. In the last stages of this skin cancer, it can be very aggressive.
This type of skin cancer also grows or spreads within the body very quickly. In this, Nodular Melanoma is the most aggressive form.
The treatment of melanoma has a particular guideline named ‘ABCD’ medical guideline. In this, the A refers to asymmetry, B refers to the border, c refers to colour, and D refers to diameter.
In the early stage, cancer can be treated just by removal. For other stages, other kinds of combined treatment are given.
For other severe stages, treatments like chemo, radiotherapy, cryotherapy, immunotherapy, target therapy, etc. In stage two, along with surgery, a sentinel node biopsy is a very common treatment.
In stage three, the treatments proceed with surgery, sentinel node, radiation, and direct chemotherapy.
In stage four, all kinds of tools are used, from surgery to all other therapies, very aggressively. Awareness about these melanomas in the early stage can be cured totally, but very rarely; it can also be recurring.
For this kind of cancer, the treatment is quite the same. But since this type of cancer only makes up 20% of skin cancer, it is rare.

What is Carcinomas?
Carcinomas make up to 80% of skin cancers. This type of skin cancer is not as dangerous as a melanoma. Just the process can mainly cure these cancers through surgery.
But if cancer reaches the 4th stage, it can also be aggressive. Radiation can cure this cancer along with surgery in the 4th stage.
There are two types of carcinoma based on the cells it is produced from. First is Basal cell carcinomas, which comprise 70% to 80% of the chances of skin cancer.
The formation of this skin cancer happens in the mother cell, which also gives a high chance of mutation as all other cells of the skin are produced from this mother cell.
The second type is Squamous cell carcinomas which fill the gap of the rest of the 20% of Carcinoma skin cancer. By the name itself, we can understand that this kind of skin cancer grows from a squamous cell.
The squamous cells are common plane cells present in many organisms. It is seen to be present in the inner lining of most of the organs in the human body, like the lungs.
Squamous cell carcinomas are rare of all but also are not deadly. The mortality rate of this kind of skin cancer is very high. Along with the high medical technology of nowadays, the mortality rate is very high.
Along with this, the mortality rate of Basal cell carcinomas is high. This type of cancer has the highest mortality rate, with 100%.
Main Differences Between Melanomas and Carcinomas
- Melanomas are much more dangerous and aggressive than Carcinomas.
- Melanomas are uncommon and even have less mortality rate than Carcinomas.
- Melanomas occur from melanocyte cells, while carcinoma occurs from two kinds of cells Basal cells and Squamous cells.
- These makeup around 99% of skin cancer Melanomas have a 20% chance of occurrence, and Carcinomas have 80%.
- Ultraviolet rays mainly cause melanomas, but Carcinomas and UV rays also show that Tanning beds can cause them.
- Melanomas in the 4th stage have aggressive treatment with all kinds of possible techniques, but we see less aggressiveness in the 4th stage of carcinoma.
- https://cebp.aacrjournals.org/content/8/2/153.short
- https://www.nature.com/articles/6602982
- https://jcp.bmj.com/content/48/3/242.short
- https://search.proquest.com/openview/208de5d4764eb7e219b86c21528d34c3/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=42082

The fact that basal cells are the most lethal type is interesting
Interesting how melanomas are tied to UV rays
It is surprising to learn there are different types of skin cancer
I don’t think the treatment for melanomas is as described here
I find the composition very informative
It has to be informative given the source of the references
I agree
I think the fact that melanomas are rare is something to think about