Scientific words can be confusing to comprehend because of their diction similarities. Chromosomes and Chromatids are one such pair of words.
Although the two words are associated with one another, it is scientifically inappropriate to use them interchangeably because they are considerably different.
Key Takeaways
- A chromosome is a thread-like structure of DNA that carries genetic information. A chromatid is one of two identical copies of a replicated chromosome that are joined at the centromere.
- Chromosomes are present in pairs in most cells, while chromatids are only present during cell division.
- Chromosomes are visible during cell division, while chromatids cannot be seen individually without specialized techniques.
Chromosome vs Chromatid
Chromosome is hereditary substance which transmits genetic information from cell to cell during cell division. Chromatid is a substance which makes a chromosome. A chromatid is one half of a chromosome. Two sister chromatids joined in the center with a centriole make a chromosome. Chromatids double during cell division.
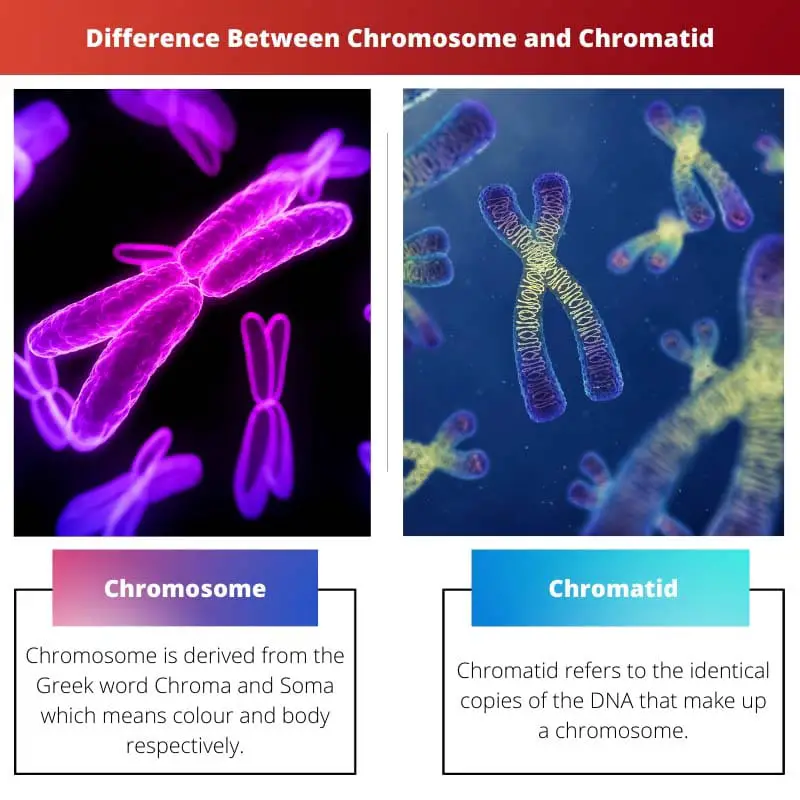
Chromosome is derived from the Greek word Chroma and Soma, which means colour and body, respectively. By definition, a chromosome is a genetic material responsible for all the features and characteristics of organisms.
In human beings, chromosomes are divided into autosomes and allosomes. Autosomes are the body’s chromosomes.
Chromosomes are responsible for genetic diversity in sexually reproducing organisms like humans. The term chromatid was given by McClung and is derived from the Greek word chroma, which means colour.
Chromatid refers to the identical copies of the DNA that make up a chromosome. There are two types of chromatids: sister chromatids and non-sister chromatids.
Moreover, chromatids may be homozygous or heterozygous. Chromatids are unable to transcribe proteins.
But they are crucial during the meiosis of cell division.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Chromosome | Chromatid |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chromosome refers to a ribbon-like structure found in the nuclear region or nucleus of the cytoplasm. | Chromatid refers to an identical half of a duplicated chromosome. |
| Structure | The structural composition of chromosomes is thin and ribbon-like. | The structural composition of chromatids is fibrous, long, and thin. |
| DNA | In a chromosome, the DNA molecules are tightly packed. | In a chromatid, the DNA molecule is free and unwounded. |
| Replication | Chromosomes are capable of replicating or duplicating themselves. | Chromatids are unable to duplicate themselves. |
| Present | Chromosomes are present throughout the lifetime of all cells. | Chromatids come into existence during the interphase. Additionally, they exist only till the metaphase of cell division. |
What is Chromosome?
Chromosome refers to a ribbon-like structure found in the nucleus of the cytoplasm. The composition of a chromosome consists of proteins and a single molecule of Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA).
Only during the metaphase of the cell cycle can one observe chromosomes under a light microscope. There are two categories of chromosomes in humans: autosomes and allosomes.
The body chromosomes are known as autosomes. On the other hand, the sex chromosomes are allosomes.
Additionally, there are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the human body. While 22 pairs of chromosomes are autosomes, there is one pair of allsomes.
In total, there are 46 chromosomes in the human body. The structure of the chromosome varies according to the phase of the cell cycle.
Prokaryotic organisms have a single circular chromosome due to the absence of a specified nuclear region. In contrast, in eukaryotic organisms like humans, chromosomes are packed into a condensed structure to fit in the nucleus.
In sexually reproducing organisms like humans, chromosomes play a vital role in ensuring genetic diversity. Chromosomes are the carriers of genetic materials that are essential for a number of functions, such as division and reproduction and protein generation.
Chromosomal deformities may cause various chromosomal disorders that are detrimental to an organism.

What is Chromatid?
