Bone scan and bone density scan are the terms that differ from the rays used during scanning. Also, both diseases deal with different kinds of bone diseases.
These terms would have come across from many of us frequently. Be a member of the family, or be it us. Most of the people might have gotten any one of these procedures done.
Key Takeaways
- Bone scans use radioactive tracers to detect abnormalities in bone metabolism and structure.
- Bone density scans measure bone mineral density to diagnose osteoporosis or assess fracture risk.
- Bone scans are more sensitive to changes in bone metabolism, while bone density scans focus on structural changes.
Bone Scan vs Bone Density Scan
A bone scan is an imaging test using a radioactive tracer that examines bone for irregularities that could indicate infection or cancer, while a bone density scan looks at the density of bone to evaluate the likelihood of a person is to develop osteoporosis using both low and high-energy X-ray beams.
The bone scan is a scientific method which helps to determine the presence of bone disease. It uses a medicine with a nuclear property that is injected into the body of the patient. The medication is injected into the arm especially.
After a wait of a few hours for this procedure, a camera that can detect gamma rays is used to see the place where bone metabolism is high, which can detect cancers, tumours spreading over to bones, infections in bones, etc.
Bone Density Scan, however, is another scientific method to determine some different types of bone diseases. It uses two distinct beams consisting of X-rays, and those beams are focused on the patient’s body.
After we subtract the number of X-rays absorbed by the soft tissues, we can determine the density of the bone. It is helpful to detect diseases like osteoporosis.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Bone Scan | Bone Density Scan |
|---|---|---|
| Rays used | It uses a nuclear medicine that is injected into the body. | It uses 2 x-rays that are projected to the body of the patients. |
| Diseases it detects | It detects serious cancers, tumors, and bone infections | It detects diseases such as osteoporosis. |
| Procedure | The medicine is INJECTED into the body. | No injecting is required, the rays are just projected over the body. |
| Age groups concerned | It can be done to any age group when symptoms are seen. | Mostly females above the age of 65 and males above the age of 70 are advised to perform this test. |
| Number of steps involved | It is a three-step procedure and is time-consuming | It has 2 stages and is less time consuming |
What is Bone Scan?
In the present day, where man is the storehouse of diseases. Due to an unhealthy lifestyle. For other internal factors, a bone scan is widely used.
Cancer, tumour, or infection can happen to anyone, be it a vegan fitness freak or an average couch potato. This test is a great way to help in taking precautions.
It is the best treatment before the condition has gotten worse. In the field of medicine, this is a true revolution.
Bone Scan, which has the scientific name of Scintigraphy, uses medicine that has a nuclear property. When the patient feels unexplainable pain in their body, or if some tumour cases are detected before, they are free to take this test.
At first, they get injected with nuclear medicine on any part of their arm. They have to wait for a few hours for the medication to move throughout the body.
After the wait, a gamma-detecting camera checks where the metabolism or changes occurring in the bone is higher than the natural level.
This procedure takes three steps. It detects bone cancer, tumours that have spread after coming in contact with the bone, infections relating to bones, and such diseases.
It is a sensitive technique and detects change quickly. The radioactive medicine slowly goes away from the body after a few days.

What is Bone Density Scan?
Bone density scan is also a method of scanning our bones. It’s different from the bone scan as its purposes and techniques are different.
It uses X-rays instead of nuclear material, which is helpful in bone density scans. Also, it is helpful in the detection of osteoporosis, which is also called low bone mineral density.
In the case of a bone scan, two different types of X-rays come into play. It is because one type of ray alone can’t accurately trace out the density of bone marrow inside our bone.
No injection of any material is needed. So, for this procedure, the patient is made to be laid down, and a bone density scanner uses two beams of X-rays on the patient’s body.
After this, the amount of X-rays passed inside the bone is measured. It is to find out the density of the bone. If the X-rays pass through soft tissues, it is neglected, and only that which passes into the bones is considered.
It has a particularly preferred age group when this test is safe. According to doctors, women above 65 years and men above 70 years should take this test.
If a person is above 50 years and their bones take a long time to heal after some injury, they should also take this test to be sure whether they have osteoporosis.
T score, which is a point given to a person after this scan, if found above 2.5, it detects osteoporosis.
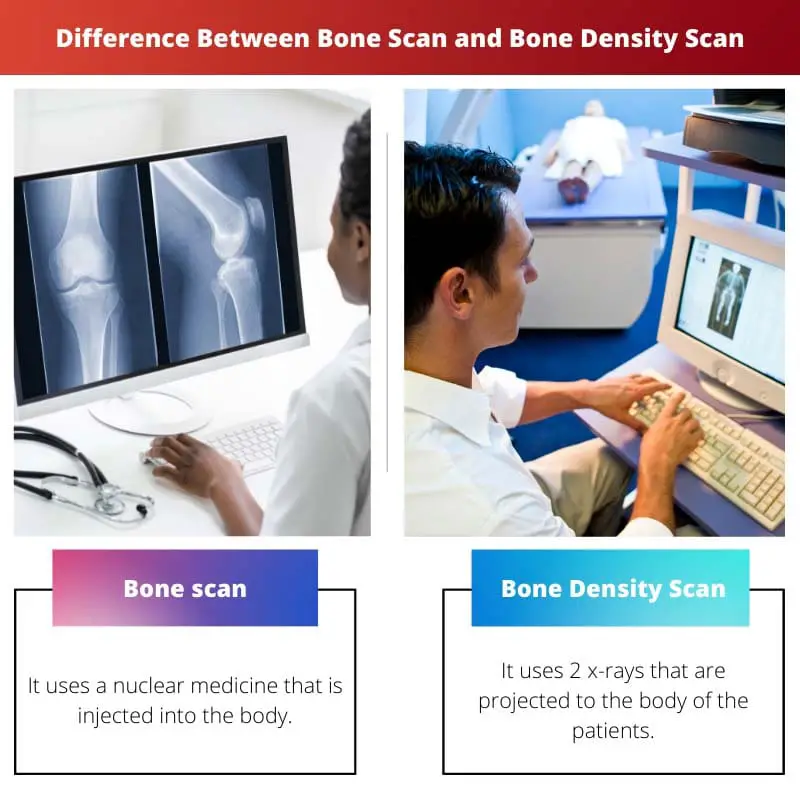
Main Difference Between Bone Scan and Bone Density Scan
- A bone scan uses nuclear medicine that’s injected into the body for the scan. However, a bone density scan uses X-rays for conducting the scan.
