Aquaculture and pisciculture are two modern-day cultivation techniques. Aquaculture and pisciculture are cultivated in both marine water and fresh water under monitored habitat and nutrition.
In both types of cultivation, the product so obtained is used in gaining commercial values and incomes. Aquaculture relatively develops commercially profitable flora.
Key Takeaways
- Aquaculture cultivates and harvests aquatic organisms, including fish, shellfish, and plants, for food or other purposes.
- Pisciculture explicitly involves the breeding, raising, and harvesting of fish, making it a subset of aquaculture.
- Aquaculture encompasses a broader range of species and techniques than pisciculture, which focuses solely on fish production.
Aquaculture vs Pisciculture
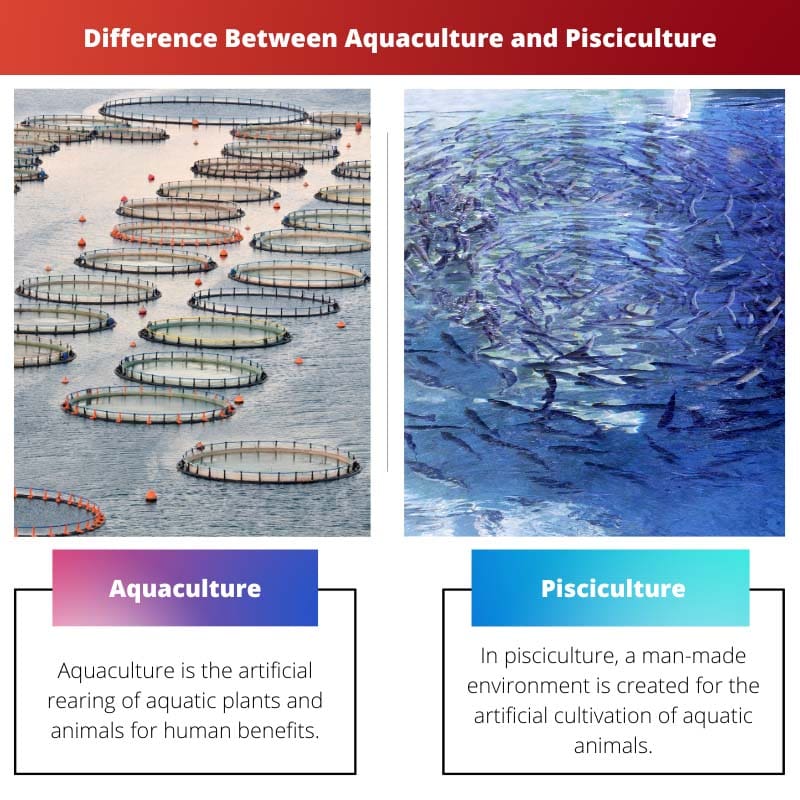
The difference between aquaculture and pisciculture is that aquaculture is the rearing and breeding of aquatic flora and fauna of seawater and freshwater. On the other hand, pisciculture deals with only fish and crustaceans. Also, pisciculture is a branch or category of aquaculture.

Aquaculture is the artificial cultivation of aquatic animals as well as plants. This rearing of aquatic livestock is monitored under a controlled environment.
Lotus, Lily, algae culture, and many more aquatic plants and aquatic animals such as fish, molluscs, and many more species are harvested after they are fully matured.
Pisciculture is the controlled cultivation of fishes, molluscs, and many more species of aquatic animals in the artificial habitat. These aquatic animals belong to freshwater or marine water.
