Pollution is one trouble that almost all countries are facing in different intensities. It comes in different types, each affecting a different aspect of the environment, such as air, water, land or soil and noise.
Amongst these four types, air pollution is considered the most dangerous and impacting, being both visible and invisible simultaneously.
Air pollution is measured in terms of the pollutants in the atmosphere at unnatural levels, negatively affecting all living organisms.
The pollutants also vary in form, such as solid, liquid and gas.
Based on the source from which pollutants are emitted, there are two types of pollutants: primary and secondary.
Key Takeaways
- Primary pollutants are directly emitted from sources like factories and vehicles and harm human health and the environment.
- Chemical reactions between primary pollutants and other atmospheric substances form secondary pollutants.
- Primary pollutants include carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter, while secondary pollutants include ozone and acid rain.
Primary Pollutants vs Secondary Pollutants
The main difference between primary and secondary pollutants is their sources of emissions. While primary pollutants are emitted from a source directly into the atmosphere, secondary pollutants are formed due to any reaction amongst primary pollutants or between any primary pollutant and any other atmospheric particle.

Comparison Table
| Parameter of Comparison | Primary Pollutant | Secondary Pollutant |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Primary pollutants are emitted from a source directly into the atmosphere. | Secondary pollutants are pollutants formed either due to a reaction between primary pollutants or between a primary pollutant and any other atmospheric particle. |
| Form | Primary pollutants are particulate, aerosol, reduced or oxidised. | Secondary pollutants are oxidising. |
| Effect | Primary pollutants affect both directly and indirectly by impacting the atmosphere and through secondary pollutants, respectively. | Secondary pollutants might have a limited effect, except in the case of ozone, where it is highly reactive. |
| Control | Controlling primary pollutants can be done directly by controlling anthropogenic emissions. | Controlling secondary pollutants is quite complicated since it involves studying their creation process. |
| Example | Sulphur dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides and particulate matter are a few examples of primary pollutants. | Ozone, secondary particulate matter, etc., are a few examples of secondary pollutants. |
What are Primary Pollutants?
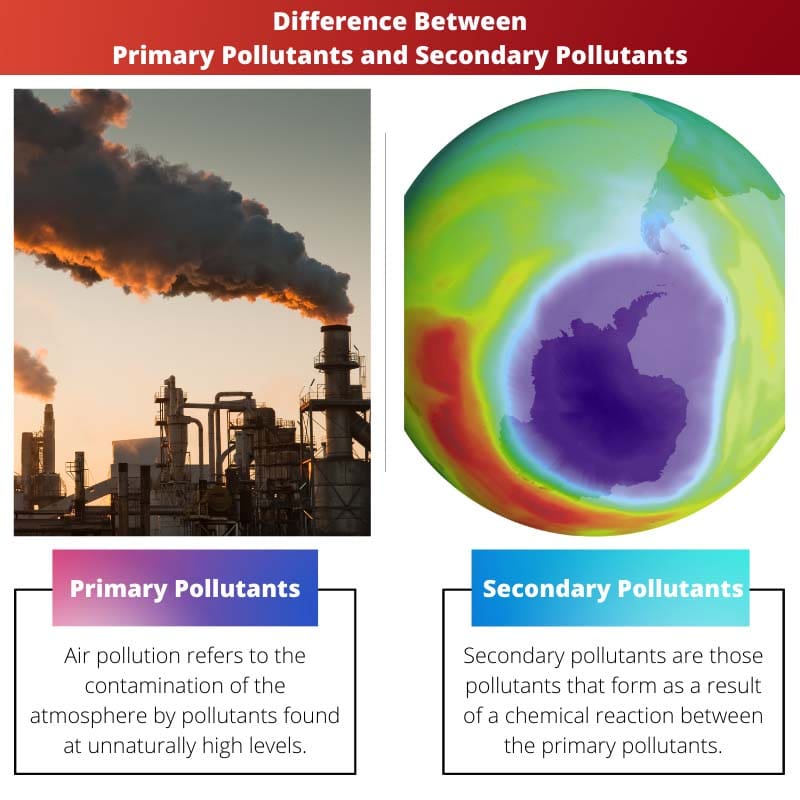
Air pollution refers to the contamination of the atmosphere by pollutants found at unnaturally high levels.
There are two types of pollutants: – Primary and Secondary. Primary pollutants are directly emitted into the atmosphere by a source.
These pollutants might be emitted by natural processes such as volcanic eruptions or man-made actions such as industrial emissions.
A primary pollutant is particulate matter, aerosol, reduced or oxidised. The effect of primary pollutants is both direct and indirect.
Primary pollutants are emitted by a source directly into the atmosphere, affecting all living organisms.
They also undergo a chemical reaction, forming secondary pollutants and indirectly affecting the ecosystem. For example, the formation of sulphur dioxide is a direct effect of primary pollutants.
Whereas sulphur dioxide reacting with water to form sulphuric acid, which is responsible for acid rain, is an indirect effect. The two main sources of these pollutants are natural and man-made.
And since nothing much can be done about the natural sources, the only way to control primary pollutants is by controlling the anthropogenic emissions such as vehicles and industries.
A few examples of primary pollutants are as follows: –
- Sulphur dioxide (SO2)
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx)
- Particulate Matter (PM)

What are Secondary Pollutants?
Secondary pollutants form as a result of a chemical reaction between the primary pollutants themselves or between any primary pollutant and any other particle in the atmosphere.
They are found in the oxidised form.
Secondary pollutants are said to have limited effects. These pollutants are products of primary pollutants and other atmospheric particles.
Thus, they are said to be inert or inactive. However, ozone is an exception in this case. Ozone is formed as a result of photoactivation.
This process makes the chemical reaction extremely reactive. Thus, in the case of ozone(O3), the effect is not limited.
The main source of secondary pollutants as primary pollutants and secondary pollutants are formed due to a chemical reaction between primary pollutants and other atmospheric particles.
Thus, controlling the production or emission of secondary pollutants is challenging since it involves understanding the complicated process of their creation. A few examples of secondary pollutants are as follows: –
- Ozone (O3)
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
- Sulphur trioxide (SO3)
These are called photochemical oxidants.
- Secondary particulate matter

Main Differences Between Primary Pollutants and Secondary Pollutants
- Primary pollutants are emitted directly into the atmosphere by a source. But secondary pollutants are formed due to a chemical reaction between primary pollutants or any other atmospheric particle.
- Primary pollutants are particulate matter, aerosol, reduced or oxidised. But secondary pollutants are in an oxidised form.
- While primary pollutants affect the ecosystem directly and indirectly, secondary pollutants have a limited and inert effect. However, ozone is an exceptional case of secondary pollutants. It undergoes the process of photoactivation, making the chemical reaction highly reactive and dangerous.
- Controlling the emission of primary pollutants can be done by reducing anthropogenic emissions such as vehicle emissions and industrial emissions. However, controlling the emission of secondary pollutants is arduous because it is formed through a reaction between primary pollutants and atmospheric particles. Thus, reducing its emissions involves thoroughly understanding the process of its creation and the elements involved.
- Sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides and particulate matter (PM) are a few examples of primary pollutants. But ozone, secondary particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide are a few examples of secondary pollutants.