There are numerous distinctions within the group of tumors known as leukemias and among disorders categorized as lymphomas.
We’ll go over some of these differences, including definitions and origins, as well as cells, but it’s crucial to understand that there are certain exceptions.
One of leukemia’s traits is more common in some types of lymphoma than in others, and vice versa.
Key Takeaways
- Lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system, while Leukemia is a cancer of the blood cells.
- Lymphoma presents with enlarged lymph nodes, while Leukemia can present with symptoms such as fatigue, fever and frequent infections.
- Lymphoma is treated with chemotherapy and radiation, while Leukemia is treated with chemotherapy, radiation and bone marrow transplant.
Lymphoma vs Leukemia
Lymphoma is the growth of abnormal cells in the lymphatic system. It is a malignant tumor that spreads to other organs of the body. The symptoms are painless and this cancer is seen in older people. Leukemia is a type of blood cancer that affect young children. The symptoms of leukemia include weakness and bruising.

“Any cancer of the lymphatic tissue” is defined as lymphoma. Both cells and organs make up lymphoid tissue.
Organs such as the thymus, bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen, and cells (including certain white blood cells). The lymphocyte is the most frequent cell type in lymphoid tissue.
In addition to tissues, lymphoid tissue contains groups of cells that are strategically placed all through the body to fight off invaders.
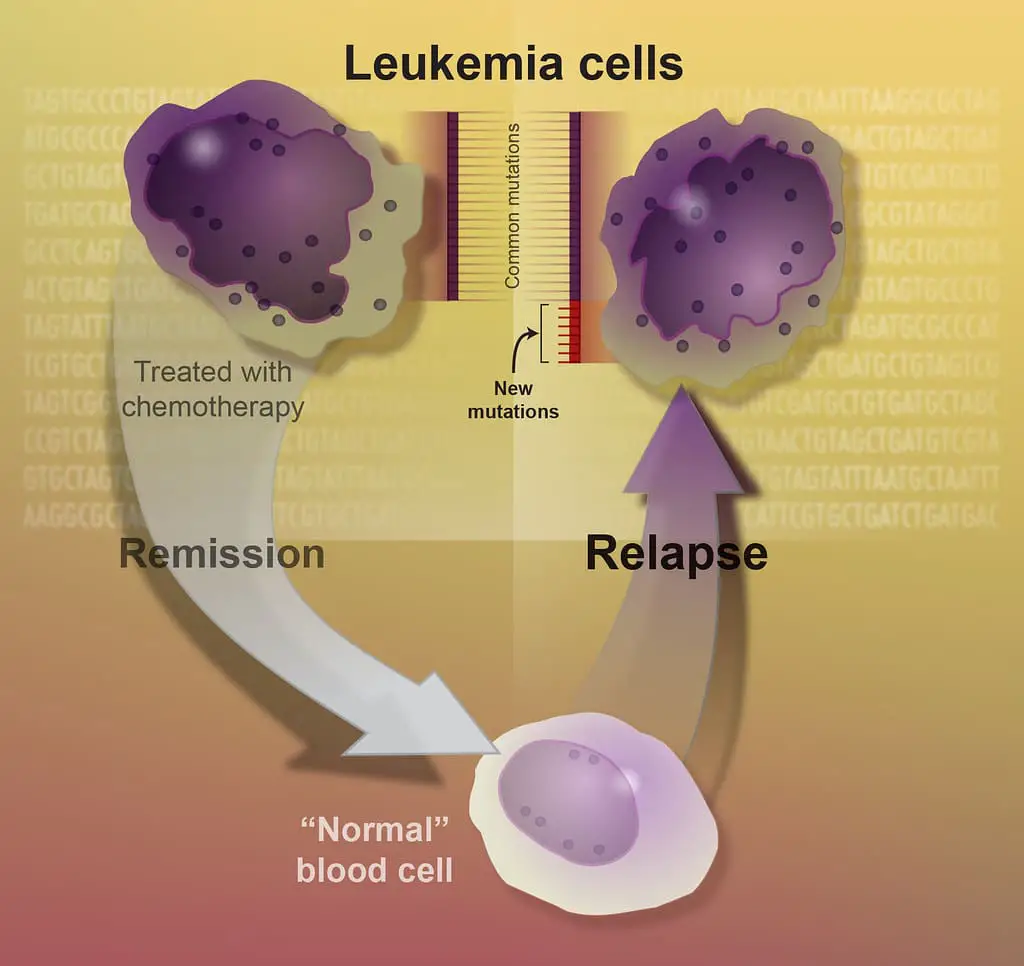
A persistent, malignant illness of the blood-forming tissues characterized by aberrant proliferation & evolution of leukocytes and their progenitors in the blood and bone marrow” is defined as Leukemia.