The cultivation is processed under a controlled environment of temperature, competition, predation, and nutrition. More than 70% of the world’s demand for fish is fulfilled through pisciculture.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Aquaculture | Pisciculture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Aquaculture is the artificial rearing of aquatic plants and animals for human benefits. | In pisciculture, a man-made environment is created for the artificial cultivation of aquatic animals. |
| Types | Aquaculture is categorized into two categories namely inshore and onshore aquaculture | In pisciculture, the harvesting of fish is done in offshore cultivation. |
| Uses | The products obtained from aquaculture are supplied to the food industry, medicinal industry, and floral industry. | The products obtained from pisciculture is supplied only to the food industry |
| Factors | Aquaculture is affected by many factors such as humidity, temperature, and sunlight. | Pisciculture is affected by factors such as competition, predation, matting, and nutrition. |
| Habitat | In aquaculture, the habitat of cultivating species may be seawater, freshwater, and brackish water. | In pisciculture, the cultivating species of aquatic animals may belong to seawater and freshwater habitat. |
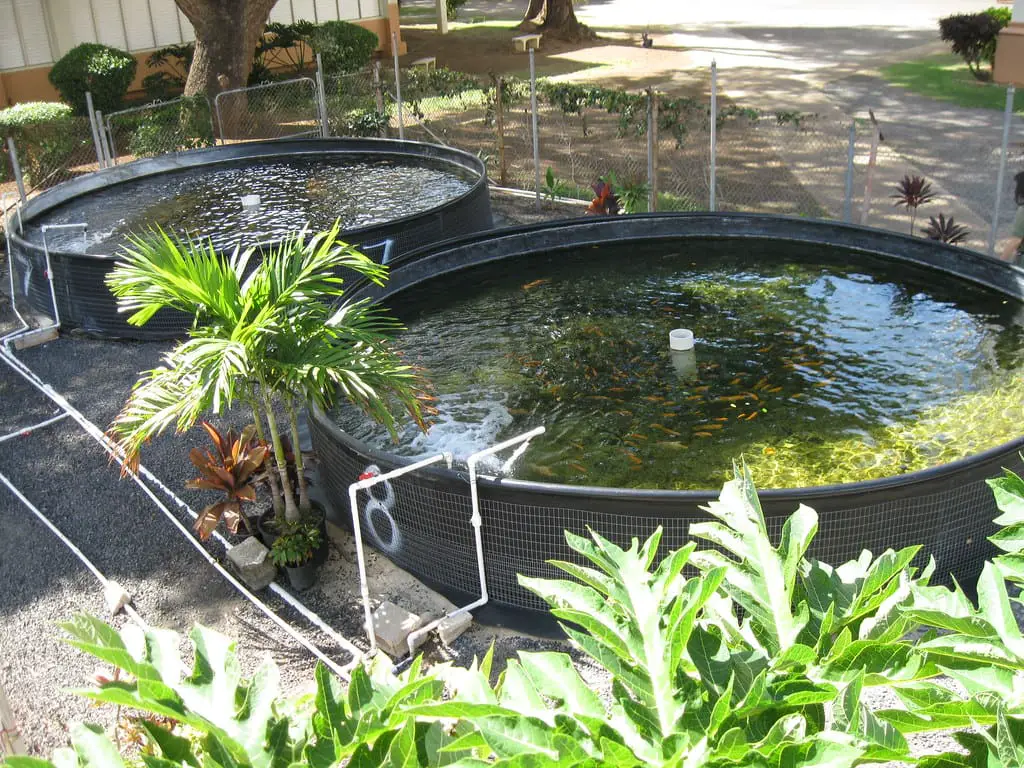
What is Aquaculture?
Aquaculture is known as aquaculture or aquafarming. Aquaculture is the cultivation of aquatic animals and plants in a controlled environment.
These aquatic animals belong to the category of fish, molluscs, and crustaceans whereas aquatic plants such as lily, lotus, and algae culture.
The aquaculture contains fish culture and mariculture. Aquaculture involves the cultivation of organisms from brackish water, freshwater, and saltwater habitat.
The ecosystem developed for rearing these organisms is very controlled and suitable for their development. Also, very aquaculture is performed for commercial purposes such as selling fish, molluscs, etc.
Mariculture is defined as the controlled cultivation of marine or seawater fishes for commercial purposes.
This is a specialized type of aquaculture exercised in salty water climates or lagoons. Depending upon the environment, aquaculture is broadly classified into two categories.
In the first category, cultivation is practiced in an artificial environment built on land and is preferably known as onshore aquaculture.
All the living factors such as humidity, oxygen saturation, temperature, and food intake are managed by humans. Some of the common examples of onshore aquaculture are fish tanks, raceways, and aquariums.
While talking about the inshore aquaculture, a well-constructed shelter beside the shore is maintained to provide a natural habitat and ecosystem. Also, this facilitates the natural migration of organisms and maintenance of main nutrient cycles.
