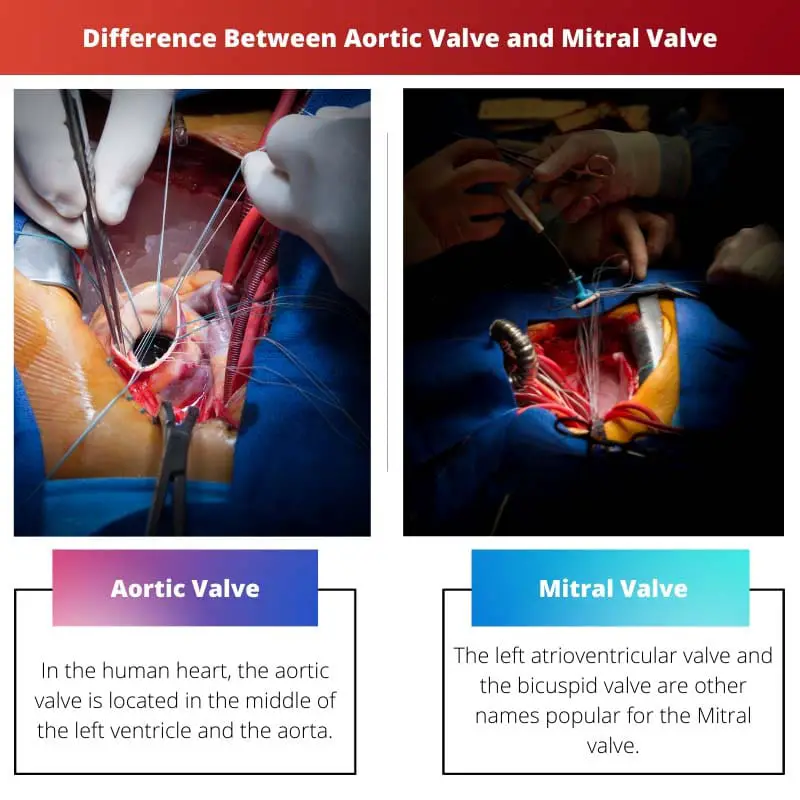
For the whole circulatory system, valves perform an important function. The aortic valve and mitral valve are two kinds of valves.
The aortic valve and mitral valve ensure that blood flows through the heart and should be unidirectional. They both are located in the heart’s left side, allowing oxygenated blood to flow.
Key Takeaways
- The aortic valve regulates blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta, while the mitral valve controls blood flow between the left atrium and the left ventricle.
- The aortic valve has three cusps or leaflets, whereas the mitral valve has two.
- Aortic stenosis and regurgitation are common issues with the aortic valve, while mitral valve prolapse and regurgitation affect the mitral valve.
Aortic Valve vs Mitral Valve
The aortic valve is a one-way valve located between the left ventricle of the heart and the aorta, regulates the flow of oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the body. The mitral valve is a heart valve that separates the heart’s chambers, ensures the proper one-way flow of blood, present between the left atrium and the left ventricle.
In the human heart, the aortic valve is located in the middle of the left ventricle and the aorta. It consists of three leaflets or cusps.
