Protein is an important component of our diet. It helps build strength and muscles. It repairs the cells and supports growth. The makeup of this protein includes amino acids.
Amino acids are organic compounds that are responsible for producing proteins. There are two kinds of amino acids, namely, Essential and Non-Essential Amino Acids. Their categorization is established upon the body’s ability to synthesize them.
Key Takeaways
- The body cannot synthesize essential amino acids, which must be obtained through diet.
- The body can produce non-essential amino acids not required from dietary sources.
- Both types are crucial for protein synthesis and overall bodily function.
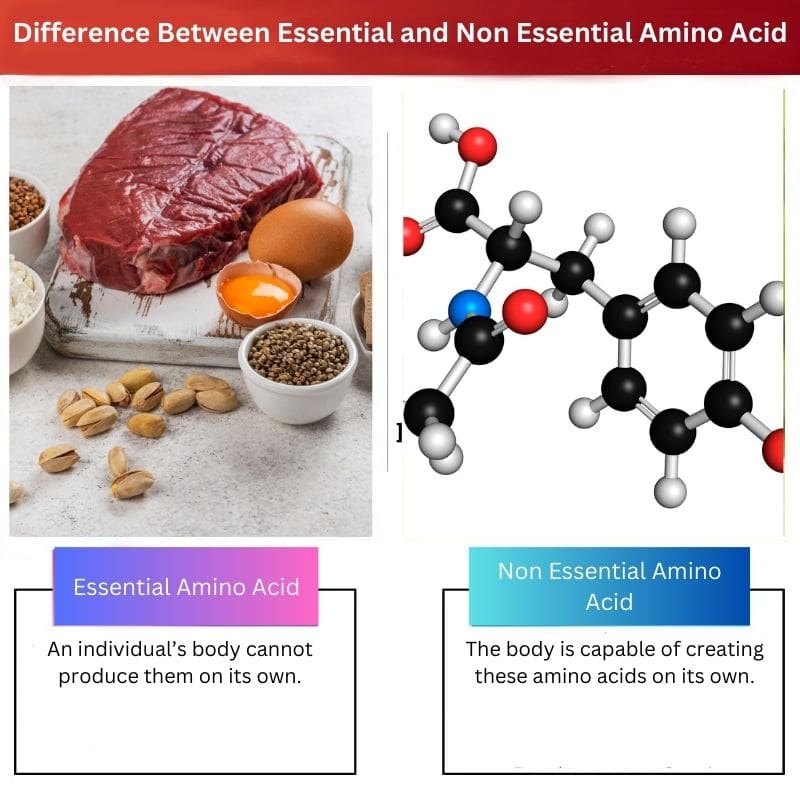
Essential vs Non Essential Amino Acid
Essential amino acids are those that can’t be synthesized by the body and must come from food sources. There are 9 essential amino acids. Our bodies can produce non-essential amino acids even without getting them from external food sources. There are 11 non-essential amino acids.

The amino acid that an organism’s system cannot produce is known as an essential amino acid. Therefore, it must be taken in from external sources and included in the diet.
Out of twenty amino acids, there are nine that are called essential amino acids. Yet another term used for these amino acids is indispensable amino acids.
The amino acid that an individual’s system can create and synthesize by itself is called a nonessential amino acid. One does not need to include them in their dietary habit.
Of the twenty amino known to humanity, eleven are nonessential. These amino acids are quite beneficial in ousting toxins from the body.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Essential Amino Acid | Non Essential Amino Acid |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An individual’s body cannot produce them on its own. | The body is capable of creating these amino acids on its own. |
| Function | They work to repair and build muscle tissues. For the formation of the neurotransmitters in the brain, they produce precursor molecules. | They work to remove toxins, help in the functioning of the brain, and are also efficient in synthesizing RBCs and WBCs. |
| Sources | As they need to be included in the diet, their sources include egg, chicken, quinoa, meat, etc. | The body creates them by itself after breakdown the already existing amino acids. |
| Number | There are nine essential amino acids. | These are eleven in number. |
| Deficiency | One may likely face a deficiency of these as they are not self-produced by the body. | Even though it’s rare to experience a deficiency of these, it still might occur due to poor health or starvation. |
What is Essential Amino Acid?