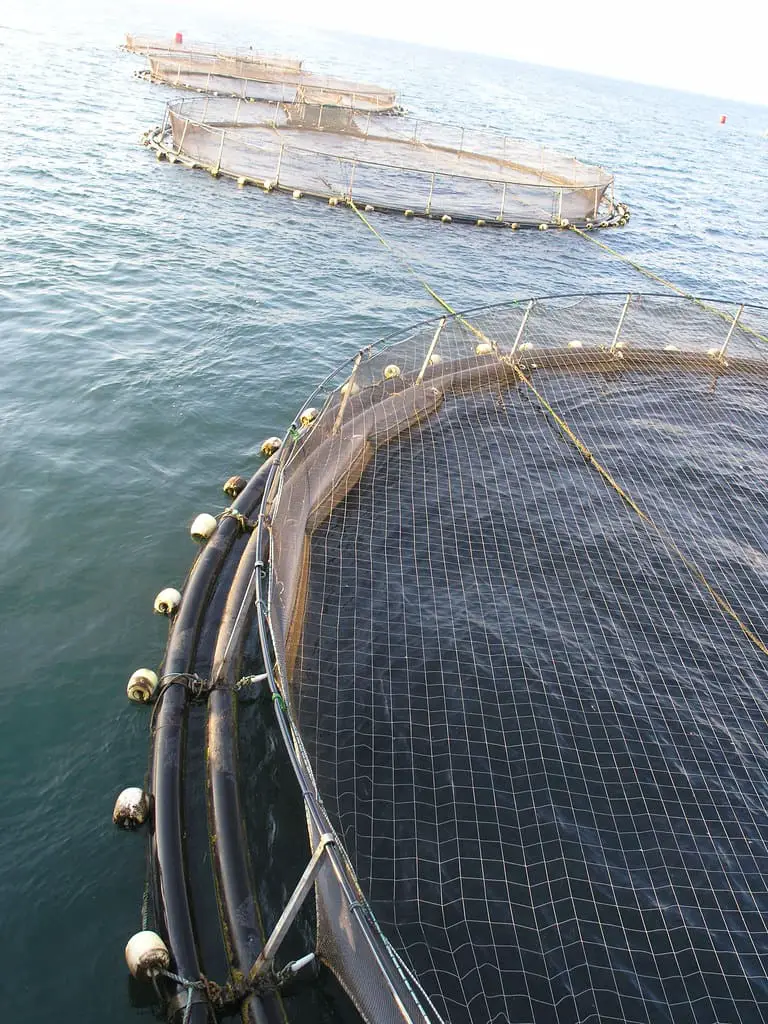

What is Pisciculture?
Pisciculture is commonly known as fish culture or fish farming. Pisciculture includes the commercial cultivation of marine and freshwater aquatic organisms in natural and man-made environments.
These organisms undergo commercial breeding for the supply in the food industry.
The aquatic organisms which are commercially cultivated belong to the crustacean, fishes, and molluscs categories.
According to the worldwide fishery industry, the most significant species of fish included in commercial breeding are salmon, rohu, catla, and carp.
The environment developed for breeding is somewhat similar to the natural habitat or artificial habitat with a natural presence.
A well-known fact about fish is that they are full of dietary proteins and fibers. The global demand for these fishes has increased suddenly which leads to overfishing and a decrease in the number of fishes or even the vanishing of whole species.
The cultivation of fish artificially helps them to prevent competition, escape from natural predators, and proper nutrition. According to the world stats, China itself supplies 62% of the total world’s fishery production.
Fish farms are named cage systems and open net-pen systems. These integrated fish cages are positioned in ponds, lakes, and rivers, to defend the fishes until they are matured.
This procedure is known as “off-shore cultivation”. These fish cages are provided with artificial food and reared the fishes with until they get fully matured.

Main Differences between Aquaculture and Pisciculture
- In aquaculture, aquatic flora and fauna are harvested during the cultivation whereas, in pisciculture, only aquatic animals are cultured.
- In aquaculture, the fishes are maintained to avoid competitive predation and exploitation whereas, in pisciculture, the cultivation reduces overexploitation.
- Aquaculture helps to increase the number of cultivated species of either flora or fauna whereas, in pisciculture, the nutrient quality and flesh and oil composition are the defining factors.
- The products of aquaculture are fish, flowers, oil, and flesh whereas the products of pisciculture are fish, flesh, and oil.
- In aquaculture, the oxygen level of the water body is maintained by plants cultivated in the habitat whereas, in pisciculture, the oxygen level is maintained by the cultivator.