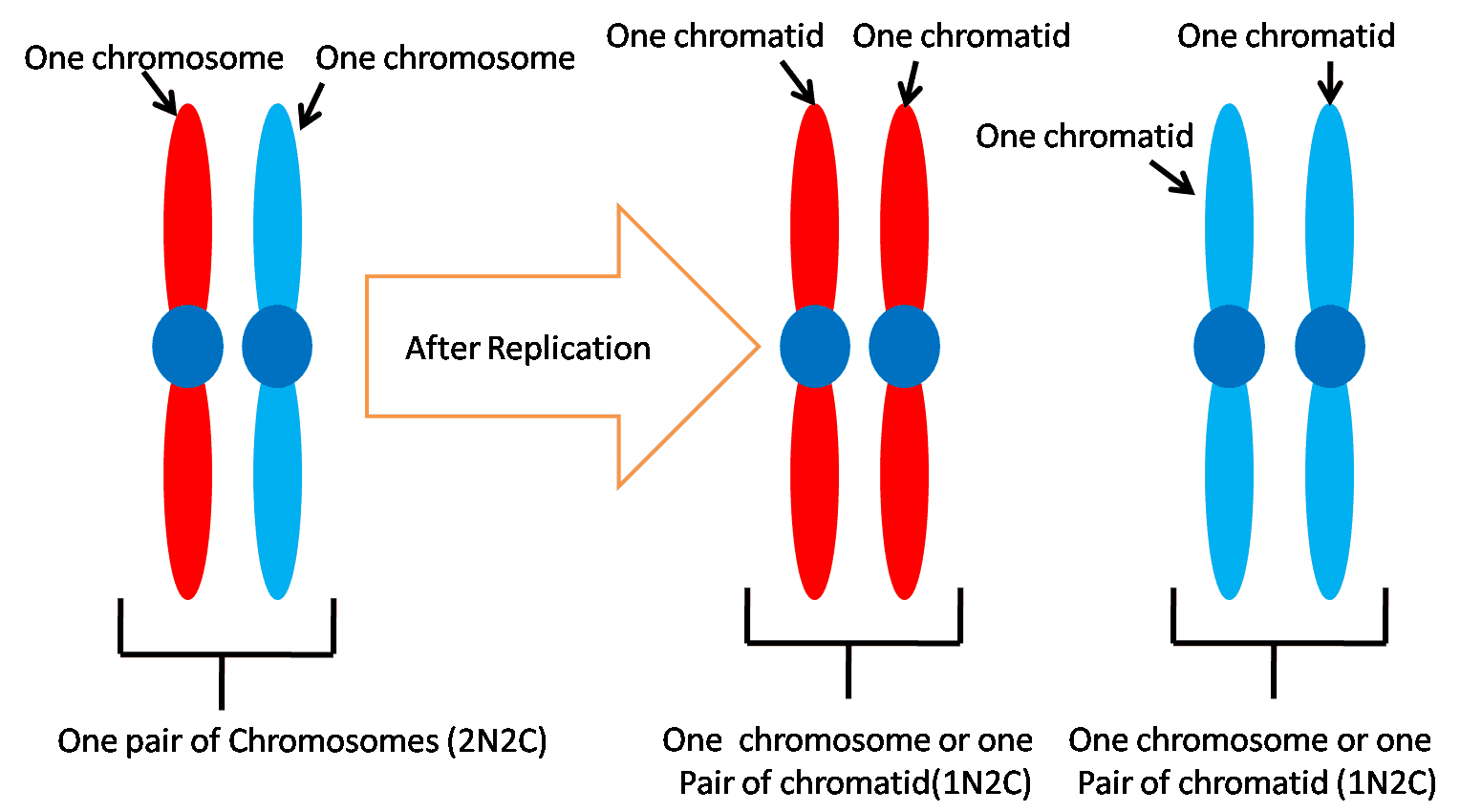
Chromatid refers to an identical half of a duplicated chromosome. The duplication of chromosomes results in the formation of two identical halves; each one of these halves is a chromatid.
As compared to chromosomes, chromatids are less condensed because chromatids form when chromosomes are uncoiled. There are two types of chromatids: sister chromatids and non-sister chromatids.
Sister chromatids refer to the chromatids from the same chromosomes. On the other hand, non-sister chromatids refer to chromatids from two different chromosomes.
Additionally, non-sister chromatids connect via chiasmata for the exchange of genetic material. Chromatids are homozygous because they are identical.
However, they may be heterozygous sometimes when mutations cause a change in either one or both chromatids. More importantly, chromatids are temporary structures that assist in the process of chromosome duplication and separation.
Chromatids are unable to transcribe proteins. But they are crucial during the meiosis of cell division.
As a cell divides itself, chromatids separate themselves to form individual chromosomes. This event ensures the genetic diversity within the species as well as genetic variability.
Thus, chromatids are less condensed structures crucial for sexual reproduction.
Main Differences Between Chromosome and Chromatid
- Chromosome refers to a thread-like structure in the cytoplasm’s nuclear region or nucleus. In contrast, chromatid refers to an identical half of a duplicated chromosome.
- Chromosomes are present throughout the lifetime of all cells. On the other hand, chromatids come into existence during the interphase. Additionally, they exist only till the metaphase of cell division.
- While chromosomes have a thin ribbon-like structure, chromatids have a long and lean fibrous structure.
- Chromosomes are capable of replicating or duplicating themselves. On the other hand, chromatids are unable to replicate themselves.
- In a chromosome, the DNA molecules are tightly packed. In contrast, the DNA molecule is free and unwounded in a chromatid.