The bone marrow produces all red blood cells in adults, as well as the majority of white blood cells termed granulocytes, which are targeted in this form of malignancy.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Lymphoma | Leukemia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Defined as a malignant disease of blood-forming | Defined as any of the lymphoid tissue causing cancer |
| Causes | Lymphoma cells appear in the bloodstream | Excess white cells appear in the bloodstream |
| Age group | Mostly older people are affected | Happens among children |
| Common | It is a common type of cancer | It is a very rare cancer |
| Symptoms | Many painless symptoms | Many systems fall under this which is painful. |
What is Lymphoma?
Lymphoma is a type of cancer affecting the lymphatic system, a part of the body’s germ-fighting mechanism.
The lymphatic system (lymph glands), spleen, thymus gland, & bone marrow are all part of the lymphatic system.
All of these locations and other organs throughout the body can be affected by lymphoma.
Lymphoma comes in a variety of forms. Hodgkin’s lymphoma (previously known as Hodgkin’s disease) and Non-lymphoma Hodgkin’s are the two primary subtypes.
The type and severity of your lymphoma determine the optimal lymphoma therapy for you.
Chemotherapy, immunotherapy medicines, radiation therapy, a bone marrow transplant, or a combination of these treatments may be used to treat lymphoma.
Lymphoma is caused by an unknown factor, according to doctors. But it all starts with a genetic mutation in a disease-fighting white blood cell called a lymphocyte.
The mutation causes the cell to grow quickly, resulting in a large number of sick lymphocytes that continue to multiply. Lymphoma can be caused by several factors, including: What is your age?
Some lymphoma kinds are more common in young individuals, whereas others are diagnosed more frequently in persons over 55.
Males are somewhat more prone to get lymphoma than are females. Having an immune system that isn’t working properly.
Lymphoma is more likely in those who have immune system illnesses or who take immune-suppressing medications. The onset of certain infections.
For example, the Epstein-Barr virus and Helicobacter pylori infection are linked to an increased risk of lymphoma.
What is Leukemia?
Growth in the white blood cell count in your body causes leukemia, a blood cancer. White blood cells squeeze out all the red blood cells and platelets your body requires to stay healthy.
The additional white blood cells aren’t functioning properly.
Different forms of leukemia might result in various complications. You may not notice any symptoms in the early stages of some kind.
Symptoms that you may experience include: weakness or weariness, Bruising, and bleeding are easy to come by.
Whether it’s a fever or the chills, Severe infections, or infections that recur, Bone or joint pain is a common ailment. Seizures, Headaches, and Vomiting. Losing weight, Shortness of breath, and night sweats
Blood includes 3 types of cells: white cells, which fight infection, RBCs, which transport oxygen, and platelets, which aid in blood clotting.
Billions of red blood cells are produced by the bone marrow every day, the majority of which are red cells. When there is, the leukemia body produces more white blood cells than required.
Healthy white blood cells can fight off infection, but leukemia cells can’t. They start to alter the way your organs function because there are so many of them.
Red blood cells get reduced so much it could cause oxygen deficiency due to a shortage of carriers, and blood gets clotted by platelets or regular white blood cells to fight infection over time.
Main Differences Between Lymphoma and Leukemia
- Lymphoma is defined as a malignant disease that happens to the blood-forming tissues, whereas Leukemia is a cancer that affects the lymphoid tissues targeting tissues and organs.
- Lymphoma tissues appear in the bloodstream, whereas in Leukemia, white blood cells increase and become an issue for the bloodstream.
- The most affected age group is older people, whereas Leukemia is seen among children.
- Lymphoma is a common type of cancer, whereas Leukemia is very rare.
- Lymphoma symptoms are not painful, whereas it’s just the opposite case when it comes to Leukemia cancer.
- https://rupress.org/jem/article/154/5/1403/57112/Human-cutaneous-T-cell-lymphoma-and-leukemia-cell
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/gcc.10178

The differences in prevalence, causes, and origins of lymphoma and leukemia are well-articulated, adding depth to the understanding of these distinct types of cancers.
This article provides an excellent explanation about the differences between leukemia and lymphoma, providing a clear and concise comparison. The references are also very reliable.
The article elucidates the genetic and biological basis of lymphoma and leukemia effectively, laying a solid foundation for understanding the complexities of these diseases.
While the article provides valuable distinctions between lymphoma and leukemia, it would be beneficial to delve into the treatment modalities in more depth for a comprehensive understanding.
The comparison of symptoms and age groups between lymphoma and leukemia is particularly informative, shedding light on the distinct characteristics of each disease.
The information is presented in an organized and clear manner, making it easy to understand. The comparison table is particularly helpful in highlighting the key differences between lymphoma and leukemia.
I completely agree. The systematic approach of the article makes it an excellent resource for understanding the complex nature of these diseases.