The Solar System has one star, eight planets, and one dwarf planet. However, what many people are not aware of is that these eight planets are divided into two categories which are known as Terrestrial Planets and Jovian Planets.
The group of Terrestrial Planets consists of Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are in the group of Jovian Planets.
So, how do these planets differ?
To understand this difference, we need to look into the composition of these planets. Terrestrial Planets have a solid surface, whereas Jovian planets have a gaseous surface.
Key Takeaways
- Terrestrial planets are rocky, more minor, and closer to the sun, with a solid surface and a thin or non-existent atmosphere; Jovian planets are larger, gaseous, farther from the sun, and have thick atmospheres.
- Terrestrial planets have shorter orbital periods, taking less time to revolve around the sun; Jovian planets have longer orbital periods due to their greater distance from the sun.
- Terrestrial planets have fewer moons, if any; Jovian planets have more moons and more extensive ring systems.
Terrestrial vs. Jovian Planets
Terrestrial planets are small and rocky planets located closer to the Sun, with a solid, rocky surface and thin atmosphere. Jovian planets are large and gaseous planets located farther from the Sun, mostly gas and ice, with no solid surface. They have thick, dense atmospheres and are colder than terrestrial planets.

Theoretically, the Terrestrial Planets have a surface similar to Earth’s, with a metallic core and a surface with a vast amount of silicate materials. On the other hand, Jovian Planets constitute mainly gases.
The gases present in major amounts are ammonia, hydrogen, helium, and methane. These planets supposedly have a molten rock as their core, though.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Terrestrial Planets | Jovian Planets |
|---|---|---|
| Main Difference | Terrestrial Planets have a solid surface. | Jovian Planets are primarily gas-covered planets. |
| Abundant Gases | Carbon Dioxide and Nitrogen. | Hydrogen, Helium, Ammonia. |
| Core | Usually, a dense metallic core. | A comparatively less dense, molten rock core. |