The left atrioventricular and bicuspid valves are other names popular for the Mitral valve. It lies in the middle of the left atrium and left ventricle.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Compadrison | Aortic Valve | Mitral Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Location | In the middle of the left ventricle and the aorta | In the middle of the left atrium and left ventricle |
| Type of valve | Semilunar valves | Atrioventricular valves |
| Rhythm | When the mitral valve opens aortic valve closes | When the aortic valve opens, the mitral valves close |
| Role | Supplies blood to the aorta | Supplies blood to the left ventricle |
| Flaps | Three flaps | Two flaps |
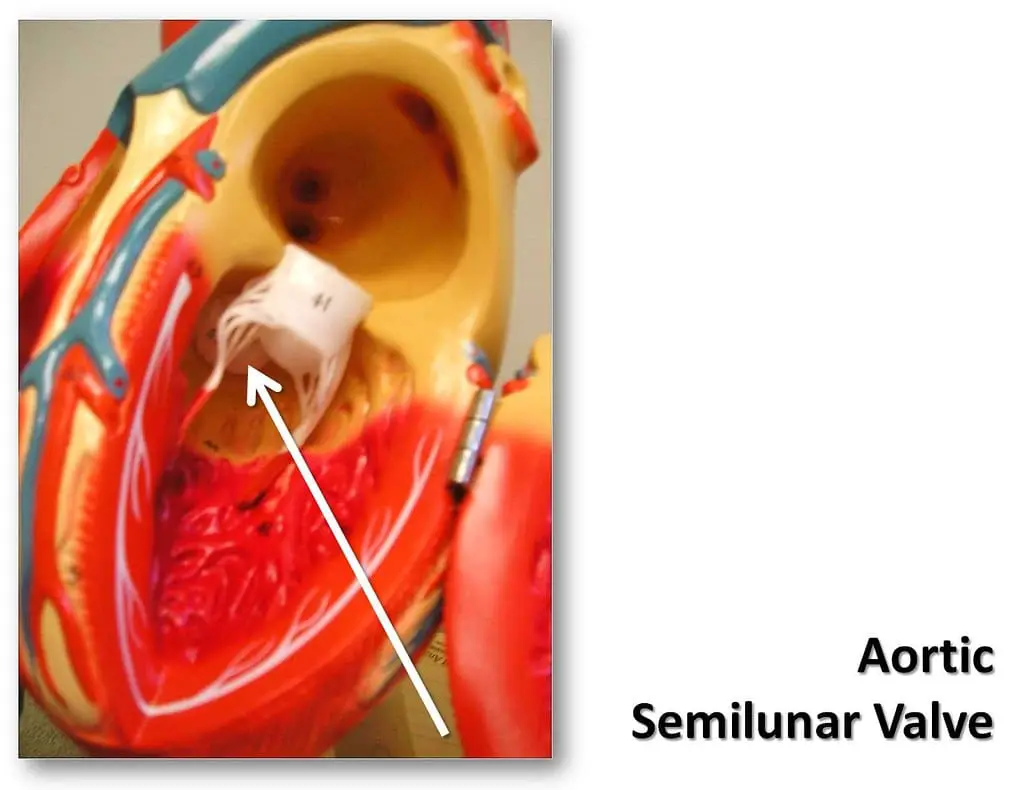
What is an Aortic Valve?
The aortic valve is one of the two kinds of the semilunar valve. It is located in the middle of the left ventricle and the aorta.
The left ventricle contracts to allow the flow into the aorta of the oxygenated blood at the ventricle systole. The chief artery of the body is the aorta, which supplies oxygenated blood throughout the body.
The ventricle relaxes at diastole, and inside the ventricle leads to low pressure. As a result, the blood present inside the aorta moves back to the left ventricle. But to prevent this situation, the aortic valves close themselves.
This process allows the supply of blood with pressure to the aorta. There are mainly two types of clinical conditions related to aortic valve aortic stenosis and aortic insufficiency/ aortic regurgitation.
What is Mitral Valve?
The mitral valve is one of the two types of left atrioventricular valves. It is in the middle of the left atrium and ventricle.
Through the pulmonary veins, the left atrium from the lungs receives oxygenated blood. With the help of the left ventricle, this blood is transferred to the aorta.
After this, the mitral valve comes into the role of preventing the blood flow in the backward direction. At this moment, the mitral valve is closed. .
There are mainly three types of clinical problems that occur in the mitral valve. The first is the mitral valve prolapse, in which the valve muscles start losing. The second is mitral valve stenosis, and the last is mitral valve regurgitation.
Main Differences Between Aortic Valve and Mitral Valve
- The semilunar valve closure, together with the aortic valve, produces the second heart or dub sound, while the closure of the atrioventricular valves, together with the mitral valve, produces the first heart or club sound.
- From the left ventricle, the aortic valve supplies the blood. On the flip side, the mitral valve supplies the blood from the left atrium.