The human respiratory system is composed of various organs and tissues. It enables breathing. It transports oxygen to the various cells and removes carbon dioxide and other gases.
The different parts include the Nostrils, nasal cavity, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. The bronchi branch and branch once after it enters the lungs.
Key Takeaways
- Alveoli are tiny, air-filled sacs responsible for gas exchange in the lungs, whereas bronchi are large, air-carrying tubes branching from the trachea.
- Alveoli have thin walls to facilitate oxygen and carbon dioxide diffusion, while bronchi have thicker walls lined with mucus to protect from infection and irritants.
- The human lung contains millions of alveoli, while the bronchi further subdivide into smaller bronchioles to distribute air throughout the lungs.
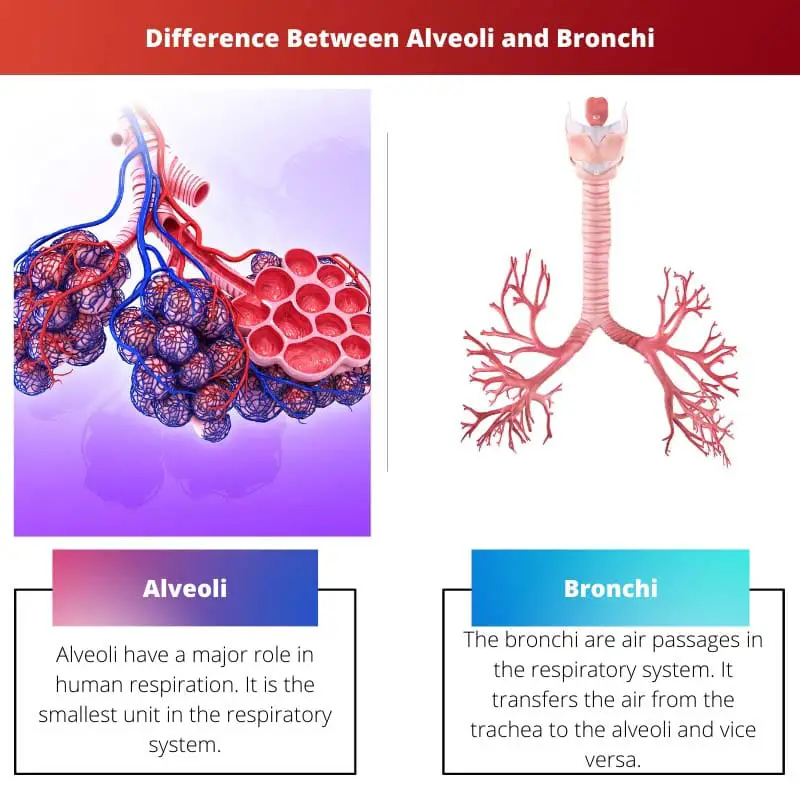
Alveoli vs Bronchi
Alveoli are small, grape-like air sacs at the end of the bronchioles in the lungs, where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place during the process of respiration. Bronchi are the two main branches of the trachea that lead to the lungs and are the larger air passages.
Alveoli are sac-like structures that are surrounded by blood capillaries. It has elastic walls and acts as the primary site for the exchange of gases. The balloon-like walls help in providing optimal surface area.
Human lungs contain billions of alveoli. The alveolar sac includes lots of alveoli. It appears as a bunch of grapes.
Bronchi are tube-like structures that lead to the lungs.
There are two primary bronchi in the human body – the right bronchus and the left bronchus. It branches out to bronchioles. It carries the air to the alveoli. Bronchi appear like the branches of a tree.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Alveoli | Bronchi |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Air sac inside the lungs. | Air passage in the respiratory tract. |
| Function | Exchanges gases. | Carries gases. |
| Divisions | Alveolar sacs | Bronchioles |
| Starting Point | Lung parenchyma. | Carina is the point where the trachea divides into bronchi. |
| Shape | Sac-like structure. | Branch-like structure. |
What are Alveoli?
Alveoli have a major role in human respiration. It is the smallest unit in the respiratory system. It is found at the end of the bronchi. The thin elastic walls of the alveoli pass oxygen and carbon dioxide into and out of the bloodstream.
The alveoli mark the end of the respiratory system. The millions of alveoli provide adequate surface area for gaseous exchange in the lungs.
The gases are exchanged by the process of diffusion. The carbon dioxide in the bloodstream is diffused out into the alveoli. On the other hand, oxygen in the alveoli diffuses and reaches the bloodstream.
The alveoli form the major part of the lungs. It constitutes more than half of the total volume of the lungs. The major development in the alveolar sac occurs from the gestation period to eight years of age.
The alveoli are made up of two kinds of cells: pneumocytes and pneumonocytes. They are called type 1 and type 2 cells. The alveolar macrophage acts as connective tissue between the cells.
The alveolar septa present in the alveolar sac separates each alveolus. It is made of elastic fibres and collagen fibres that make it stretchable.
The alveoli act as a cushion and it is the place where pathogens, drugs, and chemicals through the air are processed. It also produces pulmonary surfactants, hormones, and enzymes.