| Density | The overall density of the planet is high and more compared to Jovian Planets. | The overall density of the planet is low and lesser than Terrestrial Planets. |
| Examples | Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars. | Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. |
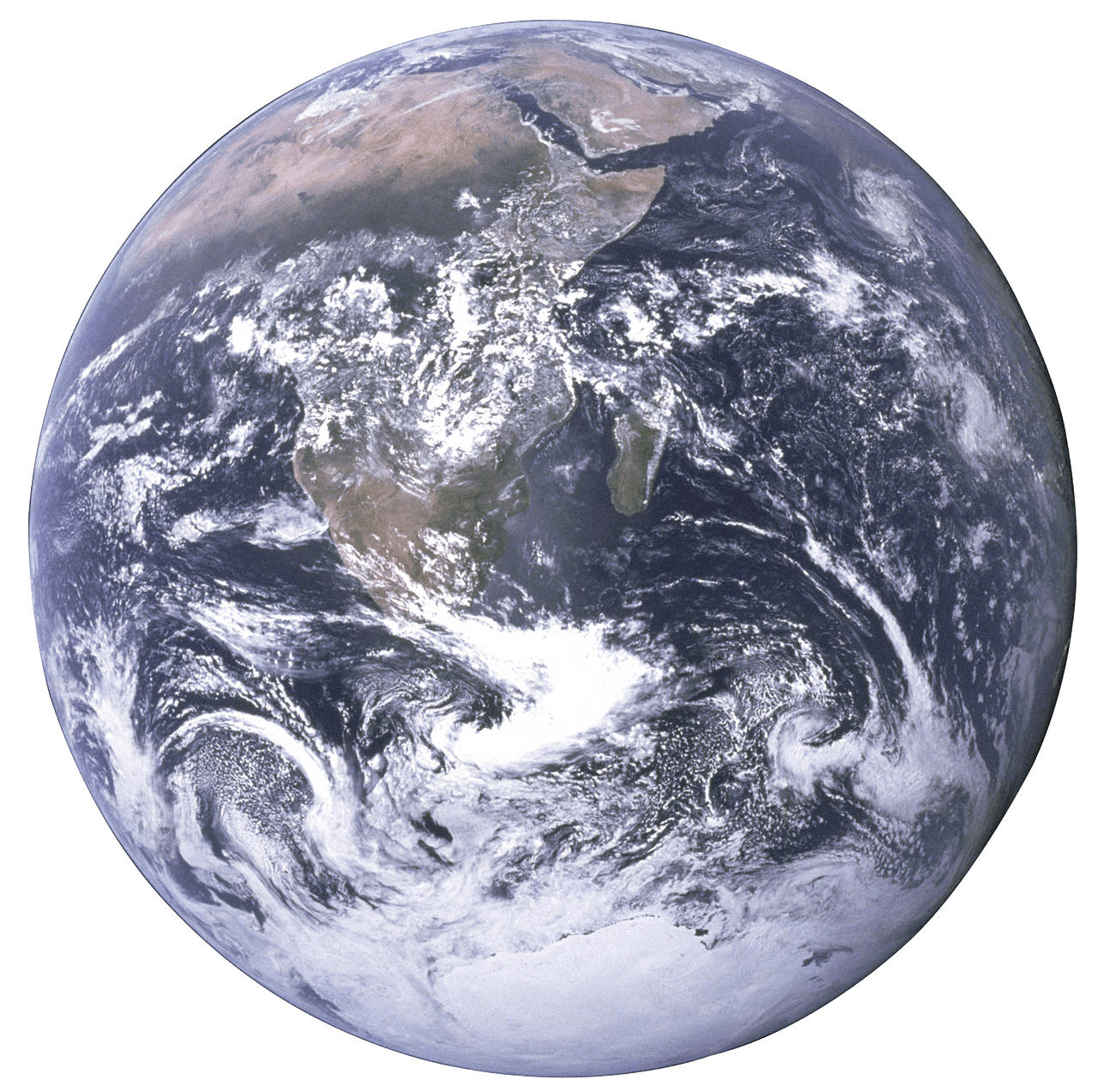
What are the Terrestrial Planets?
Terrestrial Planets can also be called Telluric planets. Both the words terrestrial and telluric have a Latin origin from the words terra and tell us; both of them mean Earth.
It is, however, important to understand that when we say Earth, we do not mean the planet Earth but the solid, rocky nature of the planet Earth. Terrestrial Planets have a rocky, solid surface made up primarily of metals and silicate substances similar to Earth’s surfaces, asteroids, etc.
Examples of Terrestrial Planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars.
One important characteristic of terrestrial planets is that none of them possess rings. We can see rings present around Saturn, but that is a Jovian Planet, and we will come to that later.
Terrestrial Planets can possess magnetic fields, but none of the terrestrial planets possess a global magnetic field, which means none of them have a unified magnetic field all around them. The moons of Mars and Earth have localized magnetic fields, but Earth is the only planet having a global magnetic field.
Only Earth, Venus, and Mars have a significant atmosphere among all the terrestrial planets. The atmosphere of Mercury does not have any solid constitution due to its proximity to relentless solar winds.
Also, among all the Terrestrial Planets, so far, Earth is the only planet that has been known to harbor life. This is due to its optimum location and distance from the Sun, thus resulting in an ambient temperature and having the perfect gaseous combination in its atmosphere to sustain life.
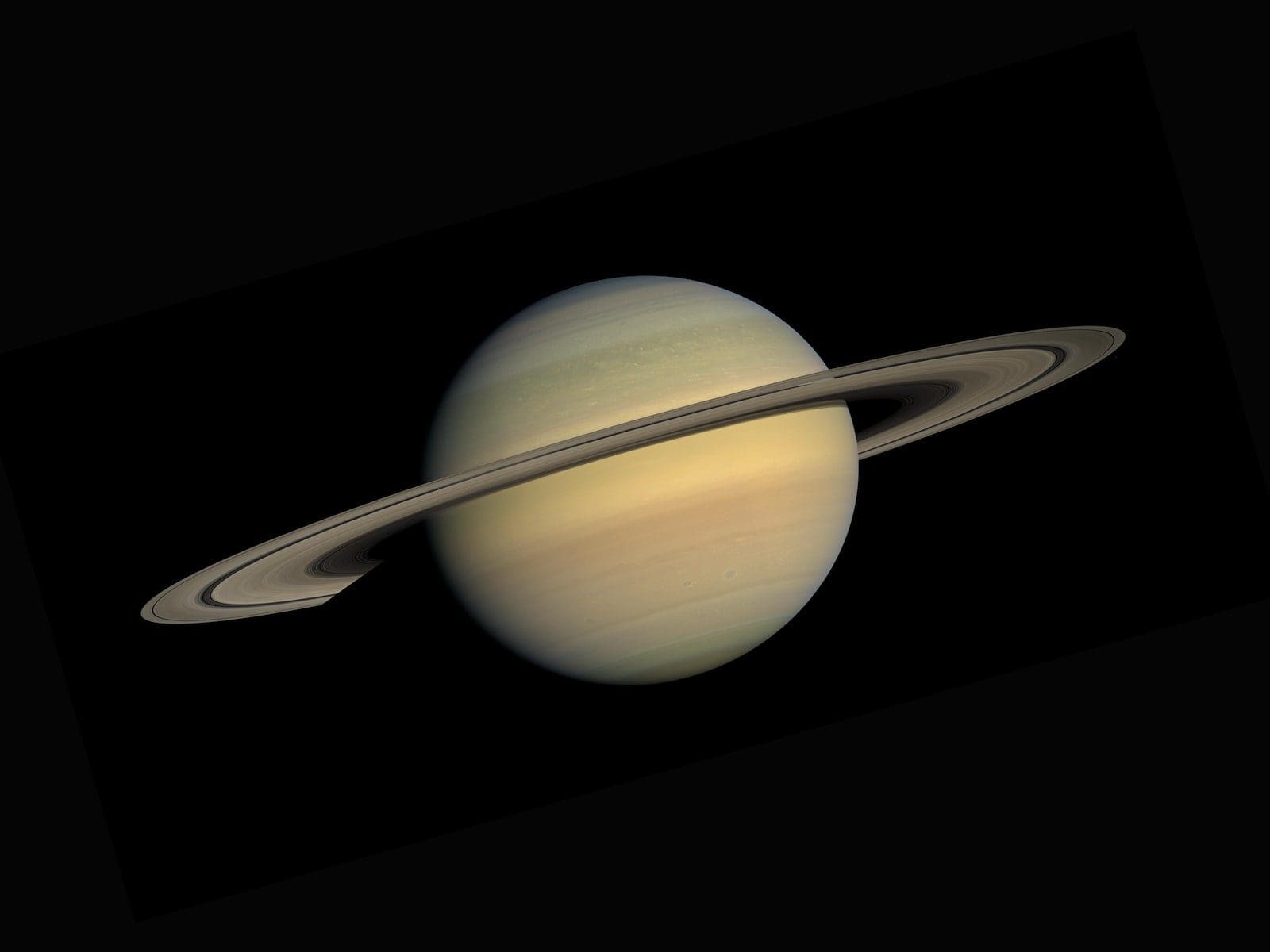
What are the Jovian Planets?
The word Jovian means Jupiter-like. This is because Jupiter is a giant gaseous planet, and all the remaining planets, which are Jovian, are gigantic compared to Earth and are largely constituted of gases.
