Disease diagnosing can be tedious if we don’t have access to amazing diagnostic tests/ scans like CT scans, MRIs, Bone scans, etc. But some of these can baffle us and create confusion about which one to go.
Key Takeaways
- Bone scans use radioactive tracers to detect abnormalities in bones, while MRIs use magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of internal organs and tissues.
- Bone scans are more sensitive to bone abnormalities but lack specificity, while MRIs provide more accurate and detailed information about soft tissues.
- MRIs are non-invasive and radiation-free, making them safer for patients, especially pregnant women and children.
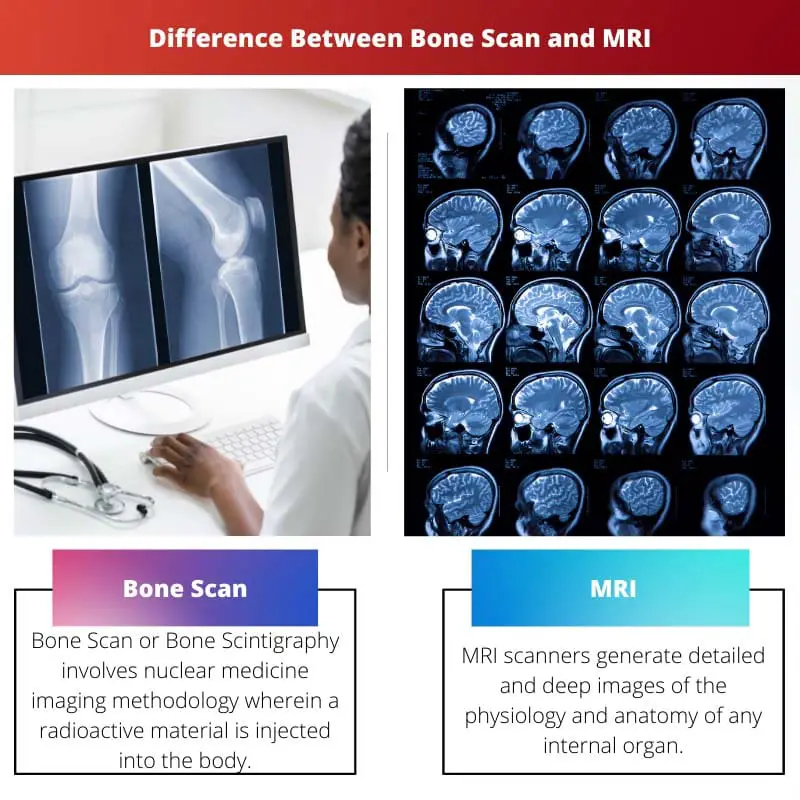
A bone scan is a nuclear medicine imaging test that uses a small amount of radioactive material to produce images of bones. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of internal structures such as organs, soft tissues, and bones.
Bone Scan or Bone Scintigraphy involves nuclear medicine imaging methodology wherein a radioactive material is injected into the body, which produces gamma rays, which in turn are captured by an imaging device(camera), thus generating images or scintigrams. Bone Scan produces two-dimensional (2D) images.
MRI scanners generate detailed and deep images of the physiology and anatomy of any internal organ, thus providing a precise and deep diagnosis of any disease or infection. MRI is considered as safer than any other tests/ scans.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Bone Scan | MRI |
|---|---|---|
| Rays/ Fields used | Radioactive-gamma rays | Strong Magnetic Fields, Radio Waves |
| Image Generated | 2-dimensional | 3-dimensional and 2-dimensional |
| Invented By | George De Hevesy (1930s) | Raymond Damadian (1970s-1980s) |
| Risk Factor | For pregnant and breastfeeding women | No threat to pregnant women |
| Specificity | Peculiarly Bone | Any anatomical internal organ |
What is a Bone Scan?
It is popularly known as skeletal scintigraphy. Diagnosis of bone scan may assist in treating numerous disorders like bone cancer and metastasis, osteoblasts, minute fractures which are not visible under normal X-ray, osteoporosis, arthritis, etc.
Under Bone Scan, patients are administered radioactive substances like radiopharmaceutical or radiotracer, producing gamma rays that are then processed into images by the imaging device. These images are labelled scintigrams.
Usually, in the absence of bone disorder, the radioactive substance should be distributed evenly in the entire body. But in the presence of disease, these scintigrams highlight dark/ hot spots, thus locating the affected segment of the bone.
Patients are asked to wait after injecting the radiotracer before undergoing the scan. Bone scan to date emerges to be one of the safest options for scan, leaving no side effects or risks.
If the ailment is not identified on the first go, physicians advise the bone scan to be redone. In some cases, a bone scan is followed by SPECT (Single-photon emission computed tomography), SPECT provides 3-Dimensional images, thus enhancing the results of bone scan.
What is MRI?
MRI, or Magnetic Resonance Imaging, is an imaging technique used to generate images depicting the physiology of deep internal organs. MRI helps in the timely detection and diagnosis of massive disorders involving every part of the body.
The one with the contrast medium (gadolinium) guarantees better results and images compared to the no-contrast medium. MRI is never specific; it assists in diagnosing ailments from the entire body encompassing any muscle, tissue, ligament, etc.
Often, they also detect Alzheimer’s. MRI does not involve ionizing radiations, thus distinguishing it from other diagnostic tests.
The magnetic and radio waves track and trace the water or hydrogen molecules in the body, and these atoms, in turn, produce light/ faint waves or signals, which are processed into cross-sectional images. MRI also produces 3-dimensional images.
MRI is considered the safest, the exception being that there should be not a single piece of metal attached to your body due to the presence of strong and mighty magnets. MRI is painless and carries zero side effects.
Main Differences Between Bone Scan and MRI
- Pregnant women are advised to consult doctors before undergoing a Bone Scan, while MRI poses no threat to pregnant or breastfeeding women.
- Bone Scan involves the injection of a radiotracer, while MRI does not involve the injection of any radioactive substance.

I found this article very informative and helpful in understanding the nuances involved in choosing between different diagnostic tests. Well done!
The content is rich and well-researched. I appreciate the clarity in describing the main differences between Bone Scan and MRI.
This article presents the information in a straightforward manner, making it accessible to patients looking to understand the differences between Bone Scan and MRI.
The comparison table is very useful, I agree with all the information provided here.
This article provides such an informative and comprehensive comparison between Bone Scan and MRI. The attention to detail is commendable.
The article did a great job of delineating the risks and benefits associated with both tests. I do believe that patients should be well-informed before making a decision.