Diseases like pneumonia, emphysema, tuberculosis, and ARDS occur in the alveoli.
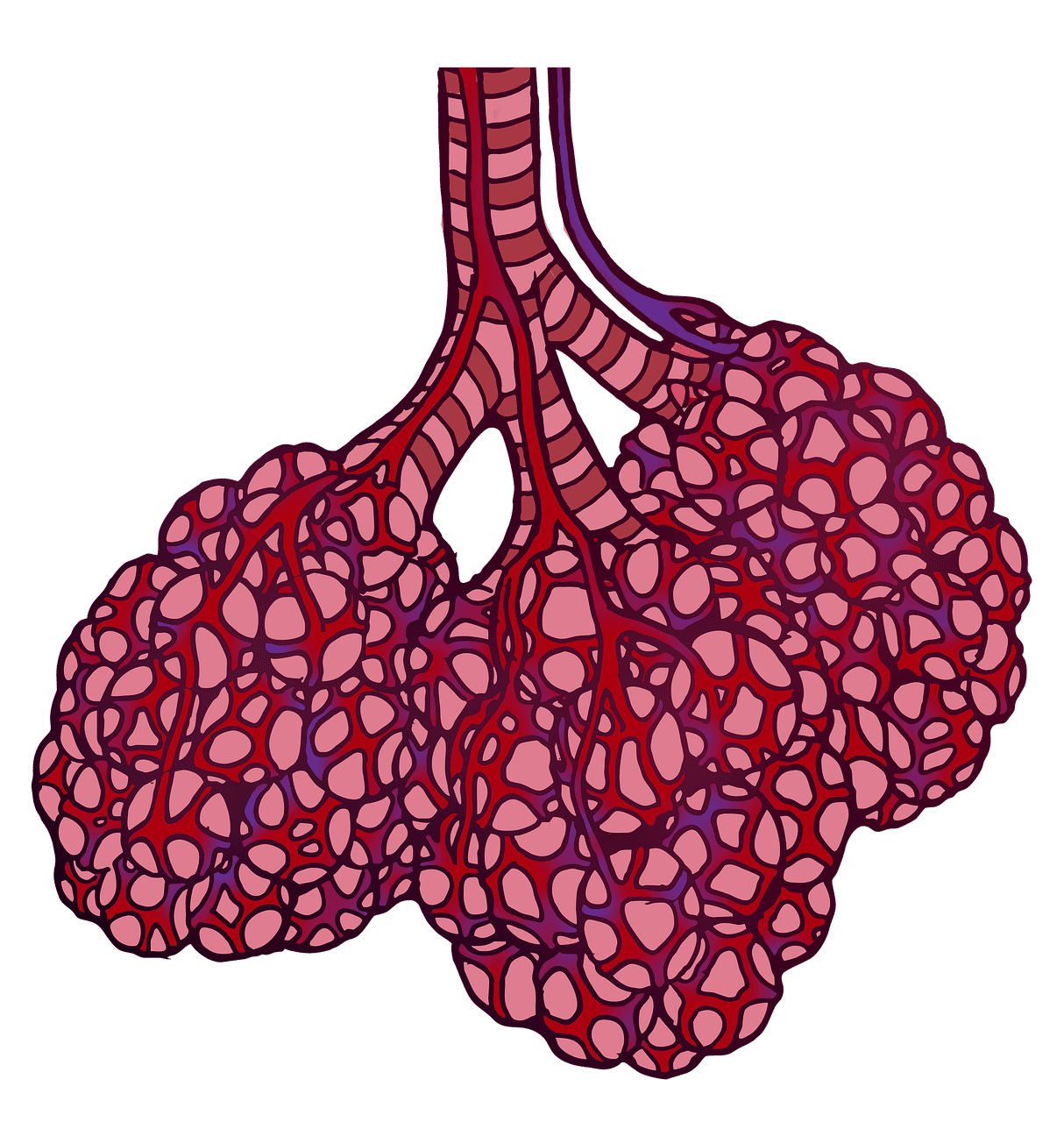
What are Bronchi?
The bronchi are air passages in the respiratory system. It transfers the air from the trachea to the alveoli and vice versa. From the carina, the trachea divides into the two bronchi. Carina is found at the end of the trachea. It is a cartilage.
The right bronchus is wider and comparatively shorter than the left bronchus. Each bronchus enters the right and left lung, respectively. The bronchi contain cartilage, smooth muscle, and mucous membranes.
The cartilage present in the bronchi prevents its collapse and supports it during respiration. The mucous membranes prevent the entry of harmful substances into the lungs and avoid infectious agents. The mucous blanket purifies the air.
The subdivision of bronchi is called bronchioles. Unlike bronchi, bronchioles don’t have hyaline cartilage, but the number of smooth muscles increases.
The bronchial tree, also known as the respiratory tree, is constituted by trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and respiratory bronchioles. The bronchus enters the lung at a notch called the hilum.
The primary bronchi further divide into lobar bronchi or secondary bronchi. There are two lobar bronchi in the left lung and three in the right lung.
The lobar bronchi split into tertiary bronchi, which form bronchopulmonary segments on further division.