It is not possible for the body to create the essential amino acids on its own. Therefore, it needs to be accessed through external sources, which means it must be included in the diet.
In totality, there are nine such essential amino acids. For a high degree of net protein utilization, it is necessary that one must have an intake of balanced essential amino acids.
All in all, twenty-one amino acids are known to exist, and these are common to all living organisms. Out of these, nine essential amino acids cannot be synthesized from scratch by an organism at a speed quick enough to meet the requirement of the body.
The daily recommended intake of these amino acids varies and keeps changing over time.
These essential amino acids are important for building and repairing muscle tissues of the organism’s body. It also undergoes a process that catalyzes the production of precursor molecules.
These molecules, in turn, assist in the development of neurotransmitters in the brain. Because they are obtained from external sources, it is usual for them to become deficient in the body.
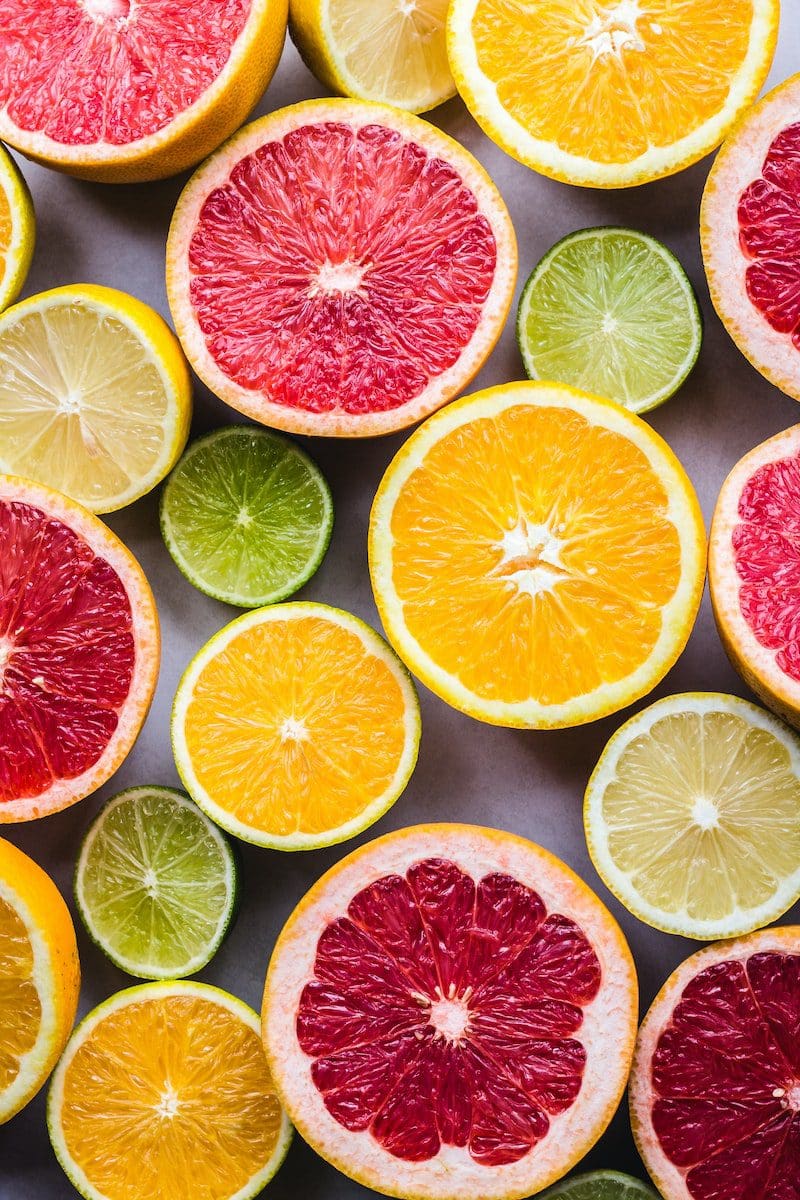
These amino acids are acquired through food items. These food items include eggs, meat, quinoa, chicken, vegetable protein, etc. The intake that is required for these amino acids on a daily basis is higher in minors as compared to fully grown adults.

