Cytokinesis is one of the crucial topics of reproduction. It plays a major part while dividing the cells for regeneration, which divides the cytoplasm from parental cells into daughter cells either through the mitosis or the meiosis phase.
During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm splits into two equal halves, nothing but two daughter cells to ensure genetic segregation.
Key Takeaways
- Plant cells form a cell plate during cytokinesis, dividing the cell into two daughter cells.
- Animal cells constrict at the cleavage furrow, eventually pinching the cell into two parts.
- A cell wall in plant cells necessitates the formation of a cell plate, whereas animal cells lack a cell wall.
Cytokinesis in Plant Cells vs Animal Cells
The difference between cytokinesis in plant cells and animal cells is that cytokinesis begins in prophase in the case of plant cells. On the other hand, cytokinesis begins in anaphase in the case of animal cells. Over and above, Cytokinesis happens due to the presence of cell plates in plant cells, while in animal cells, Cytokinesis occurs through cleavage.
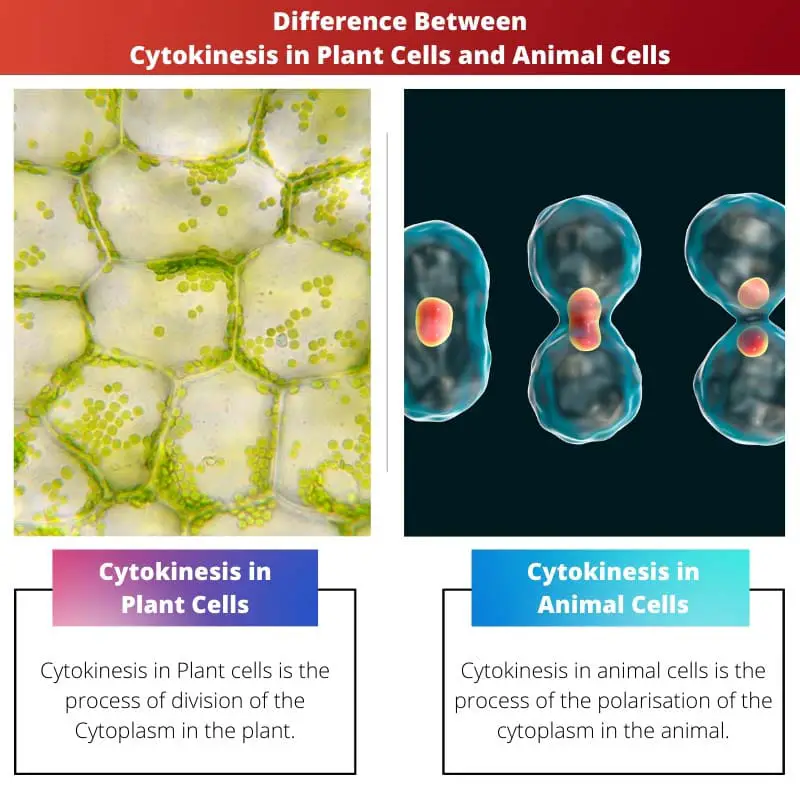
Cytokinesis in plant cells is the process of division of the cytoplasm into two cells. This occurs in the middle part of the cell plate of the plant, where Golgi vesicles coalesce to form phragmoplast.
Following that, a cell plate is formed due to the fusion of vesicles in the cell wall. As a result, the fused vesicles form a plasma membrane to separate the cells into two.
On the contrary, Cytokinesis in animal cells is the process of the polarisation of the cytoplasm. This process occurs due to the cortical remodelling orchestrated by the anaphase spindle through cleavage in the animal cells.
A ring-like actin filament is formed at the metaphase plate in such a way that a cleavage furrow is formed, which catalyzes the division of a cell into two.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Cytokinesis in Plant Cells | Cytokinesis in Animal Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Cytokinesis in Plant cells is the process of division of the Cytoplasm in the plant, where there is a cell plate formed in the middle that separates the cells into two, which brews Cytokinesis in Plant Cells. | Cytokinesis in animal cells is the process of the polarisation of the cytoplasm in the animal, where Cytokinesis happens through cleavage. |
| Process | The process began, when a cell plate is formed, with the help of the Golgi apparatus which releases vesicles and ultimately forms a cell plate that creates division on the plant cells. | The process of Cytokinesis occurs, when there is a constriction in the animal cell during late anaphase or precocious telophase. |
| Formation | Cytokinesis engenders vesicles in the middle of the cell during plant cells Cytokinesis. | Cytokinesis in animal cells is formed by cortical remodelling orchestrated by the anaphase spindle through cleavage and actin filaments assembled together in the middle of a cell to form a contractile ring that divides two parts of cells. |
| Cell wall formation | Cytokinesis in plant cells forms cell walls | Cytokinesis in animal cells doesn’t form cell walls. |
| Spindle Apparatus | Spindle, the middle part of it appears active in plant cells during Cytokinesis and as a result, generates Phragmoplast. | Spindle degenerates during Cytokinesis in animal cells. |
| New cell membrane | Vesicles of Golgi apparatus bestow new cell membranes in plant cells. | The new cell membrane derives from the Endoplasmic reticulum. |
What is Cytokinesis in Plant Cells?
Cytokinesis is the second most important stage of the mitotic phase, which divides the cell by physically separating the cytoplasm components into two daughter cells.
Speaking of which, Cytokinesis takes place in the middle part of the cell plate of the plant, where Golgi vesicles coalesce to form phragmoplast.
Following that, a cell plate is formed due to the fusion of vesicles in the cell wall. As a result, the fused vesicles form a plasma membrane to separate the cells into two.