- A bone scan helps in detecting diseases such as cancers, tumours that have spread, and infections in bones. A bone density scan, on the other hand, helps to find out if a person has osteoporosis.
- A bone scan needs the medicine to be injected into the body. But, the bone density scan doesn’t need an injection into the body.
- The bone scan is done on any age group whenever symptoms of any bone disease appear. Bone density scan has a specific age group for being conducted.
- The bone scan involved three steps. On the other hand, The bone density scan includes two steps to be done.
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1034/j.1600-0501.2001.012001079.x
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0278416584900047

The scientific methods employed in bone scans and bone density scans contribute significantly to the detection of bone diseases. Understanding the nuances between these procedures is essential for effective medical diagnosis and treatment.
Indeed, the use of nuclear medicine for bone scans and X-rays for bone density scans provides valuable insights into the metabolic and structural aspects of bone health. These methods play a crucial role in disease detection and prevention.
It’s interesting to see how bone scans focus primarily on detecting cancer or infection, whereas bone density scans are more focused on diagnosing osteoporosis or assessing the risk of fractures. The use of nuclear medicine in bone scans and x-rays in bone density scans also sets them apart.
The comparison table provides a clear overview of the distinctions between bone scans and bone density scans. It serves as a helpful reference for understanding the differences in their procedures and applications.
Absolutely, the differences in the types of rays used and the diseases they detect are crucial. It helps in understanding how these procedures contribute to the diagnosis and treatment of bone-related conditions.
The ability of bone scans to detect cancers, tumors, and bone infections, while bone density scans focus on osteoporosis, showcases the diverse applications of these diagnostic procedures. It’s impressive how they cater to different aspects of bone health and pathology.
Definitely, the specialized nature of bone scans and bone density scans offers valuable insights into identifying and managing various bone diseases. It emphasizes the tailored approach to diagnosis and treatment in the medical domain.
The potential of bone scans in detecting underlying abnormalities such as cancer, tumors, and infections underscores its indispensable role in early disease detection. The nuanced application of these tests reflects the advancements in medical diagnostics for bone-related conditions.
Indeed, the ability of bone scans to detect subtle changes in bone metabolism and structure highlights their effectiveness in identifying and managing severe bone diseases, demonstrating the value of specialized diagnostic techniques.
Absolutely, the advanced methodologies employed in bone scans point towards the precision and efficacy of these diagnostic tests, showcasing their critical role in early disease detection and targeted medical interventions.
The specialized nature of bone density scans in diagnosing osteoporosis and assessing fracture risk demonstrates its clinical significance, especially for specific age groups. This reflects the importance of tailored diagnostic measures based on individual health needs and risks.
Absolutely, the focus on bone mineral density assessment through bone density scans emphasizes the need for targeted diagnostic methods to address age-related bone health concerns.
Bone scans and bone density scans are critical in determining various bone diseases and conditions. The use of radioactive tracers in bone scans has a different purpose compared to the bone density scans. It’s important to understand the key differences between these procedures.
Yes, bone scans are used to detect abnormalities in bone metabolism and structure, while bone density scans help diagnose osteoporosis.
The distinction between bone scan and bone density scan in terms of the diseases they detect and the age groups concerned is noteworthy. This information is vital for individuals to understand the relevance of these procedures based on their health conditions and risk factors.
Absolutely, the targeted nature of bone scans and bone density scans reflects their importance in the medical field. It underscores the need for specific diagnostic approaches for different bone-related conditions.
The scientific intricacies of bone scan and bone density scan procedures provide valuable insights into their utility in diagnosing diverse bone diseases. The ability of these tests to cater to different age groups and conditions highlights their versatility and clinical importance.
Agreed, the nuanced approach of bone scans and bone density scans contributes significantly to the comprehensive evaluation of bone health and detection of specific conditions, thereby guiding targeted medical interventions.
Absolutely, the precise methodologies utilized in bone density scans and bone scans underscore their clinical significance in evaluating age-related bone health concerns and ensuring tailored diagnostic approaches.
The application of bone scans in detecting conditions such as cancer, tumors, and infections underscores its significance in addressing critical bone diseases. This highlights the value of specialized diagnostic techniques in medical practice.
Indeed, the targeted approach of bone scans and the insights they offer into bone metabolism and structure showcase their indispensable role in identifying and managing severe bone-related conditions.
The in-depth coverage of bone scan and bone density scan procedures and their applications provides a comprehensive understanding of their role in diagnosing bone diseases. The distinct methodologies employed in these tests highlight their significance in clinical practices.
Agreed, the scientific principles underlying bone scans and bone density scans demonstrate the precision and efficacy of these diagnostic measures. Their ability to detect changes in bone metabolism and density contributes to early disease detection and intervention.
Absolutely, the comparison table offers a concise summary of the key differences between bone scans and bone density scans, facilitating a comprehensive grasp of their unique features and clinical relevance.