Most of these gases are Hydrogen, Helium, and traces of other gases and ices. These planets still have a solid core, a solid molten rock.
A gaseous constitution, rings, and many satellites characterize these planets. The Jovian Planets are also referred to as ‘Gas Giants.’
The planets in this category are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
A significant characteristic of Jovian Planets is their large number of individual satellites. What is interesting is that one would expect that these moons would have similar characteristics.
However, the moons of Jovian Planets have such vast characteristics that they can also be categorized into groups of themselves. Discussing the rings of these planets, they are mostly myriad particles of ice, ranging from sizes of specks of dust to large boulders.
These rings are a marvel of physics, as they have a very complex way of interacting with gravity and electrical charges. Although this has been observed easily, it is worth mentioning that the Terrestrial planets are present in the inner part of the Solar System, and the Jovian Planets are present in the outer part.
Main Differences Between Terrestrial Planets and Jovian Planets
- The main difference between Terrestrial Planets and Jovian Planets is that Terrestrial Planets have solid and rocky surfaces with a dense metallic core. Jovian Planets have a large gaseous composition and a small, molten rock core.
- The most abundant gases present on Terrestrial Planets are Carbon Dioxide and Nitrogen. The main gases present in Jovian Planets are Helium, Hydrogen, and Ammonia.
- Terrestrial Planets have a dense metallic core, whereas Jovian Planets have a less dense molten rocky core.
- Terrestrial Planets have an overall high density, while Jovian Planets have a low density compared to Terrestrial Planets.
- Examples of Terrestrial Planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The planets under Jovian Planets are Saturn, Jupiter, Uranus, and Neptune.

- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0019103573900195
- https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/abs/10.1146/annurev.aa.18.090180.000453