The final bronchi branch is the bronchioles. There are thousands of bronchioles in each lung, and they lead to the alveolar ducts.
Conditions like asthma, bronchitis, and bronchopulmonary dysplasia arise in the bronchi.
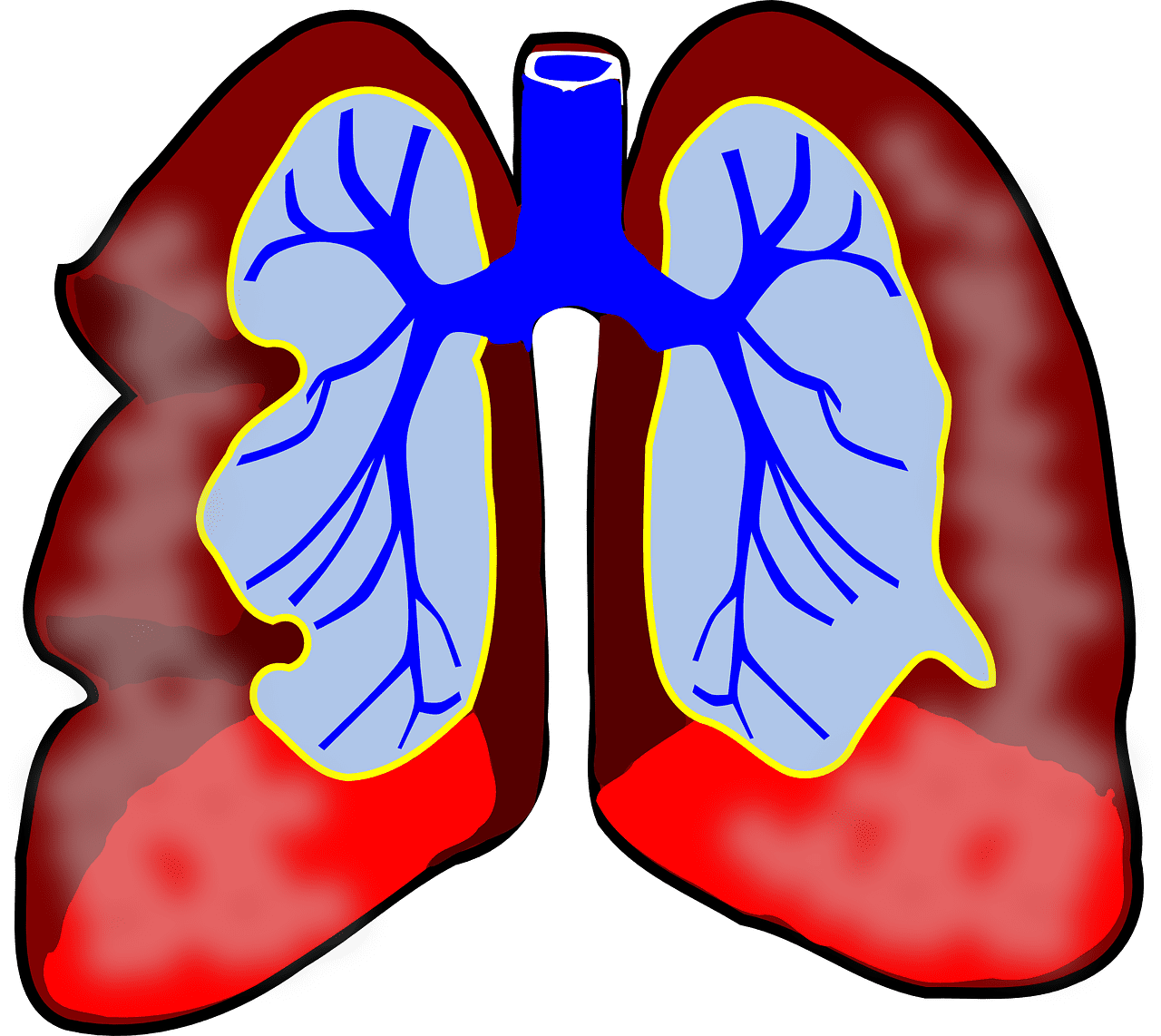
Main Differences Between Alveoli and Bronchi
- The alveoli are found at the end of the bronchioles as a tiny air sac, whereas the bronchi start at the fifth thoracic vertebra.
- The shape of the alveoli is like that of a sac or like a cup, and it is elastic. The alveolar sac has the structure of a bunch of grapes or raspberries. But the bronchi appear like a tube, and it is not so stretchable. The whole bronchial divisions together form the shape of an inverted tree.
- When it comes to functions, the alveoli do the task of gaseous exchange, while the bronchi act as an air passage that connects to the trachea.
- The bronchi have further divisions like lobar bronchi and bronchioles. However, the alveoli have only a cluster formation called an alveolar sac, and it occurs in the acini.
- The alveoli are made up of pneumocytes and pneumonocytes. The bronchi are lined by respiratory epithelial cells and contain cartilage, mucous membranes, and smooth muscles.
- There are millions of alveoli in the human lungs, but there are only two primary bronchi.