What is Non Essential Amino Acid?
The body of an individual is capable of creating nonessential amino acids. An individual’s body makes them by using the essential amino acids that have already been consumed.
They are also produced when the existing proteins disintegrate. That is the reason why one doesn’t need to consume them from external sources.
Out of the total number of amino acids, these are eleven in number. They are synthesized within the human body in various ways. They are considered to be the building blocks of protein that carry out multiple essential functions.
They are extremely helpful in the removal of toxins. It also accelerates the functioning of the brain. Also, it assists in synthesizing Red Blood Cells and White Blood Cells in the body.
Apart from this, they serve many other functions. Usually, one doesn’t encounter a deficiency of these unless they are sick or aren’t receiving enough nutrition.
Since they are produced within the body by themselves, they need not be taken in from food items. A majority of these amino acids are formed from alpha ketoacids by undergoing a chemical process known as transamination.
They are also said to be created from the disintegration of glucose present in the body.
Main Differences Between Essential and Non Essential Amino Acid
- The body of an individual does not manufacture the essential amino acid as opposed to the non-essential amino acids that the body is capable of manufacturing on its own.
- Essential Amino Acids are to be taken in from external sources, that is, via food, whereas non-essential amino acids produce themselves. They do so by breaking down the protein components already available in the body or by using the pre-existing essential amino acids that an individual may have consumed.
- Out of the total number of amino acids in organisms, nine are essential, and the remaining eleven are non-essential amino acids.
- Essential amino acids serve to repair as well as build the tissues of muscles, whereas non-essential amino acids work on removing certain toxins that are present in the body as well as help in synthesizing WBCs and RBCs.
- One can encounter a deficiency of essential amino acids, but it is quite unlikely for one to be found deficient in non-essential amino acids.

The detailed explanation of essential and non-essential amino acids, including their sources and impact on bodily health, is highly informative.
I found the section on essential amino acids particularly enlightening, emphasizing the need to include them in our diet for optimal health.
The distinction between essential and non-essential amino acids and their functions in the body is explained in a clear and concise manner.
Absolutely, the article effectively communicates the significance of essential amino acids that must be obtained from dietary sources.
The article effectively outlines the differences between essential and non-essential amino acids, providing valuable insights into their roles in protein synthesis and bodily functions.
I appreciate the inclusion of the comparison table, which neatly summarizes the key characteristics of essential and non-essential amino acids for easy reference.
The article’s explanation of the importance of essential amino acids in building and repairing muscle tissues is particularly enlightening.
The article offers a thorough overview of essential and non-essential amino acids, shedding light on their impact on overall bodily function and health.
I agree, the article effectively communicates the importance of these amino acids in maintaining optimal health and well-being.
I found the detailed explanation of both essential and non-essential amino acids to be educational and insightful.
The detailed comparison between essential and non-essential amino acids provides valuable insights into their functions and dietary requirements.
The article’s explanation of the sources and deficiency risks of essential and non-essential amino acids is highly informative and practical.
The distinction between essential and non-essential amino acids is well articulated, providing a comprehensive understanding of their sources and functions in the body.
The article effectively conveys the significance of non-essential amino acids and their role in the synthesis of essential proteins that carry out vital bodily functions.
The article’s comprehensive explanation of both essential and non-essential amino acids offers valuable knowledge on the importance of these compounds in sustaining overall bodily function and health.
Absolutely, the article effectively addresses the significance of essential and non-essential amino acids and their impact on human health and well-being.
The article provides a comprehensive understanding of essential and non-essential amino acids, highlighting their importance in protein synthesis and bodily functions.
I agree, it also sheds light on their sources and the impact of deficiencies in these amino acids.
The comparison table effectively illustrates the differences between essential and non-essential amino acids, making it easier to understand their roles.
The article effectively distinguishes between essential and non-essential amino acids, emphasizing their roles in protein synthesis and overall bodily health.
I found the section on recommended daily intake of these amino acids to be particularly insightful, providing practical guidance for maintaining a balanced diet.