In simple words, the process begins with the formation of a cell plate with the aid of the Golgi apparatus, which discharges vesicles in order to form a cell plate that creates membranes for the division of the plant cells into various daughter cells.
Unlike animal cell generation patterns, cytokinesis is said to be different in plant cells, and this is due to the presence of cell walls and cell membranes in the plant cells.
On the other hand, Cytokinesis begins in prophase in plant cells, which is formed through vesicles in the centre of a cell that causes the formation of the Cell wall and ultimately engender the division of plant cells.
What is Cytokinesis in Animal Cells?
On the other hand, Cytokinesis in animal cells is the process of the polarisation of the cytoplasm into two cells. This process occurs due to the cortical remodelling orchestrated by the anaphase spindle through cleavage in the animal cells.
A ring-like actin filament is formed at the metaphase plate in such a way that a cleavage furrow is formed, which catalyzes the division of a cell into two.
Although the first and foremost step for a cell undergoing cytokinesis in animals is to make sure that it occurs at the right time and in the appropriate place.
Having that said, the process of Cytokinesis occurs only if there is a constriction in the animal cell during late anaphase or precocious telophase.
Moreover, cytokinesis takes place by abiding by these four stages; initiation, contraction, membrane insertion, and completion.
So accordingly, the cytokinesis takes place in such an arrangement, where the anaphase spindle reorganizes initially, followed by division plane specification, actin-myosin ring assembly and contraction, and abscission, in order to divide a cell into two daughter cells.
In the end, the divided daughter cells are ensured by molecular signalling pathways throughout the tight ephemeral coordination of the phases.
Main Differences Between Cytokinesis in Plant Cells and Animal Cells
- Cytokinesis happens by division of the cytoplasm, which occurs by the formation of cell plates in plants, But when it comes to animal cells, Cytokinesis occurs through cleavage.
- Cytokinesis in plant cells forms cell walls, whereas Cytokinesis in animal cells doesn’t.
- Cytokinesis in plant cells is formed through vesicles in the centre of a cell that causes the formation of the Cell wall and ultimately engender Cytokinesis in plant cells. On the other hand, Cytokinesis in animal cells occurs through cleavage, which is caused by non-muscle myosin II and actin filaments involvement in order to form contractile rings.
- A new cell membrane is generated from the vesicles of the Golgi. Meanwhile, Cytokinesis in animal cells produces new cell membranes from the Endoplasmic reticulum.
- When it comes to the spindle, the spindle middle part stays active and vigorous during cytokinesis in plant cells, but in animal cells, the Cytokinesis spindle degenerates.
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/095506749190149S
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0074769608600595

The article offers an insightful exploration of cytokinesis in plant and animal cells, providing a detailed and coherent comparison of the distinct biological processes involved in cellular division.
I appreciated the article’s emphasis on the structural differences underlying cytokinesis in plant and animal cells, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of division mechanisms.
The comprehensive comparison of cytokinesis provides a compelling analysis of the key features distinguishing the division processes in plant and animal cells.
The article provides valuable insights into the process of cytokinesis in both plant and animal cells, explaining the formation of the cell plate in plants and the cleavage furrow in animals.
I found the comparison table particularly helpful in understanding the distinctions between cytokinesis in plant and animal cells.
The detailed description of the differences in the process of cytokinesis in plant and animal cells offers a comprehensive understanding of the biological mechanisms involved.
I appreciate how the article provides a clear and logical explanation of cytokinesis, making it easier to comprehend the respective processes in plant and animal cells.
The comprehensive comparison of cytokinesis in plant and animal cells serves as a valuable resource for understanding the underlying biological processes associated with cell division.
I appreciated the detailed explanation of how cytokinesis occurs in plant cells, emphasizing the significance of cell plate formation in division.
The article adeptly elucidates the intricacies of cytokinesis, shedding light on the unique characteristics of cell division in plant and animal cells.
This article does an excellent job explaining the difference between cytokinesis in plant and animal cells, offering a thorough and understandable comparison.
I agree! It provides an in-depth explanation of the crucial role that cytokinesis plays in the process of cell division.
Yes, the article provides a detailed comparison of the differences in cytokinesis in plant and animal cells, highlighting the role of cell plate formation in plant cells and cleavage in animal cells.
The article effectively highlights the unique aspects of cytokinesis in plant and animal cells, showcasing the role of cell wall formation in plants and cleavage in animals.
I found the information about the distinct spindle apparatus behavior in plant and animal cells to be particularly insightful.
The article’s detailed examination of cytokinesis in plant and animal cells enhances knowledge and comprehension of the unique cellular division mechanisms associated with the two biological systems.
The comprehensive discussion of cytokinesis elucidates the key distinctions between plant and animal cells, contributing to a deeper understanding of cellular division processes.
The in-depth comparison of the mechanisms of cytokinesis in plant and animal cells provides a comprehensive understanding of the distinct cellular division processes.
The article’s detailed elucidation of cytokinesis serves as a valuable educational resource, elucidating the contrasting aspects of cell division in plants and animals.
The article presents a comprehensive overview of cytokinesis, delineating the key differences between the processes in plant and animal cells, thus enhancing the understanding of cellular division.
I found the explanation of the differences in spindle behavior during cytokinesis in plant and animal cells to be particularly enlightening.
The article provides a thorough comparison of the processes of cytokinesis in plant and animal cells, contributing to a deeper understanding of the biological concepts associated with cell division.
The detailed analysis of cytokinesis elucidates the specific roles of the spindle apparatus and cell plate in plant cells, offering valuable insights into the division process.