Leukaemia is a blood cancer in common terms. It is a cancer of blood-forming tissues (including bone marrow) which inhibits the ability of the body to fight infection.
Key Takeaways
- Acute leukemia progresses rapidly and requires immediate treatment, while chronic leukemia develops slowly and may not need immediate intervention.
- Acute leukemia affects immature blood cells, whereas chronic leukemia affects more mature ones.
- Symptoms of acute leukemia are more severe and include fatigue, fever, and frequent infections, while chronic leukemia symptoms may be milder or absent.
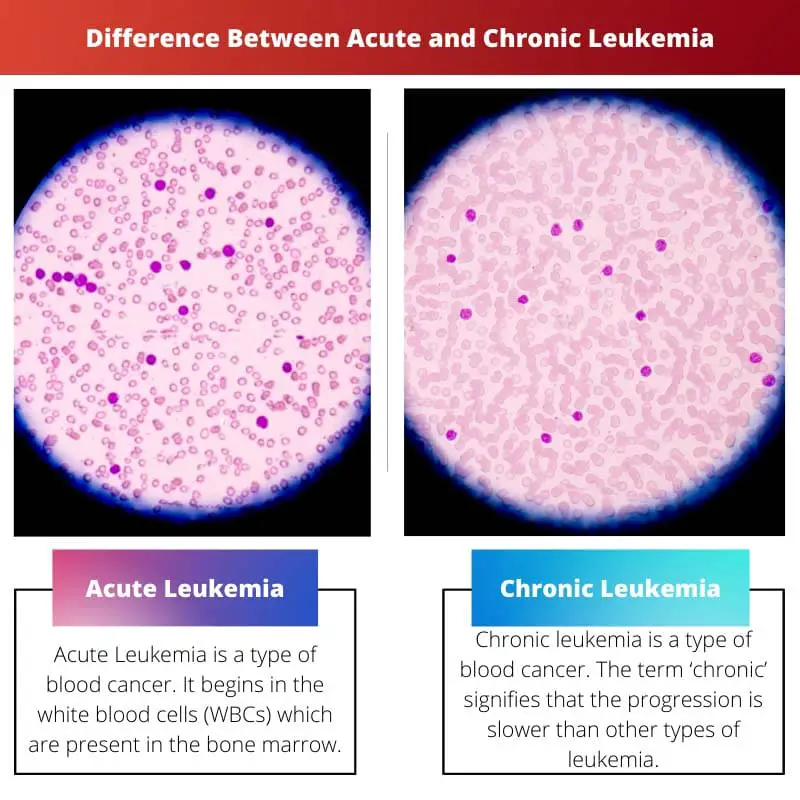
Acute vs Chronic Leukemia
Acute leukaemia is a rapidly progressing form of leukaemia with symptoms such as fatigue, fever, weight loss, bone pain, and increased susceptibility to infections. Chronic leukaemia is a slower-progressing form of leukaemia with symptoms such as fatigue, enlarged lymph nodes, and an enlarged spleen.
Acute leukaemia affects the stem cells and forms structures called blasts. It affects the lymphocytes and inhibits the functioning of the immune system. Acute leukaemia is of two types.
While chronic leukaemia hinders the development of blood stem cells, due to slow progression, the abnormal cells accumulate and stop functioning. Chronic leukaemia is of two types.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Acute Leukemia | Chronic Leukemia |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Prolonged contact with radiation and chemicals, or from infection or genetic disorders | Contact with certain chemicals, herbicides, and insecticides |
| Symptoms | Fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, stomach pain or swelling, joint pain, trouble breathing, headache, blurred vision, or unusual bleeding, pale skin | Enlargement of lymph nodes, abdominal pain in the left region, fever, weight loss, dizziness, difficulty in breathing and abnormal blood loss |
| Age group | In children | Older adults |
| Diagnosis | Examination of medical history and tests like complete blood count (CBC) test, bone marrow tests, spinal tap, imaging tests like X-rays, CT scan, or ultrasound | Lymphocytosis, complete blood count (CBC) test, smudge cell test, imaging tests like CT and PET (Positron Emission Tomography), clinical staging and Array-based karyotyping |
| Treatment | Chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, stem cell transplant, CAR T-cell therapy, and the drug tisagenlecleucel (kymriah) | Six types of treatment are available – watchful waiting, targeted therapy, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy with bone marrow (Peripheral stem cell transplant) |
What is Acute Leukemia?
Acute Leukemia is a type of blood cancer. It begins in the white blood cells (WBCs), which are present in the bone marrow.
Acute Leukemia does not form a tumour but spreads to vital organs like the brain, spleen, liver, or lymph nodes. It forms immature lymphocytes and affects the immune system.
Some common symptoms are fever, stomach pain, loss of appetite and rapid weight loss, fatigue, shortness of breath, and night sweats, while some develop red spots under the skin, which is called petechiae.
Acute leukaemia can be treated in two parts if diagnosed early – induction therapy (to kill leukaemia cells and bring them under control) and post-remission therapy (cycle of treatment for 2-3 years).
What is Chronic Leukemia?
Chronic leukaemia is a type of blood cancer. The term ‘chronic’ signifies that the progression is slower than in other types of leukaemia.
Though the exact cause of the change in DNA of the lymphocytes is not known, exposure to certain chemicals, herbicides, insecticides, or a family history of blood and bone marrow cancers or the development of Monoclonal B-cell Lymphocytes (MBL) causes excessive lymphocytes.
Chronic leukaemia does not develop major symptoms for a long time. Some common symptoms are fever, fatigue, night sweats, weight loss, enlargement of lymph nodes, blood loss from a small bruise or wound, pain in the abdomen, or the occurrence of frequent infections.
It can be diagnosed through blood tests, bone marrow biopsy, and Imaging tests. Six major types of treatment can be provided to a patient with Chronic leukemia while there are several types of treatment tested in clinical trials.
Main Differences Between Acute and Chronic Leukemia
- Acute leukaemia affects the stem cells and is called blasts, while chronic leukaemia affects the partially matured abnormal lymphocytic cells
- Acute leukaemia can include risk factors like smoking cigarettes, genetic abnormalities, exposure to radiation, or ongoing radiation therapy while chronic leukaemia includes risk factors like being a European descendant, age over 60, radiation exposure, or chemicals (like benzene and Agent Orange).